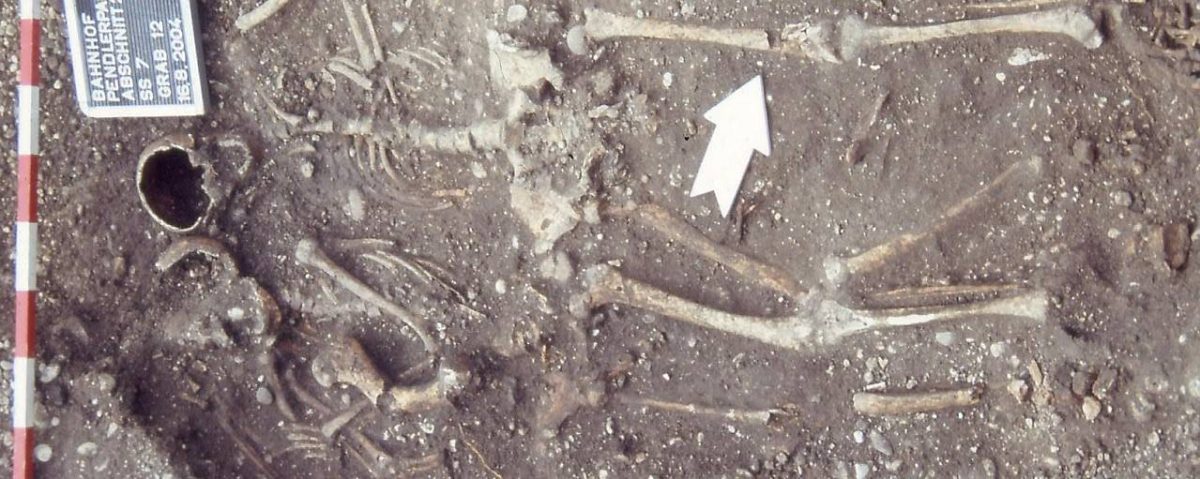
Modern scientific methods are increasingly uncovering spectacular results from archaeological finds dating back a long time. A grave discovered 20 years ago in Wels with the skeletons of two people and a horse has now turned out to be the first mother-daughter burial from the Roman period to be documented in Austria, according to a study by the University of Vienna.
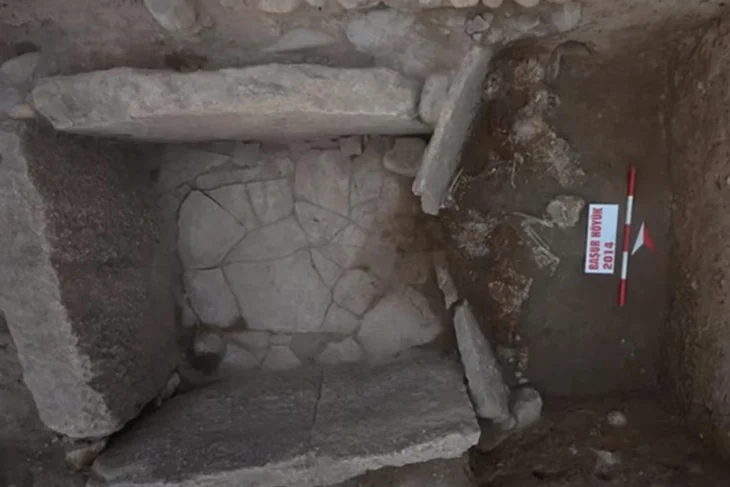
In 2004, an unusual grave was discovered during construction work in the area of the so-called eastern burial ground of the ancient Roman city of Ovilava – today’s Wels in Upper Austria. It contained the remains of two people embracing each other and at least one horse. Due to these unusual features, the find was initially thought to be an early medieval double burial.
A comprehensive new investigation, in which the latest bioarchaeological and archaeogenetic methods were used, revealed surprising findings: The grave is 500 years older than previously thought. It dates from the 2nd to 3rd century AD and can therefore be assigned to Roman antiquity in Austria, report anthropologist Sylvia Kirchengast and archaeologist Dominik Hagmann in a study published in the “Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports”.
Unexpected family relationships
“In Roman times, burials in which people were buried next to horses were very rare. But what is even more extraordinary is that this is the first burial from Roman antiquity in Austria in which genetic analyzes were able to clearly identify a biological mother and her biological daughter, who were buried at the same time. This makes our results particularly exciting,” explains Dominik Hagmann, lead author of the study.
