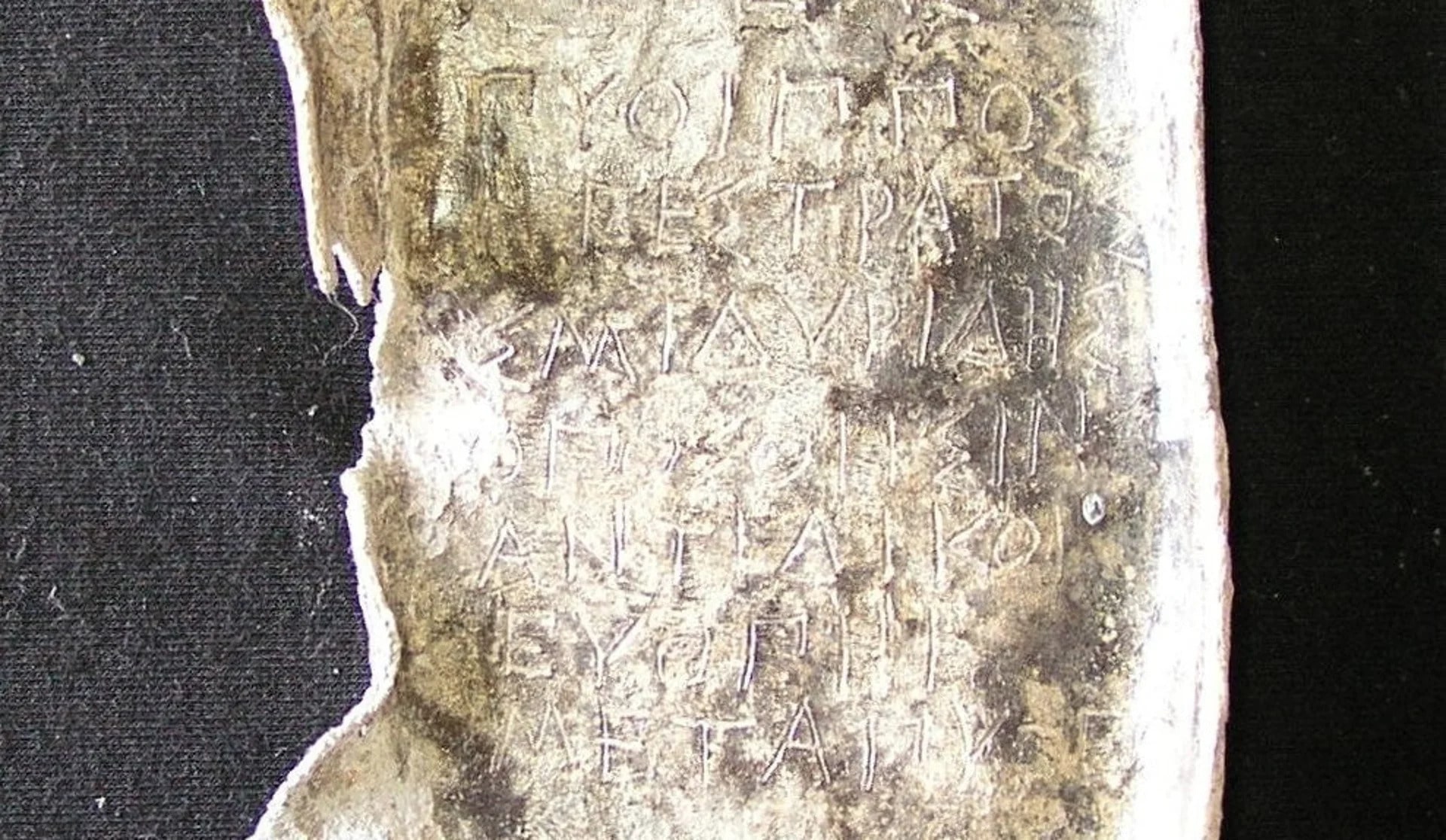
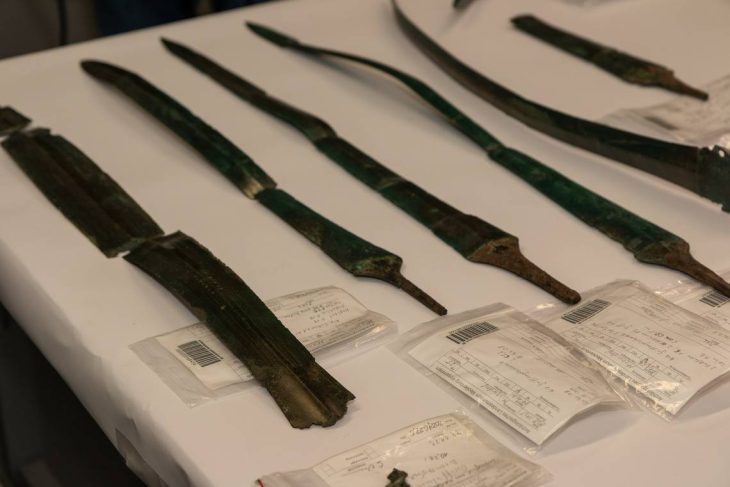
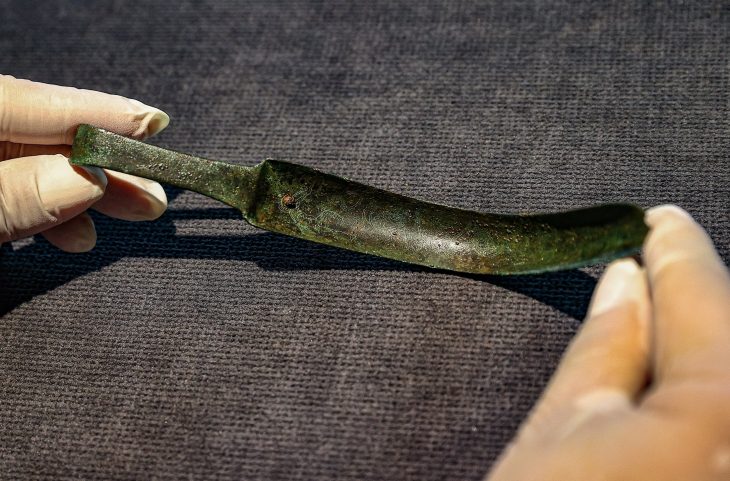
30 ancient curse tablets were found at the bottom of a 2500-year-old well in ancient Athens.
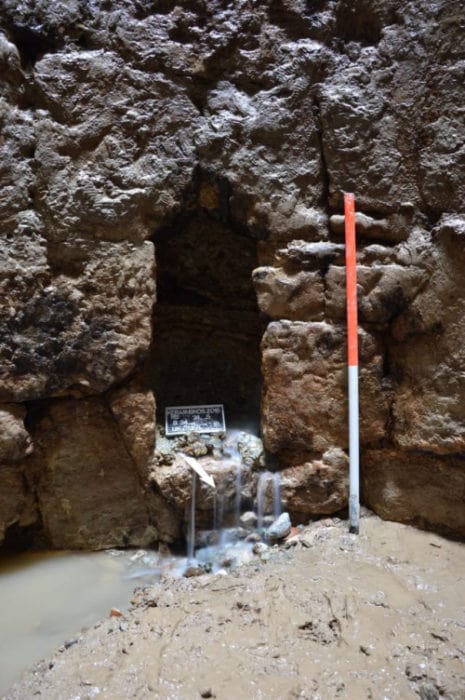
In 2020, Archaeologists from the German Archaeological Institute found 30 lead tablets engraved with curses on them at the bottom of a 2,500-year-old well in Athens‘ downtown neighborhood of Kerameikos (Ceramicus).
Discovered in the area of Kerameikos, ancient Athens’ main burial ground, the small tablets invoked the gods of the underworld in order to cause harm to others.
A total of thirty well-preserved curse tablets dating back to the Classical period ( (MÖ 480-323) were found in an ancient well which was originally discovered back in 2016, when other everyday objects—but not the tablets—were found. These curses were ritual texts, usually scratched on small lead objects.
The ancient Greeks were known to engrave curse tablets and place them to wells or graves in order to curse someone with whom they had major disagreements.
Before the discovery of the 30 specimens in the well, dozens of curses from the classical period had been found mainly in tombs of dead people who had died in an untimely manner and were therefore thought suitable to carry the spell to the underworld. One had also been found in another well. But there was good reason for the transition of ill-will from graves to wells in ancient Athens.

The tablets would be placed near tombs because they believed that the souls of the dead would carry these curses to the gods of the underworld.
