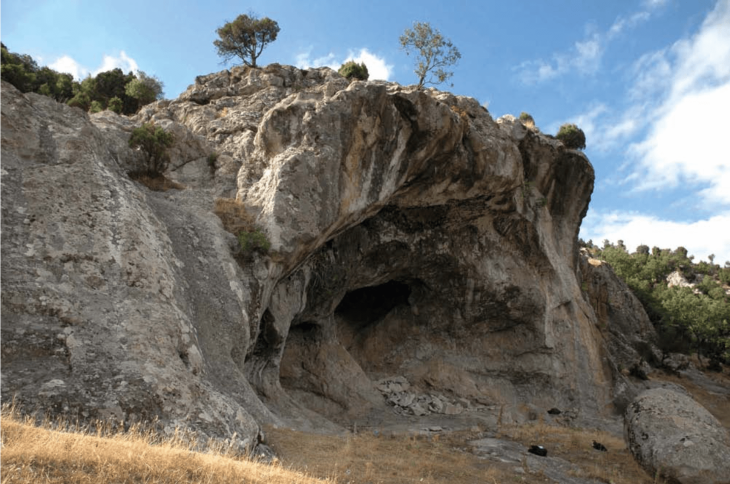
Treasure hunters revealed a 2,700-year-old Urartian temple
A group of treasure hunters, who were digging illegally to find treasure in Garibin Tepe in Alaköy, 28 kilometers northwest of Van city center, unintentionally made an important historical discovery.
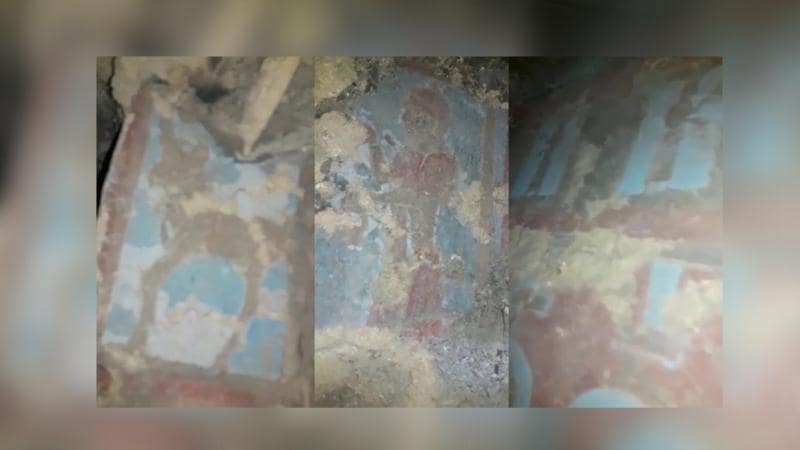
The treasure hunters, who continued their excavations in this region up to 5 meters below the ground, reached a structure with frescoes on its walls.
The group of treasure hunters, who thought it was a church, reported the situation to the Van Museum Directorate.
A video was also taken during the discovery in Garibin Tepe. However, experts think that a much more important discovery may have been made here instead of a church.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Associate Professor Erkan Konyar, who is a lecturer at Istanbul University and lectures on the history of Urartu, ancient Anatolia, and ancient Mesopotamia, also presided over many archaeological excavations in Van.
Independent Türkçe asked Konyar, who has been conducting remarkable academic studies on the Urartians, to watch the images taken from the structure in Garibin Tepe and make a comment.
Stating that this is an Urartian temple from the 7th century BC according to the images, Konyar stated that there is a castle of the Urartian King Rusa II near this region and that the structure found may be related to that castle.
Konyar said the site looks like a cult temple complex dedicated to the Urartian God Haldi.
Referring to the first encounter with an Urartian temple in its original form and untouched, Konyar said, “Maybe thanks to this structure, we will be able to understand what an Urartian temple was like for the first time.”
Noting that the building was found in its original state according to the images, Konyar said, “We can see that the wall paintings are still standing. Anyone who enters can see the state of this place 2,700 years ago. This is very impressive. As I understand from the video, this is a large building. The motifs on the wall paintings highlight the religious element. At the same time, there is also a human motif. Of course, it is very meaningful that treasure hunters found this place. I hope archaeologists and the museum get their hands on it and save this place. It will create an important destination for understanding Urartu. I think it will make a worldwide impact,” he said.
“How much material the treasure hunters take from here is important,” Konyar said that the Urartian temples are very rich in terms of finds.
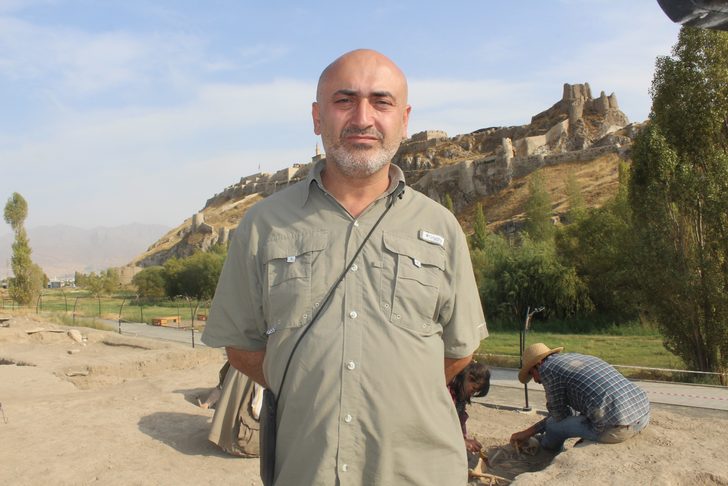

Emphasizing that there are likely to be shields, helmets, and weapons dedicated to God Haldi there, Konyar said that very unexpected and impressive things could emerge in the Urartian works, and he hoped that nothing would happen to them. “The treasure hunters usually notify the relevant institutions after they to be destroyed the places they find, and thus they legalize themselves,” he said.
“This is a magnificent invention. The area looks very impressive and magnificent in the videos you show,” said Urartian expert Associate Professor Doctor Erkan Konyar.
“I have been excavating for 30 years, but this is the first time I come across such a group of finds. Such areas are very sensitive. They were probably entered here by means of a tunnel dug from the bottom. No matter how expert you are, when you dig this place, destruction is inevitable. Here are the most beautiful murals of Urartu. There are wall paintings that have not been seen in any Urartian center before. They stand as ‘unique’.
The work here should start after suitable conditions and technology are caught. In many previous instances, we have seen magnificent finds destroyed. This destruction also occurred during the excavations at Ayanis Castle. Large areas were destroyed due to natural conditions. Maybe it would be more correct to fill in such areas and leave them unexcavated. Fresco is a very sensitive group of finds and the work requires serious expertise. It can cause unpredictable damages. It may be more appropriate to fill this area under the supervision of the museum and protect it by taking security measures.”