Archaeological analysis of a medieval horse cemetery discovered in London nearly 30 years ago has revealed the international scale of the horse-trading by the elite of Tudor England.
Horses owned by the elite in medieval England were probably imported from continental Europe, possibly traveling hundreds of kilometers, according to tooth analysis of horses.
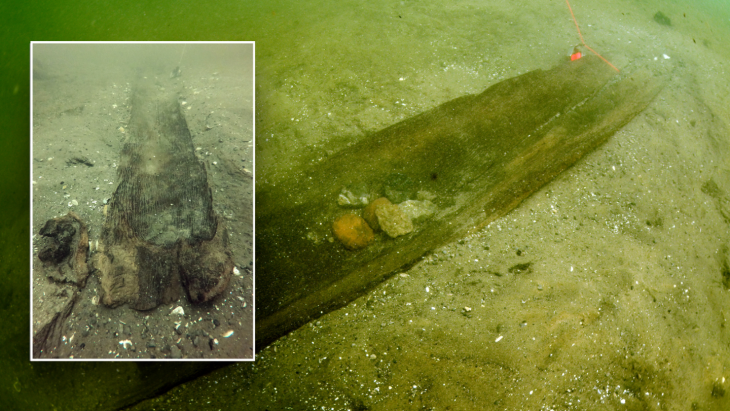
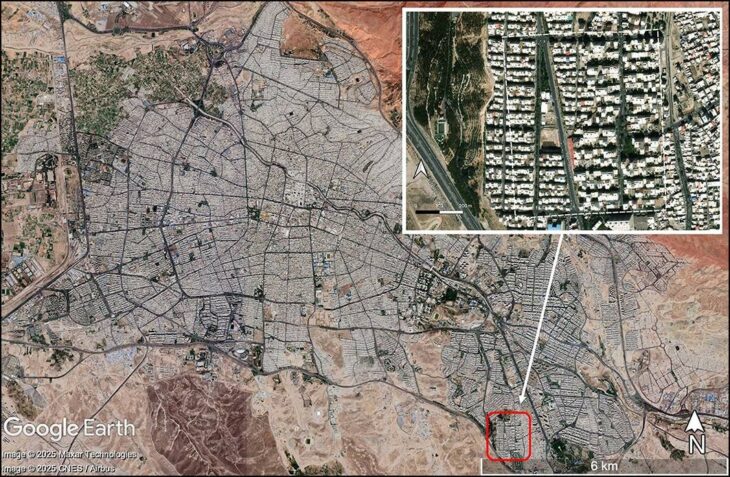
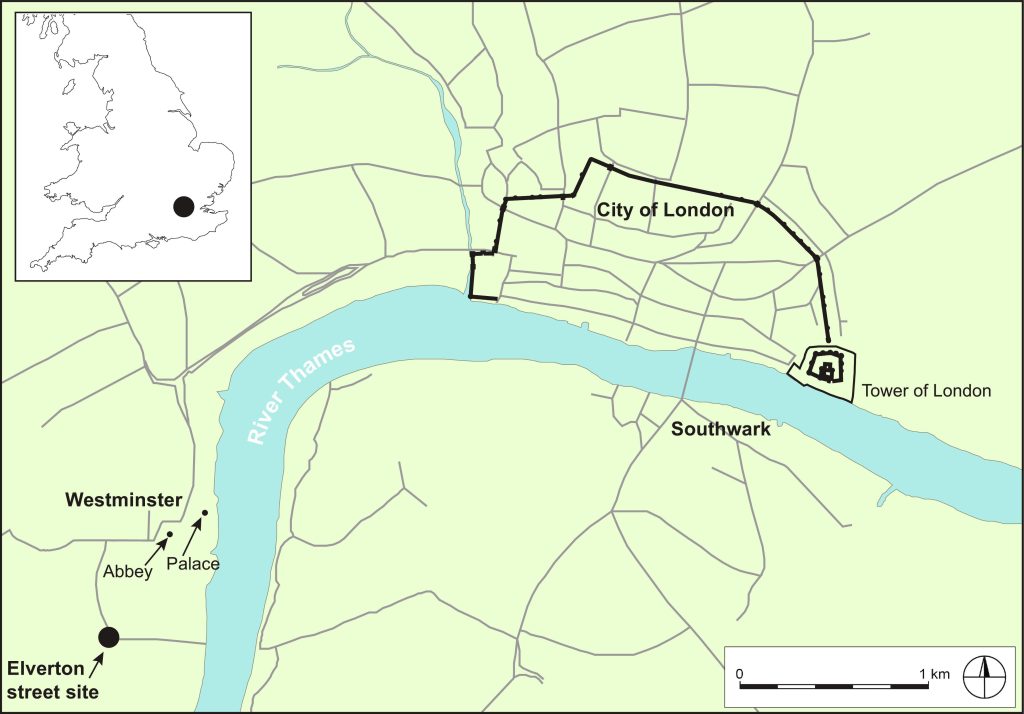
Commercial excavators discovered an unusually large horse burial site in central London during the 1990s. Seventy whole or partial horse remains have been found at the location, which is now known as the Elverton Street cemetery, during subsequent digs. Some of the graves have been dated between 1425 and 1517, but the cemetery may have been used for a longer period.