The hexes were apparently in the well for a reason. According to Cicero (De Legibus II 66), Demetrios of Phaleron, who governed Athens from 317 to 307 B.C.E., passed legislation governing tomb administration. He also established a new magistrate’s office to ensure that the law was followed: et huic procurationi certum magistratum praefecerat.
To begin with, “black arts” were frowned upon in Athens, and with the new cemetery rule, hexes couldn’t just be placed in tombs, as had been the custom (35 had been found in the graves of Kerameikos, in previous excavations).
As a result, during the late fourth century B.C.E., ill-wishers had to discover alternative ways to communicate with the underworld gods. They appear to have devised the strategy of secretly hurling their curses into wells.

Inside the well the archaeologists found a wealth of material, including drinking vessels (skyphoi), wine mixing vessels (krater), clay lamps, cooking pots, special broad-mouthed clay pots used to draw water (kadoi), wooden artifacts including a trinket box, a scraper used by potters, a wooden pulley, part of the drawing mechanism of the well) a number of bronze coins, as well as organic remains such as peach pits.
Since water, and especially drinking water, was sacred, it was believed that every well had a nymph to protect the water. And angering this nymph could have had dire consequences. Offerings like little containers carrying liquids and other gifts were thrown into the well to satisfy these emotionally unstable godlets.

