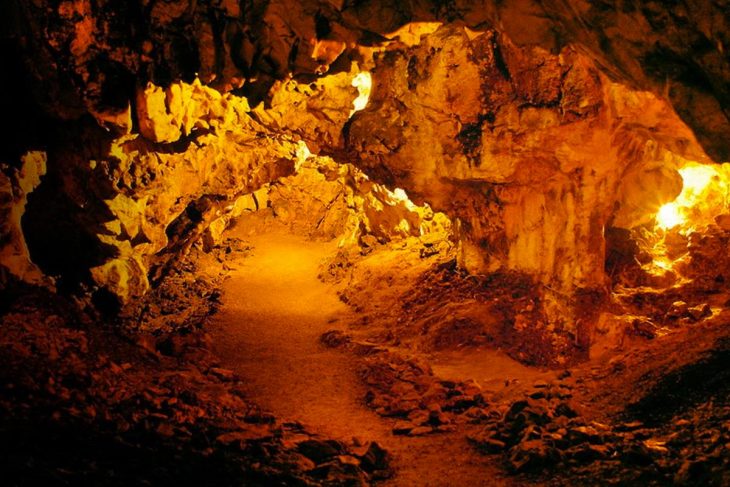
For early hunter-gatherer societies that were lucky enough to live near caves, these natural underground homes provided ideal protection from predators and competition, as well as protection from harsh weather.
Humans throughout the Paleolithic (30,000 BCE to 10,000 BCE) would spend a lot of time in these caves, preparing meals, making tools, and sleeping before venturing out to refill supplies the next day. They made a picture on the walls of the cave where they lived in their spare time.
Some hunter-gatherers may have employed lighting systems to illuminate their cave shelters, as evidenced by charcoal and paintings carved on the walls of deep passages where there was never any sunshine.
Researchers in Spain have now recreated three popular Stone Age lighting systems — torches, grease lamps, and fireplaces — as part of a new study to better comprehend what it may have been like to live and work in these surroundings.
“The artificial lighting was a crucial physical resource for expanding complex social and economic behavior in Paleolithic groups, especially for the development of the first palaeo-speleological explorations and for the origin of art in caves,” wrote Mariángeles Medina-Alcaide and colleagues in a new study published this week in the journal PLOS ONE.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
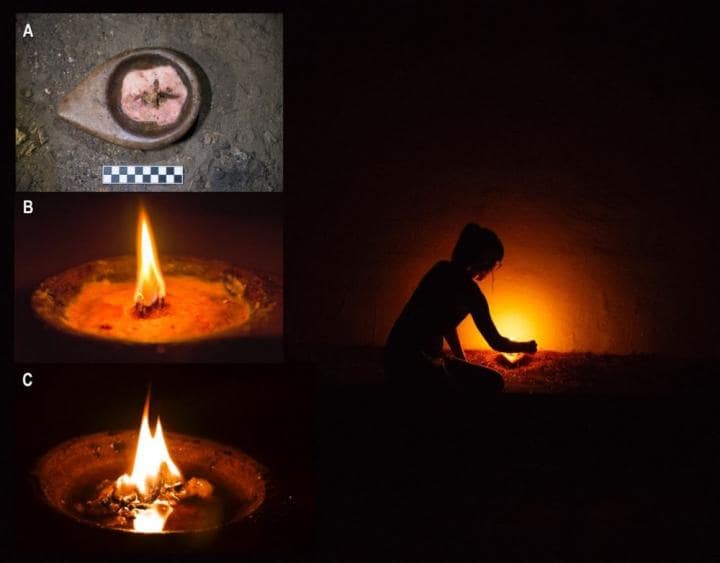

Based on archaeological evidence found in several Paleolithic caves in southwestern Europe, the team produced five replicated torches made from resins of ivy, juniper, oak, birch, and pine; two stone lamps that burn animal fat, i.e. the bone marrow of cows and deer; and a small fireplace made of oak and juniper wood.
Each lighting system had specific features and drawbacks, prompting the cave dwellers to use them in different contexts. For example, wooden torches made of many sticks had a light intensity almost five times greater than a double-wing grease lamp. The torches lasted an average of 41 minutes (the shortest torch burned for 21 minutes and the longest torch burned for 61 minutes), making them ideal for cave exploration. The light emanating from the torch sheds light in all directions up to almost six meters, which makes them perfect for wider spaces.
The torches, on the other hand, required constant attention since they burned out quickly. To maximize oxygen flow and keep the torch burning, the handler had to continually wag the torch back and forth. Their primary downside was the amount of smoke they produced, which may pose problems in a cave’s narrower corridors.
Grease lamps are perfect for illuminating tiny places for an extended length of time. They produce light with a similar intensity to that of a candle, projecting light up to three meters. A bigger space might be lit by many of these lights. Due to their dazzling impact and inadequate floor lighting, the lamps were not well suited for transiting. They did, however, burn for well over an hour.

Finally, the scientists built a fireplace. This is arguably the simplest and most widely accessible lighting system available. Inside the cave, a smoky fireplace burned for only 30 minutes before being extinguished. Because of the cave’s air currents, fireplace illumination would be inappropriate for use inside a cave network.
This study is significant from a variety of perspectives, and it may throw insight into a variety of Paleolithic people’s behaviors. Scientists can only conjecture about how ancient people lived based on fragmented data, similar to following a trail of breadcrumbs because there are no written records.
For example, some stone age cave paintings are etched hundreds of meters deep in the cave. They may have used some combination of torches and lamps, and this lighting must have affected the artistic process by changing color perception. As the brightness decreases, the human retina loses sensitivity to short wavelengths (green, blue, and purple) as well as long wavelengths (yellow, orange, and red).
As a result, red is best seen in dim light. Color perception is also affected by the light’s color temperature; incandescent or warm light (between 1000 and 2000 K), such as firelight, emits a yellow hue, and colors look more vibrant.
“In any case, our experiments on Paleolithic lighting point to planning in the human use of caves in this period and the importance of lighting studies to unravel the activities carried out by our ancestors in the deep areas of caves,” wrote the authors.