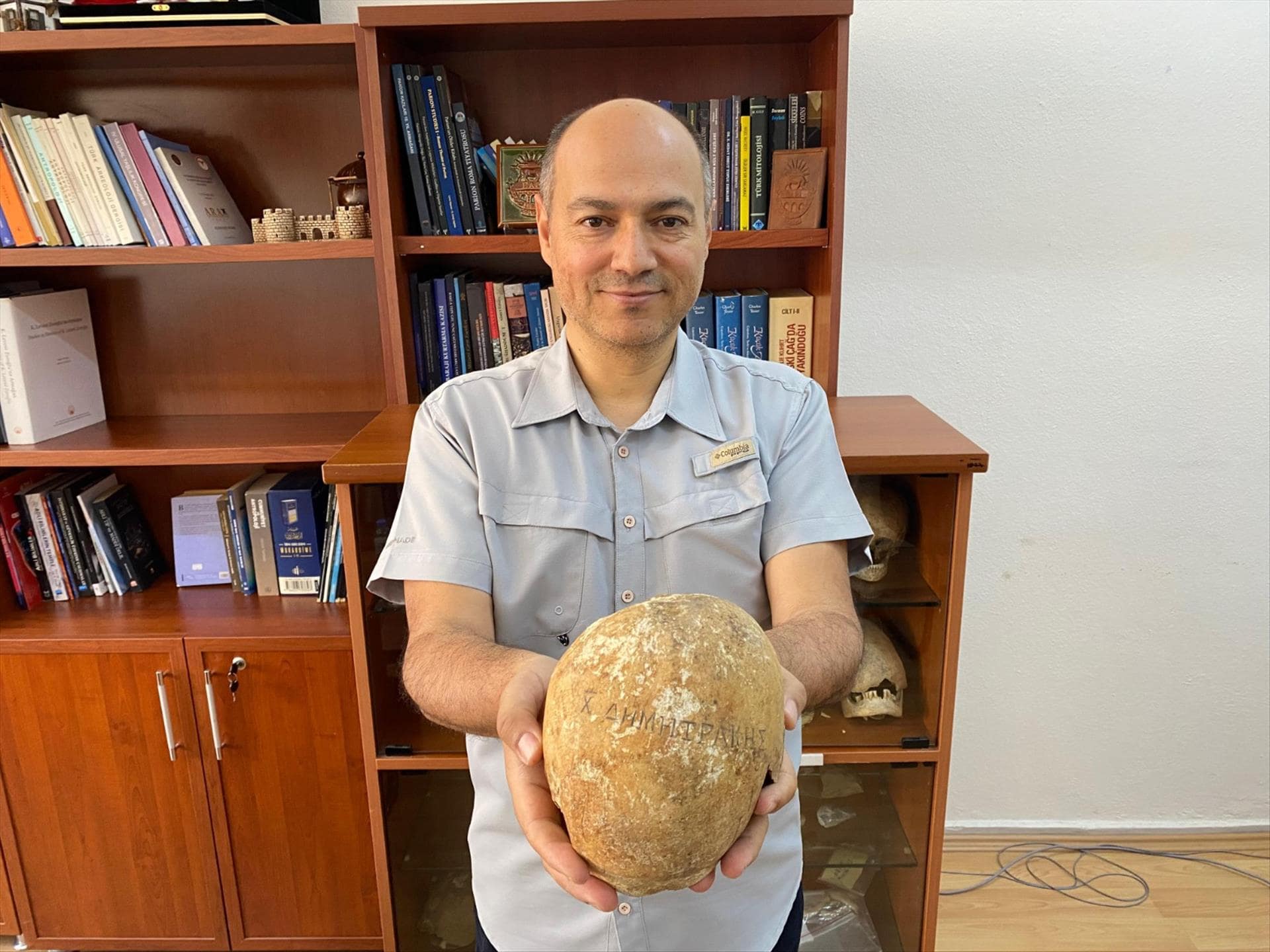
A male skull with the Greek inscription “Pilgrim Dimitrakis” was found during archaeological excavations at Balatlar Church in Sinop, on the Black Sea coast of Türkiye.
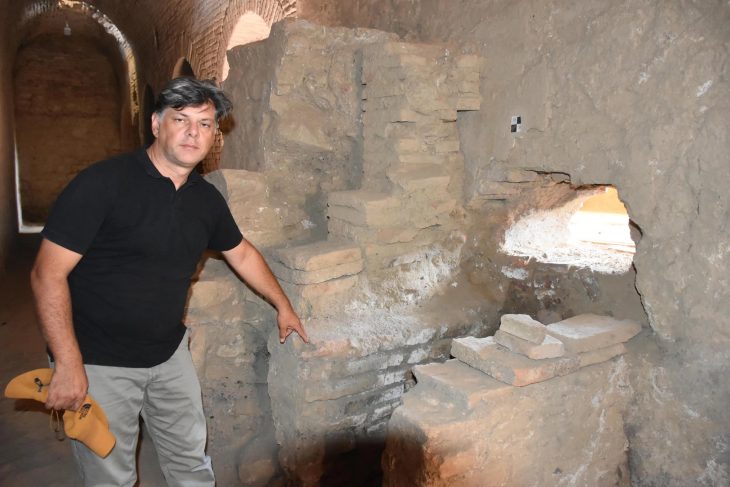
Balatlar Church or Sinope Koimesis Church, whose identity and usage phases can be determined with the excavations that started in 2010, is the only structure in Sinop City history whose purpose of use is known. During the excavations conducted under the direction of Professor Gülgün Köroğlu, the most comprehensive studies of the Byzantine period were carried out in Sinop.
