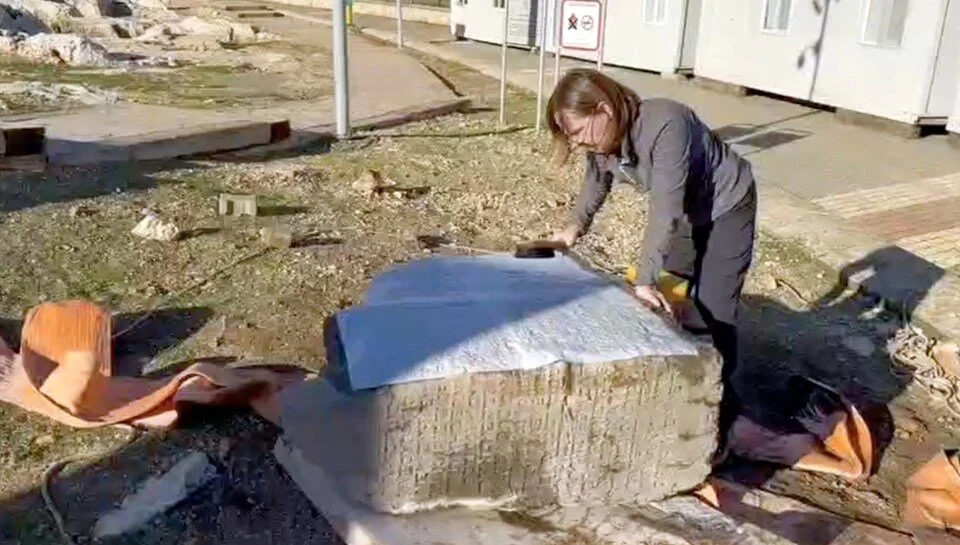
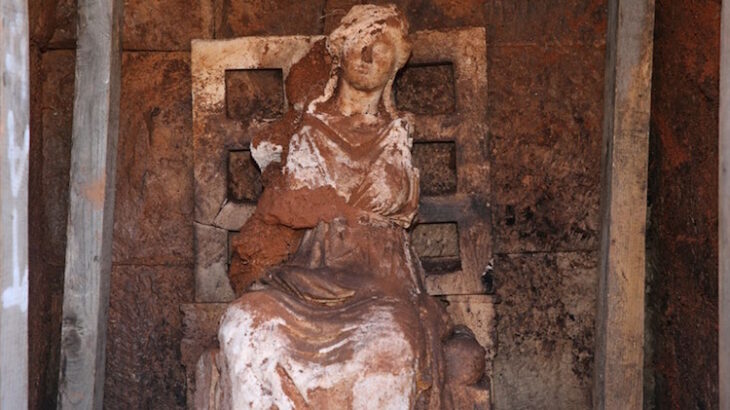
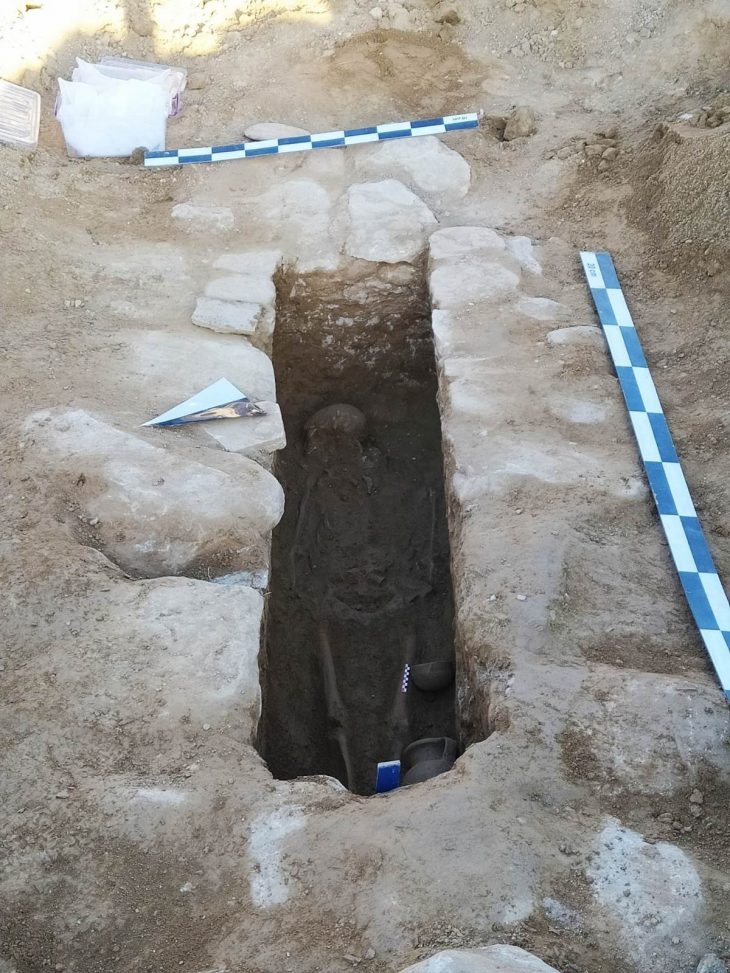
The ancient inscription found near Kımıldağı (Kımıl Mount) in Önevler village of Adıyaman’s Gerger district in 2023 will shed light on the history of Commagene.
The Kingdom of Commagene the ruling dynasty boasted descent from both Alexander and the Achaemenids. King Antiochus I (69–34 BC) claimed descent from Darius I through Orontes the Bactrian, an ardent supporter of Atraxerxes II against Cyrus and the 10,000, who married Artaxerxes’ daughter.
A small kingdom that tried to balance its Iranian heritage with the political reality of being part of the Graeco-Roman world. It kept its identity from 163 BC until it became part of the Roman province of Syria in AD 72.
