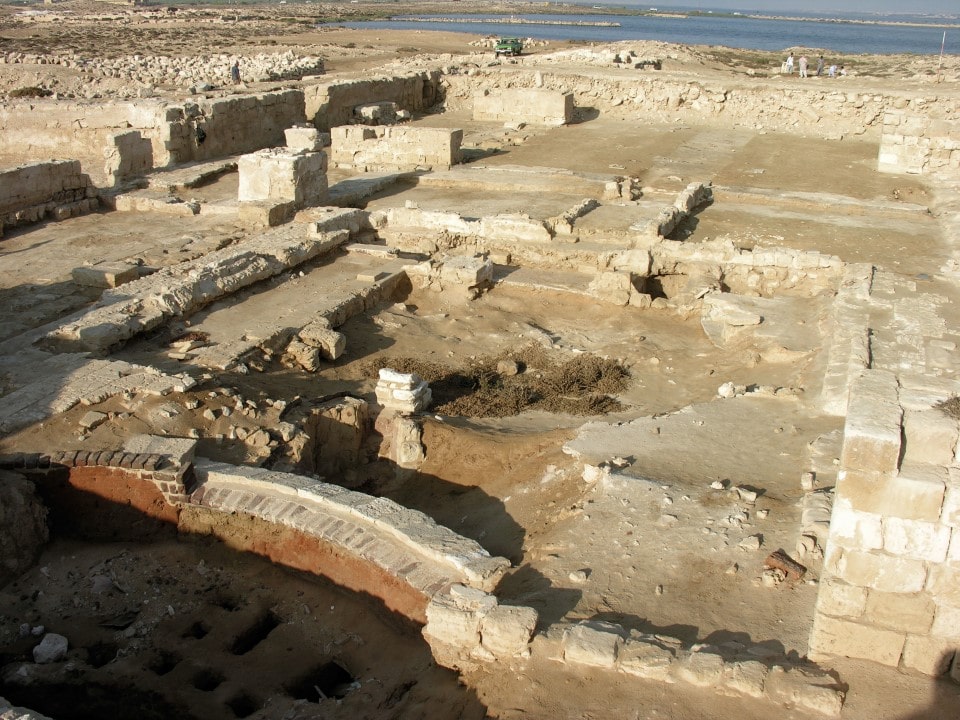
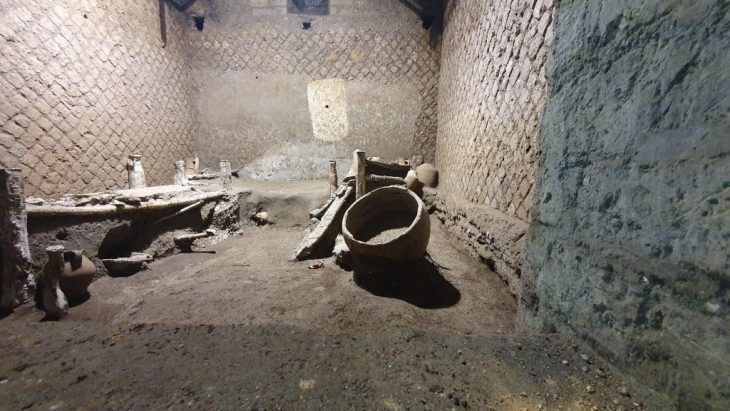
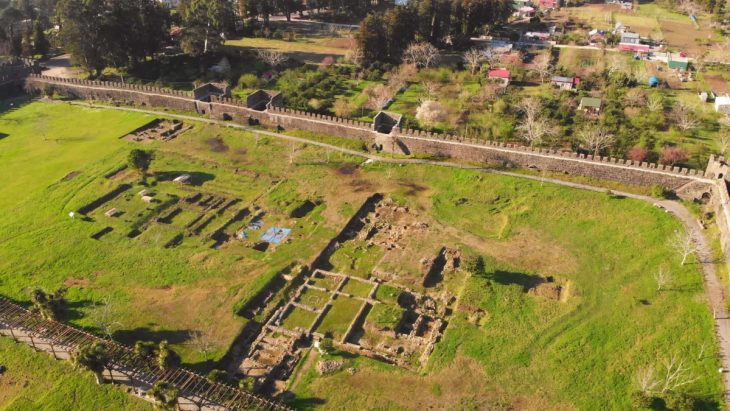
Archaeologists excavating the ancient port settlement and cemetery of Marea in Egypt have revealed that a significant part of the site was a large-scale well-planned urban enterprise established in the second half of the sixth century AD. In late antiquity, such newly designed urban sites were exceedingly rare.
Marea is located on the southern coast of Lake Mareotis in northern Egypt, some 40 kilometers southwest of Alexandria and 17 kilometers north.