Kerameikos excavations
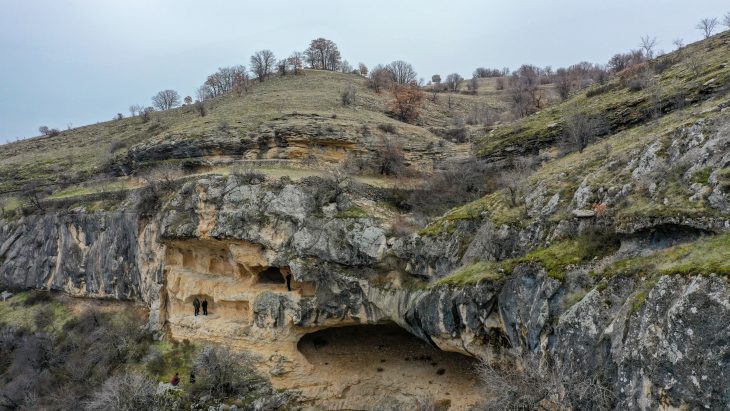
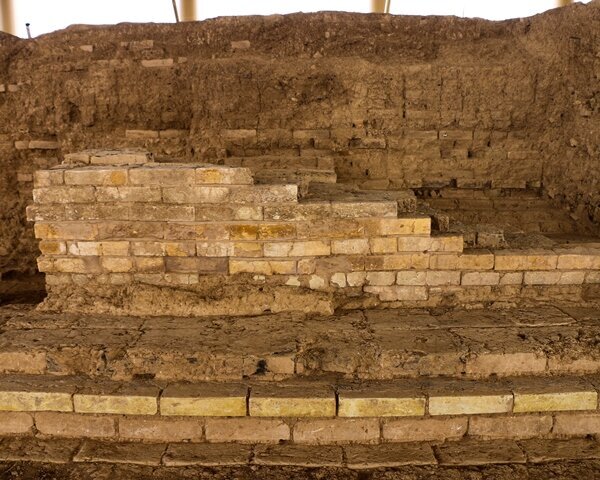
The well had not been investigated before to this, despite more than a century of excavations at Kerameikos. The archaeologist Kurt Gebauer and architect Heinz Johannes had previously worked on the area, but World War II put a stop to their efforts. None of the excavators made it through the war; Gebauer perished in an aircraft accident over Vienna in 1942, and Johannes was deployed to the Russian front and died there in 1945. Only recently were the excavations at the bathhouse resumed.
The excavations conducted by the German Archaeological Institute in the Kerameikos since 1913 unearthed about 6,500 burials.

The curse tablets were accidentally found in 2020 while archaeologists were investigating the supply of water to a 1st century BC bathhouse that was close to the well.
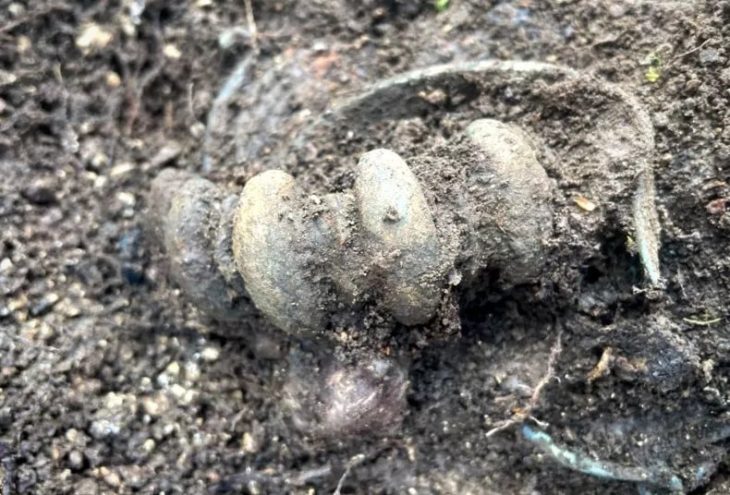
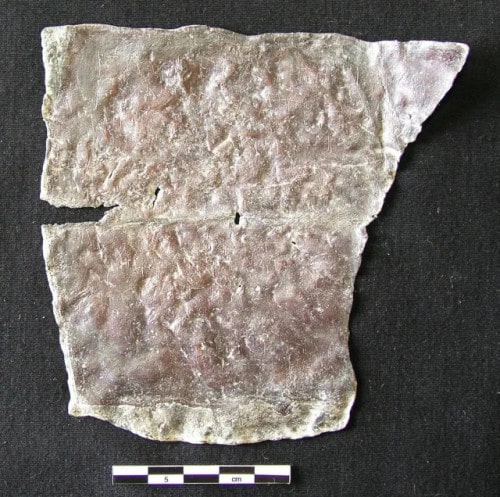
Cover Photo: Oval led “coffin” with a spell against Pytheas et al., ordered by Pytheas’ opponent in an Athenian law court (reading: W. Peek). Dr. Jutta Stroszeck / German Archaeological Institute.