It has been determined through excavations that the building known as Balatlar Church was a Roman Empire bath constructed in the second century. As a consequence of the studies, it was established that the bath complex comprising the Palaestra, Frigidarium, Tepidarium, Caldarium, and Laconicum venues started to be used as a church in the late 4th or early 5th century. It is noteworthy that the structure was converted into a church in an early period.
The skull found in the ossuary section of the church has no other example in Turkey.

In the examination conducted under the chairmanship of Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mustafa Tolga Çırak, Head of the Anthropology Department of Hitit University Faculty of Arts and Sciences, it was determined that the skull belonged to an Orthodox cleric who went to Jerusalem to make a pilgrimage.
The inscribed skull has an important place for the world of science as one of the most interesting applications as well as being one of the latest examples of the skull cult dating back thousands of years in Anatolia. The inscribed skull reveals that the cultures in Anatolia did not disappear even after thousands of years and continued in different communities by changing their forms.
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mustafa Tolga Çırak said that there is no other example of an inscribed skull in Turkey.
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mustafa Tolga Çırak said, “The historical building is not known as a bath among the people, but rather as a church. The building community was used as a service area during the Roman, Byzantine, Seljuk, and Ottoman periods. Balatlar Church turned into a cemetery area in the late Ottoman period from the 17th century to the 20th century. Especially in the garden and interior of the church, burials were made intensively. The church became the cemetery of the Orthodox.”
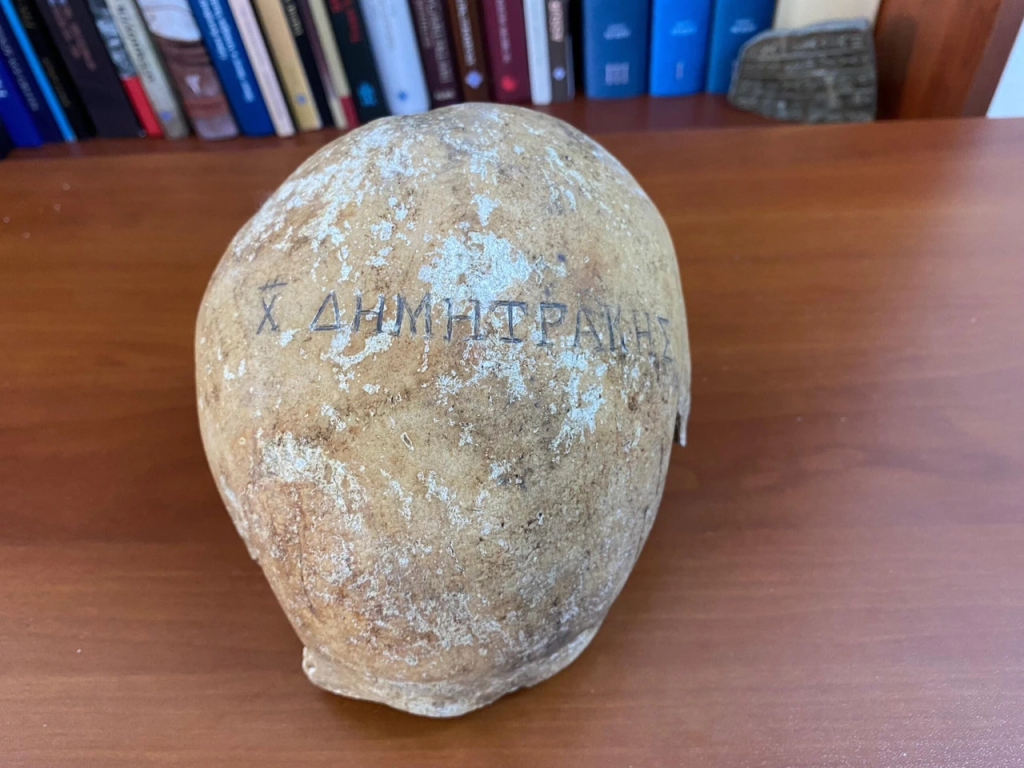

Çırak pointed out that no example of an inscribed skull was found in any excavation in Anatolia and said, “The tradition of writing on the skull was not found in Anatolia. No such example was found in any excavation. However, we knew that there were similar examples in Greece and Egypt, but it is an important finding for us because it is the first in Anatolia. The ritual of writing on the skull is one of the important Orthodox burial traditions. According to this tradition, the skull of the deceased is removed from the place where it was found, and then the name of the person is written on the skull with a hard object. Here you can see that the name is neatly written on the skull. After the writing process, the skull was placed on the shelf in the relevant section of the church to be exhibited. There are examples of this in Greece and Egypt.”
Çırak noted that rituals with skulls were seen until the Neolithic period and said, “The custom of keeping and honoring the skull separately from the rest of the skeleton seems to have persisted in various forms throughout prehistoric times, having probably started as early as the Early Paleolithic Period. Culturally, this has found a place in the Orthodox as a ritual. It was determined that the skull belonged to the 19th century. Some archaeological objects and coins found next to it say that this individual lived in the 19th century.”
Source: O. HETTO, G. KÖROĞLU, N. ÇORAĞAN, 2022 “Mosaic Panel on Refrigerium from Sinop Balatlar Church and its Place in Byzantine Iconography”, DOI:10.26650/artsanat.2022.17.946096