The horse burial site is located outside the walls of the ancient city of London, but close to the royal palace complex at Westminster, where jousting and stables were known to have been common.
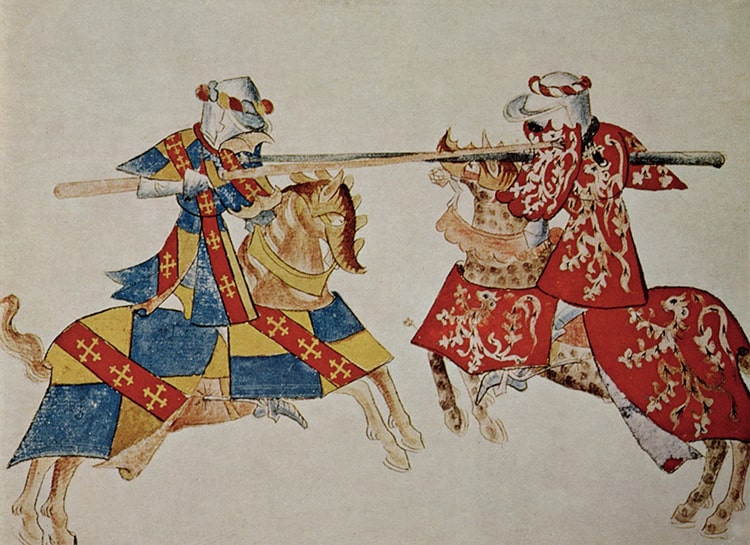
Medieval English knights donned armor, mounted highly trained horses, and jousted with long lances in spectacular ritual combats. But the steeds used in these contests weren’t all home-grown, a new study finds.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The research, led by the University of Exeter, is published in Science Advances.
These animals—akin to modern supercars—were sourced from a variety of locations across Europe specifically for their height and strength and imported for use in jousting tournaments and as status symbols of 14th- to 16th-century life. They include three of the tallest animals known from late medieval England, standing up to 1.6 meters or 15.3 hands high, which while quite small by modern standards would have been very impressive for their day.
An analysis of dozens of medieval horses buried reveals a far-flung European horse trading network, with some of the animals coming from as far away as northern Italy. The findings, experts say, open a new window into the life of medieval English elites and their favorite hobby.
“The finest medieval horses were like modern supercars—inordinately expensive and finely tuned vehicles that proclaimed their owner’s status,” said Professor Oliver Creighton, a medieval specialist at the University of Exeter and part of the research team.
Historical documents show England’s medieval elite took great interest in horses. A record of royal horses called the Equitium Regis, for example, lists hundreds of horses belonging to the royal family in the late 13th and early 14th century C.E., often by name and sometimes geographic origin.
Based on such written evidence, historians assumed England’s elite spent fortunes on the animals and sometimes imported them from Spain and Italy at great cost. But the archaeological record offered little corroboration, because horse remains from the medieval period are very rare.
“And at Elverton Street, our research team seem to have found evidence for horses used in jousting—the sport of kings, in which riders showcased their fighting skills and horsemanship on elite mounts,” said Professor Oliver Creighton.

“The new findings provide a tangible archaeological signature of this trade, emphasizing its international scale. It is apparent that the medieval London elite was explicitly targeting the highest quality horses they could find at a European scale,” added Professor Oliver Creighton.
