Spain has been subjected to more invasions and conquests than any other European country. And, while the Roman, Visigothic, and Muslim legacies are still alive and well today, the medieval legacy of the Vikings in Spain is less well known. We wanted to share with you a good article about Spain and its Viking history.
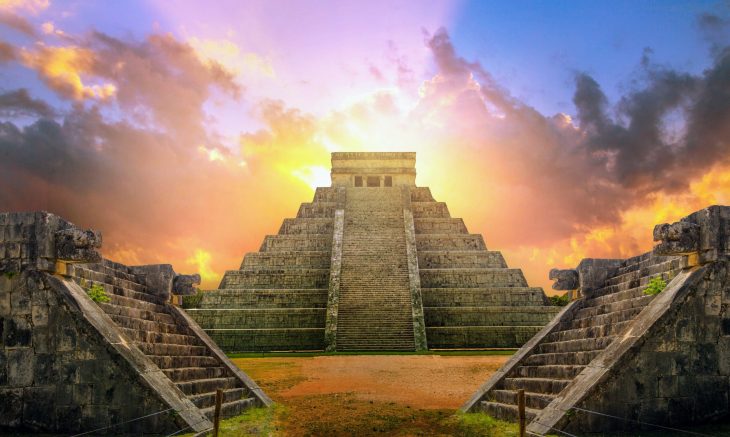
Every year, on the first Sunday in August, the replica of an 11th-century Viking longboat sails up the river Ulla to the town of Catoira in northern Spain. The boat, manned by townsfolk disguised as Viking warriors, stages a ferocious onslaught on the town which is successfully fended off by the other residents in a tussle that ends up with both sides soaked not in blood, but wine.
After the battle, both victors and Vikings share a traditional lunch of mussels and octopus, and perform the verbena, a traditional Galician dance. This year there were actually six Viking longboats in the festival, a reflection of its growing popularity in the region.
The festival commemorates Galicia’s resistance to the Viking raids that took place there a more than 1,000 years ago, when the invaders tried to plunder the treasures of the cathedral of Santiago de Compostela.
Spain has suffered invasion and conquest more than any other European country except perhaps Russia. And, while Roman, Visigothic and Muslim heritages all live on today in varying degrees, the medieval legacy of the Vikings in Spain is more obscure. This may partly be due to the fact that their raids on Spain from the ninth to the 11th centuries coincided with the ascendancy of Muslim rule there – a key focus of historians since the 1980s.
Since the transition to democracy and greater freedom after the death of Franco in 1975, Spain has delved deeper into its Roman, Visigothic and Viking past. The incursions of the Norsemen into what is now Spain and Portugal have been the focus of new research on this largely forgotten history.
Archaeologists have discovered the anchors of Viking longboats in Galicia washed ashore during a storm near what appears to be a longphort or Viking encampment. But most of what we know about the Viking raids comes from accounts written mainly by Arab historians, who referred to the Scandinavian interlopers as majūs (مَجوس) meaning “heathen or worshipper of many gods”.
The Vikings had launched attacks on the British Isles as well as on the western Carolingian empire ruled by the Franks, now present-day France, at the end of the eighth century. They were then emboldened to push further south, reaching Algeciras and Cadiz on the south coast of Spain, and possibly even northern Morocco.