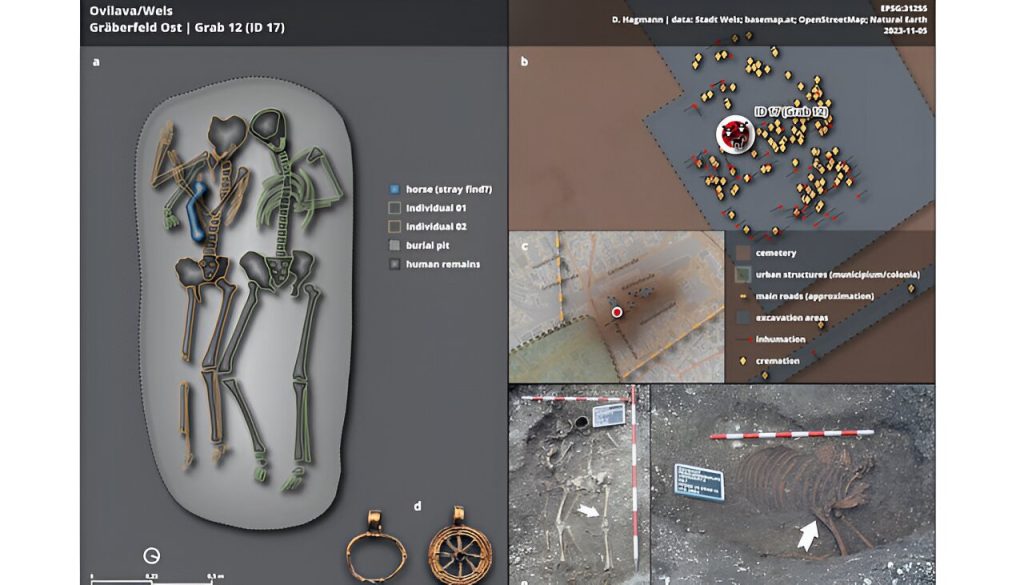
Osteological findings in conjunction with new research methods such as the analysis of ancient DNA revealed the biological sex and also suggested a family connection between the two human individuals. Radiocarbon dating finally enabled a more precise chronological classification of both the human skeletons and the horse skeleton.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Modern technology reveals the ancient connection
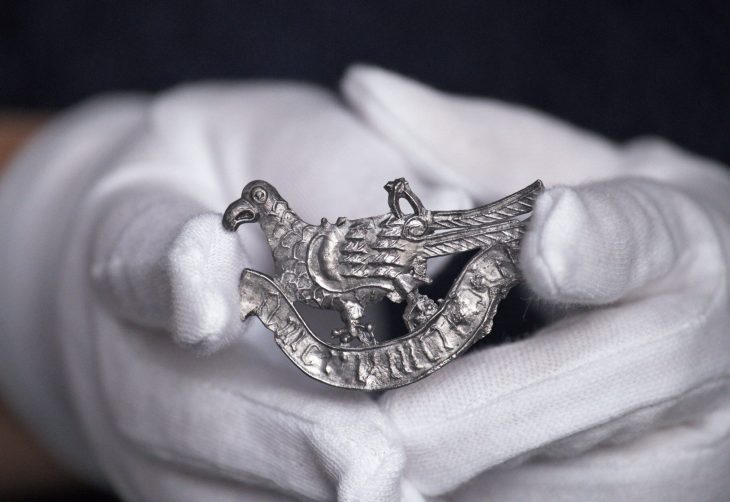
The detailed examination of the golden grave goods provided additional information for the new dating of the site. Archaeozoological examinations of the buried horse expanded our understanding of the entire burial context.
“In summary, our investigations showed that the burial was of two biological women—probably a mother aged around 40 to 60 and her daughter aged around 20 to 25—from the second and third centuries. “The grave is around 500 years older than initially assumed and clearly dates from Roman times,” says study director Sylvia Kirchengast.
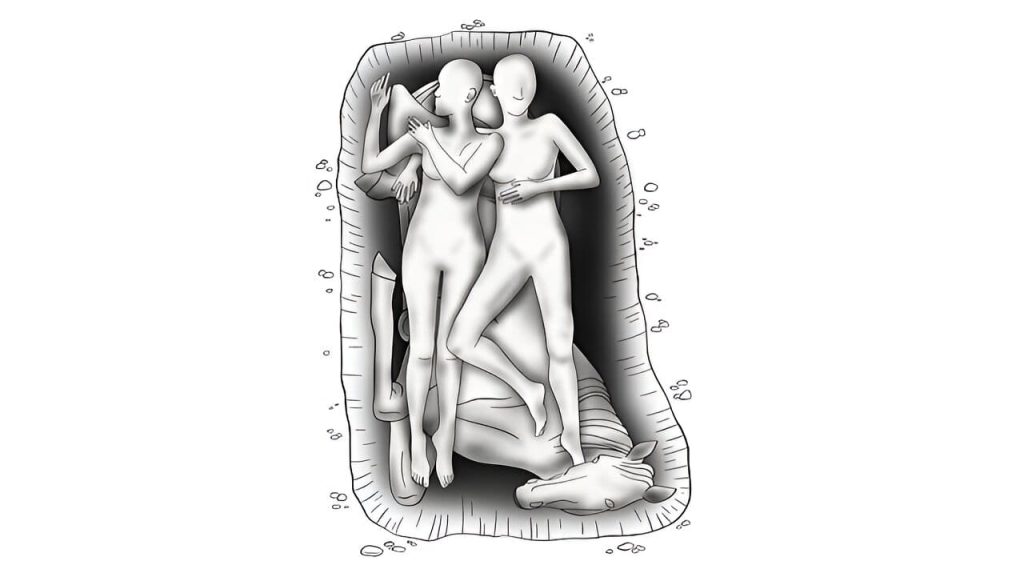
The exact background of the double burial is not clear, the scientists’ theory is that both may have died of an illness at the same time and, according to a tradition from the late Iron Age, were buried together with their horse—the older person has skeletal features that indicate frequent riding could.
Ultimately, this study shows the enormous potential that the application of modern, scientific methods in combination with traditional research approaches offers for archaeology in Roman Austria.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2024.104479
Cover Photo: University of Vienna