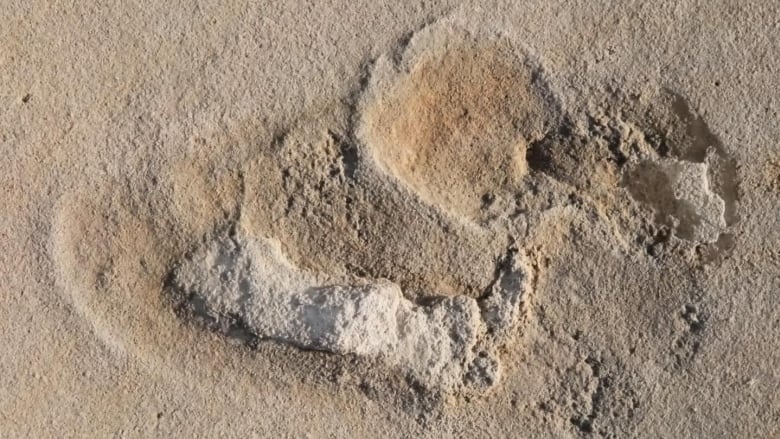
Six million-year-old fossilized footprints on the island show the human foot had begun to develop.
The oldest known footprints of pre-humans were found on the Mediterranean island of Crete and are at least six million years old, says an international team of researchers from Germany, Sweden, Greece, Egypt, and England, led by Tübingen scientists Uwe Kirscher and Madelaine Böhme of the Senckenberg Center for Human Evolution and Palaeoenvironment at the University of Tübingen. Their study has been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The footprints from fossilized beach sediments were found near the west Cretan village of Trachilos and published in 2017. Using geophysical and micropaleontological methods, researchers have now dated them to 6.05 million years before the present day, making them the oldest direct evidence of a human-like foot used for walking. “The tracks are almost 2.5 million years older than the tracks attributed to Australopithecus afarensis (Lucy) from Laetoli in Tanzania,” Uwe Kirscher says. This puts the Trachilos footprints at the same age as the fossils of the upright-walking Orrorin tugenensis from Kenya. Finds connected with this biped include femurs, but there are no foot bones or footprints.
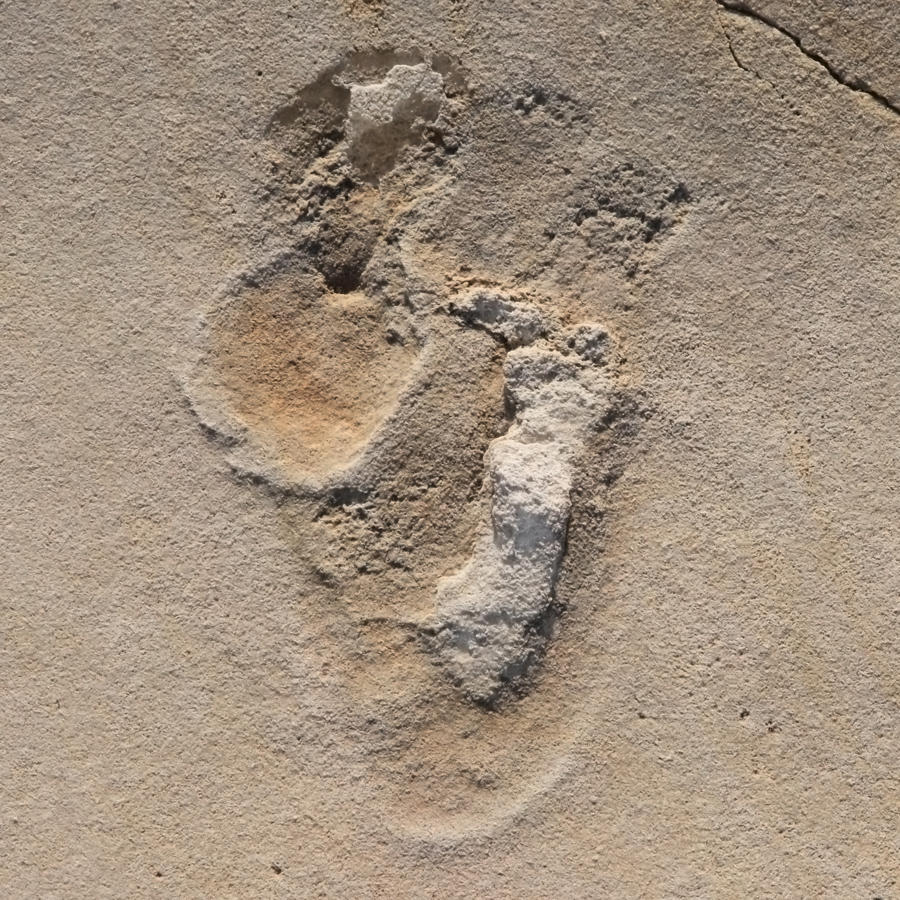

The dating of the Cretan footprints, therefore, sheds new light on the early evolution of human perambulation more than six million years ago. “The oldest human foot used for upright walking had a ball, with a strong parallel big toe, and successively shorter side toes,” Per Ahlberg, professor at Uppsala University and co-author of the study, explains. “The foot had a shorter sole than Australopithecus. An arch was not yet pronounced and the heel was narrower.”
Six million years ago, Crete was connected to the Greek mainland via the Peloponnese. According to Professor Madelaine Böhme, “We cannot rule out a connection between the producer of the tracks and the possible pre-human Graecopithecus freybergi.” Several years ago, Böhme’s team identified that previously unknown pre-human species in what is now Europe on the basis of fossils from 7.2 million-year-old deposits in Athens, just 250 kilometers away.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The study furthermore confirms recent research and theses of the Böhme team, according to which six million years ago the European and Near East mainland were separated from humid East Africa by a relatively brief expansion of the Sahara. Geochemical analysis of Crete’s six-million-year-old beach deposits suggests that desert dust from North Africa was transported there by the wind. The team arrived at an age of between 500 and 900 million years before the present when dating dust-sized mineral grains. These time periods are typical for North African desert dust, the authors said.
Recent research in paleoanthropology also suggested that the African ape Sahelanthropus could be ruled out as a biped and that Orrorin tugenensis, which originated in Kenya and lived 6.1 to 5.8 million years ago, is the oldest pre-human in Africa, Böhme says. Short-term desertification and the geographic distribution of early human predecessors could therefore be more closely related than previously thought. On the one hand, a desertification phase 6.25 million years ago in Mesopotamia could have initiated a migration of European mammals, possibly including apes, to Africa. On the other hand, the second-phase sealing off of the continents by the Sahara 6 million years ago could have enabled a separate development of the African pre-human Orrorin tugenensis in parallel with a European pre-human. According to this principle, called “desert swing” by Böhme, successive short-term desertification in Mesopotamia and the Sahara caused a migration of mammals from Eurasia to Africa.
DOI: http://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98618-0; www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-98618-0