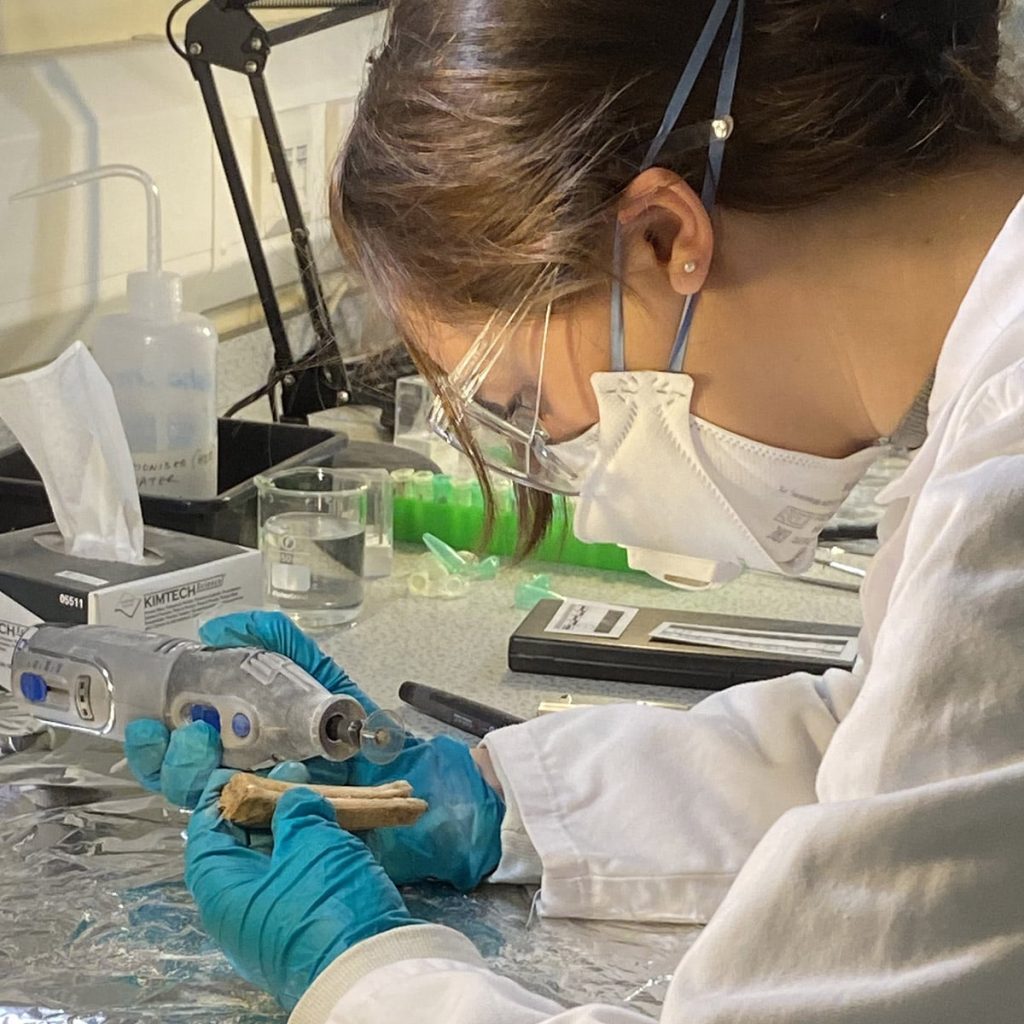
In the first experiment of its kind to be conducted on medieval horse remains, the researchers took 22 molar teeth from 15 individual animals and drilled out portions of the enamel for isotope analysis.
By measuring isotope ratios of the elements strontium, oxygen and carbon present within the teeth and comparing the results with known ranges in different geographies, the team was able to identify the potential origin of each horse—and accurately rule out others, including prime European horse-breeding centers such as Spain and southern Italy.
Dr. Alex Pryor said that at least half of the horses had diverse international origins, possibly Scandinavia, the Alps, and other northern and eastern European locations. The results, the researchers conclude, were consistent with the breeding patterns of royal stud farms, where horses would reside until their second or third year before they would either be broken and trained or sent elsewhere to be sold.
Physical analysis of the teeth revealed wear suggestive of heavy use of a curb bit, often employed with elite animals, especially those groomed for war and tournaments after the 14th century.
Bit wear on two of the mares also suggested they were used under saddle or in harness and for breeding. An analysis of the skeletons revealed many of them to be well above average size, with several instances of fused lower thoracic and lumbar vertebrae indicative of a life of riding and hard work.
Cover Photo: Jousting knights, an illustration from an English manuscript, 15th century