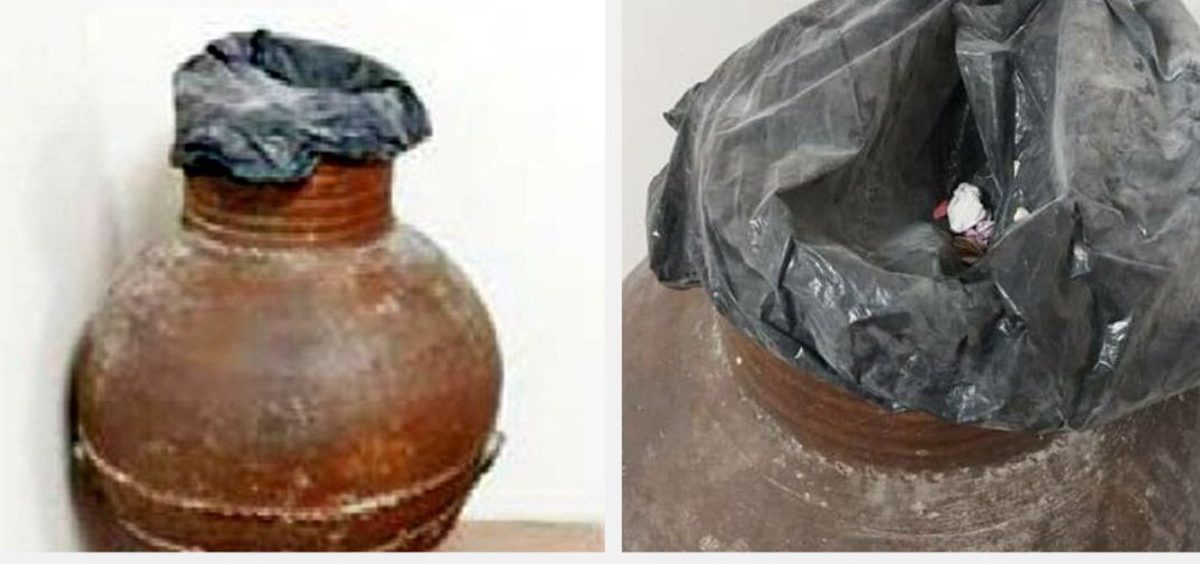
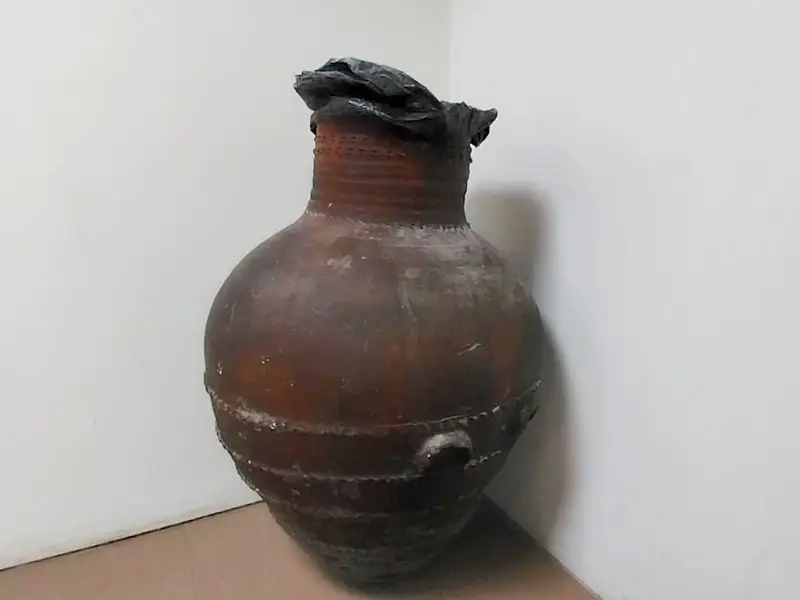
A clay pot dating back to the 2600-year-old Medes period is now serving as a trash bin in a museum in Rasht, the capital of Gilan province in northern Iran.
Iran’s Archaeological Museum of Rasht has come under fire after Etemad newspaper reported the museum’s use of a clay pot dating back to the Median era as a trash bin.
A curator has tried to justify the negligence by saying that plastic or wooden trash bins would have been stolen from the museum.
Rasht Museum opened in 1971. The archeology section of the museum is on the basement level and includes 40 displays that hold pre-Islamic archeological finds from Gilan and other parts of the country.
The Medes were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran 678 BC–c. 549 BC). Medes are documented in the Assyrian sources from the late 9th century BC.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The Greek historian Herodotus describes the early history of the Medes in his Mêdikos Logos. He credits one Deioces with uniting the six Median tribes and thereby founding a Median empire, with Ecbatana as its capital; the Medes supposedly elected him to be their king, and Herodotus goes on to trace Median history until the 6th century BC.
According to Herodotus, the Median state reached as far west as the River Halys in central Anatolia. Yet contemporary evidence for a unified Median state in the 8th and 7th centuries BC has, so far, proven elusive.
However, recently, new information about the Medes began to be obtained, especially during the excavations carried out in Amasya Oluzhöyük (Central Anatolia/Türkiye).
Iran, renowned for its millennia-old cultural heritage, faces difficulties in preserving such priceless artifacts. The neglect, insufficient maintenance, and environmental impacts on some historical sites and artifacts further intensify worries about the overall state of preservation.
Since the 1979 Islamic Revolution, the emphasis on Islamic culture has often resulted in a more conservative attitude toward pre-Islamic relics. Despite having presided over the world’s largest empire, the current Iranian regime appears hesitant to fully embrace its profound historical legacy.
The development unfolds amid the backdrop of extensive collections of ancient Persian artifacts excavated by foreign archaeologists before the twentieth century.