Antiochus I supported Pompey against Mithradates VI of Pontus and proudly referred to himself as Philoromaios (“Rome lover”). Not only did he consider himself a god, but he also aspired to be the ecumenist who reconciled all religions: his four divinities, in addition to himself, were Zeus/Ahuramazda, Apollo/Hermes/Mithra/Helios, Artagnes/Heracles/Ares and Commagene. His tomb is now located at the summit of Mount Nemrut.

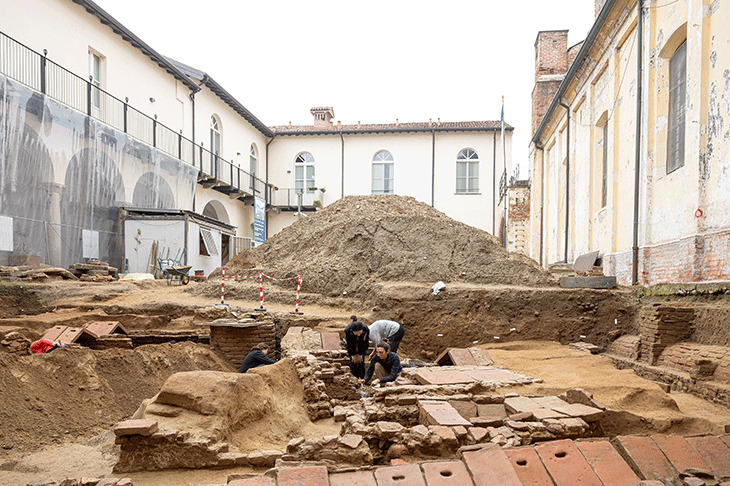
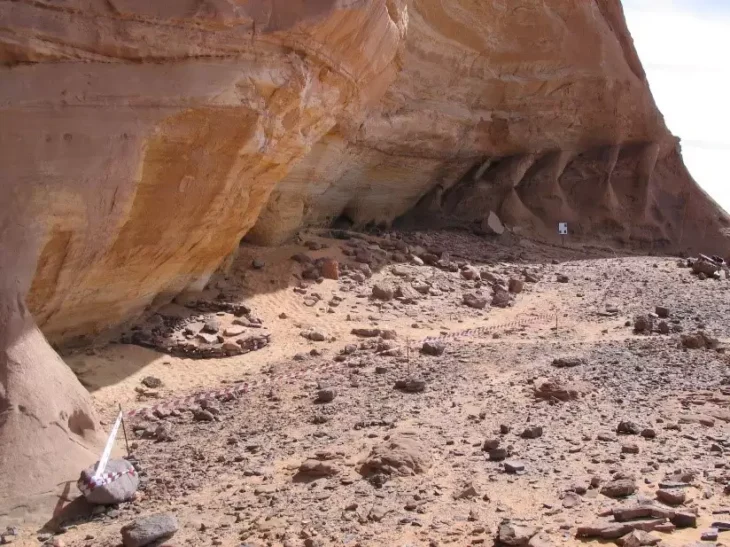
On Sept. 26, 2023, villagers who saw a relief sculpture near Kimildagi reported it to the Adiyaman Museum Directorate. The relevant teams investigated the site and determined that the area was a cult (sacred area).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
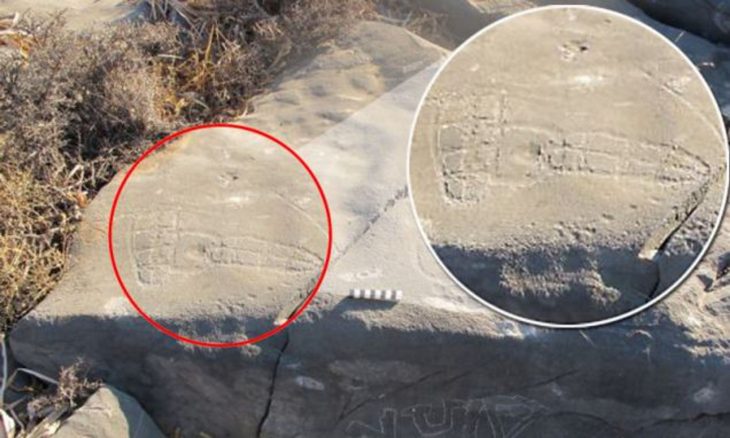
Archaeological teams discovered a relief depicting a handshake scene and steles bearing inscriptions in the area. Due to the rugged terrain and steep rocky slopes, the retrieved artifacts were airlifted to the ancient city of Perre using a military helicopter and ropes.