Archaeologists from Egypt, the United States, France, and Poland have been excavating at this site since the late 1970s. Since 2017, the University of Warsaw has been conducting a non-invasive survey of the entire site, along with archaeological probing in selected sections, in order to maximize the potential of this site.
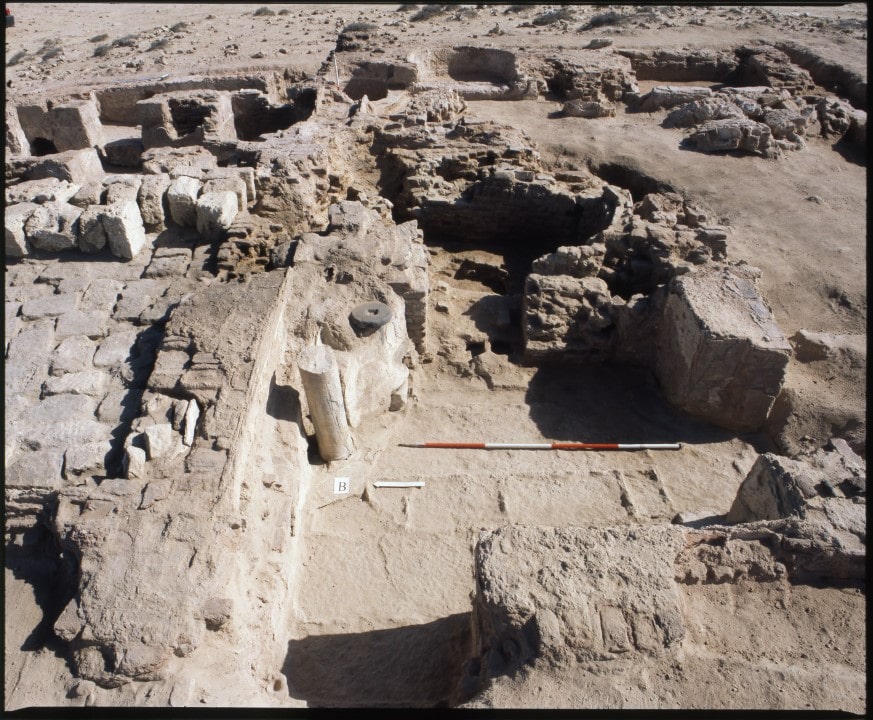

The study revealed a detailed plan for a one-story “modular” building from the 6th to 8th centuries AD, built on the ruins of a Roman farm producing wine, covering an area of 13 hectares. This area may be neatly lined with shops and houses, as well as buildings used by pilgrims who went to the Christian shrine of Abu Mena in the 6th century.

The first building boom in the area occurred during the Hellenistic period, and the Romans later conquered it. In the Islamic period, the number of urbanized settlements meant that there was no need to build more population centers. Dr. Mariusz Gwiazda of PCMA said: “It was a big surprise for us because around this period there were no new cities built in Egypt”.
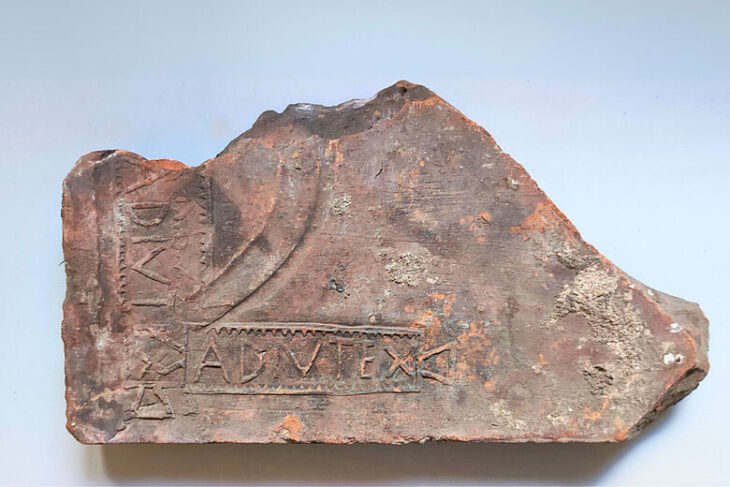
A set of ostraca (pottery with writing on the surface) records the records of workshops engaged in restoration activities between the 6th and 7th centuries AD, which also provides very important information about the operation of the settlement. They proved that, among other things, there existed a nosokomeion or hospital, a building that became common in the Byzantine period. The existence of such a building, together with two baths and toilets, indicates the care taken by the town’s planners over the health of the residents.
The Polish National Science Centre (grant 2017/25/B/HS3/01841) financed this project.