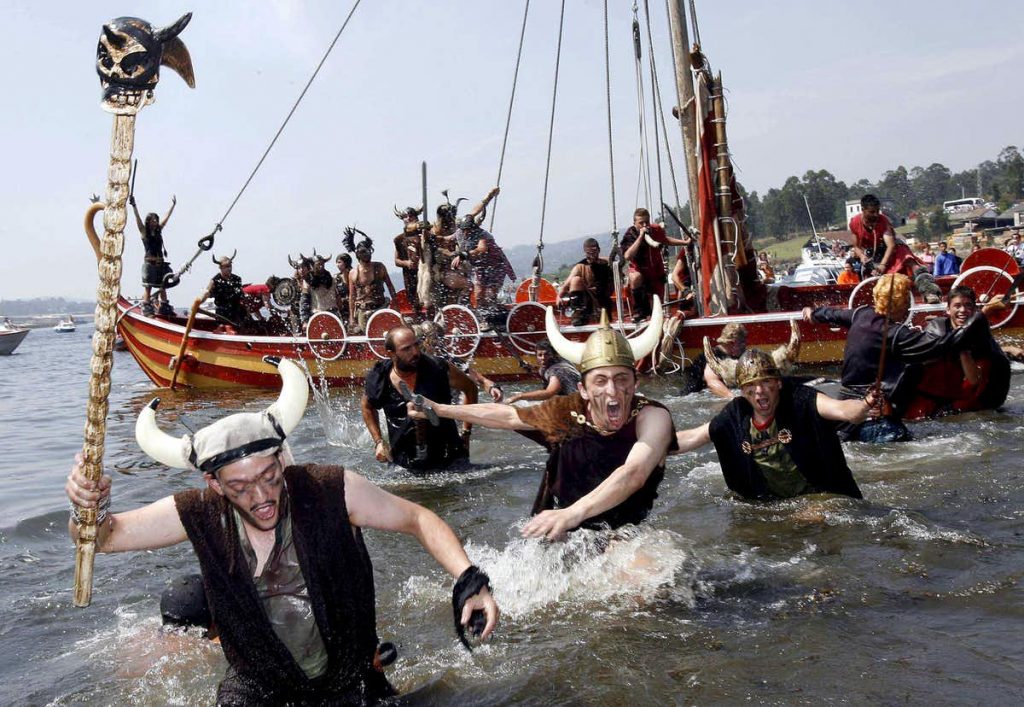

Red sails
The earliest Viking raid on Spain took place in the year 844. A Norse fleet with its blood red sails landed in Galicia after sacking Bordeaux, and proceeded to plunder the coastal villages until they were halted by the troops of King Ramiro I of Asturias near A Coruña on the northwestern coast of Galicia. A local legend recounts that when the Vikings arrived at the mouth of the northern river Masma, the bishop, Gonzalo, prayed for protection from the heavens. His prayer was answered as a major storm arose and sank most of the fleet.
The best documented and most dramatic Viking assault occurred in September of the same year. The Norsemen sailed south from Galicia, ransacking en route the city of Lisbon, which was part of Muslim al-Andalus, and set their sights on Seville, then known by its Muslim name of Išbīliya.
They captured the city in early October after heavy fighting, although its citadel remained under Muslim control. According to the Muslim historian Nowairi, these Vikings, who had been defeated in Galicia, terrorised the inhabitants of Seville and threatened them with imprisonment or death if they did not yield their city.
The emir of Cordoba, Abd al-Rahman II, acted swiftly. He sent troops who were said to have destroyed thirty longboats, burning them with the incendiary weapon “Greek fire”, a compound of naptha and quicklime which ignited on contact with water. Some accounts say this killed as many as 1,000 Vikings. Those captured were hanged from palm trees – though some converted to Islam to save their lives.
Seville was left in ruins and its people traumatised, so Abd al-Rahman II ordered a shipyard to be built with a new fleet to guard the river Guadalquivir approaches, which successfully deterred future attacks. Yet it seems the Scandinavians wanted to make peace, as a year later in 845 they sent an embassy to Abd-al-Rahman, who responded by appointing his famous court poet Al-Ghazal, the “Gazelle”, as ambassador to the Vikings at the court of King Harek of Denmark.
Pillage and plunder
Spain had not seen the last of the Norsemen, and raids continued till the end of the Viking era. The 11th-century Cordoban historian Ibn Hayyan provides early evidence of Viking attacks in the 960s and 970s, mainly in Galicia, al-Andalus and Lisbon. Galician charters some decades later describe the destruction of monasteries by the raiders, and one charter dated 996 cites an ancient Norse fortress used as a landmark.

According to the Moroccan historian Ibn Idhari, another attack on Lisbon with 28 ships in 966 was defeated, as were minor incursions around Cordoba in the 970s. Galicia continued to be plagued by Viking aggression well into the 11th century, and Santiago de Compostela was a frequent target of Viking raiders on their way to the crusades in the Holy Land. For three centuries, the Muslim realm of al-Andalus was threatened by Vikings who came not to conquer – but to pillage.
Today, that ancient violence and terror has sparked an unlikely allegiance between Galicia and Denmark. When the town council of Catoira took charge of organizing its Viking festival in 1991, an international link was created by twinning Catoira with the Danish town of Frederikssund in eastern Denmark, famous for its annual Viking games. Their alliance stands as a testament to the growing international recognition of and interest in the Viking presence in Iberia.
The article was originally published on The Conversation.
Author
Emeritus Fellow in Spanish at Murray Edwards College, University of Cambridge