Charles Crowther from Oxford University and Professor Margherita Facella from the University of Pisa came to the city and examined the work.
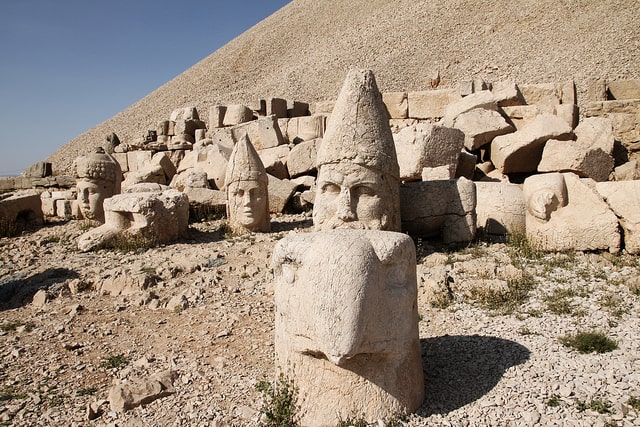

“In the inscriptions, Commagene King Antiochos I gave instructions, especially to the public,” Professor Margherita Facella said.
Stating that the inscription is important, Facella said: “It is an inscription that will shed light on the history of humanity and Commagene. We are honored to be involved in examining it and contributing to its understanding.
In the inscriptions, there are statements made by King Antiochus I of Commagene, especially to the public. Antiochos of Commagene calls on the people to ‘obey and respect the law’. On the reverse side of this important inscription, there is a relief depicting Antiochus I and Mithridates I.
Cover Photo: AA