American researchers have announced the discovery of an Imperial cult temple in Spello, Italy.
The discovery was announced by Douglas Boin, a history professor at Saint Louis University, at the annual meeting of the Archaeological Institute of America.
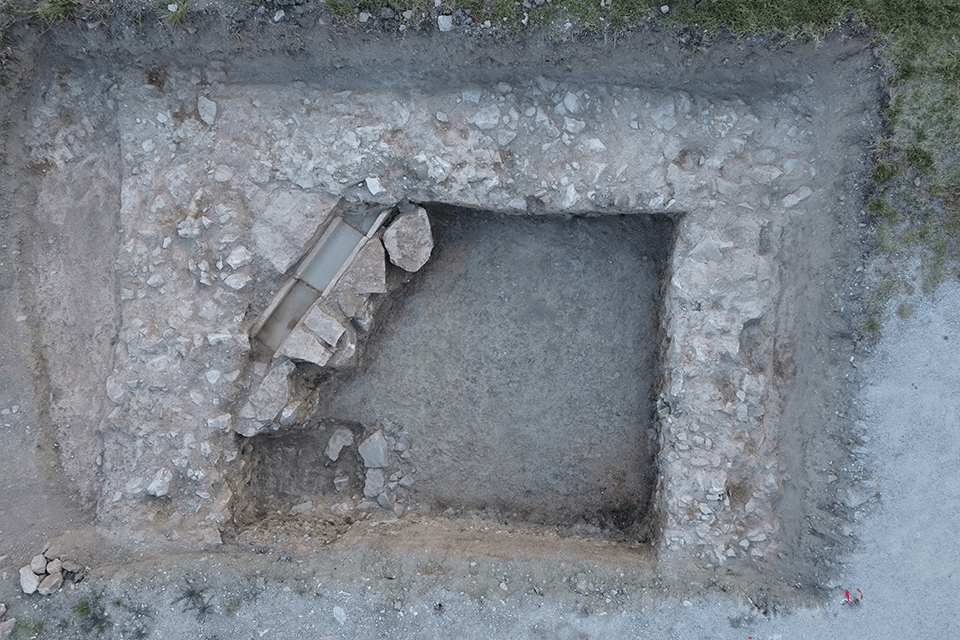
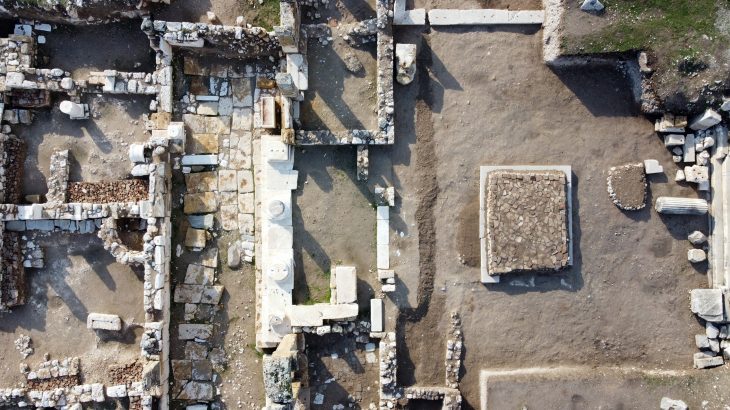
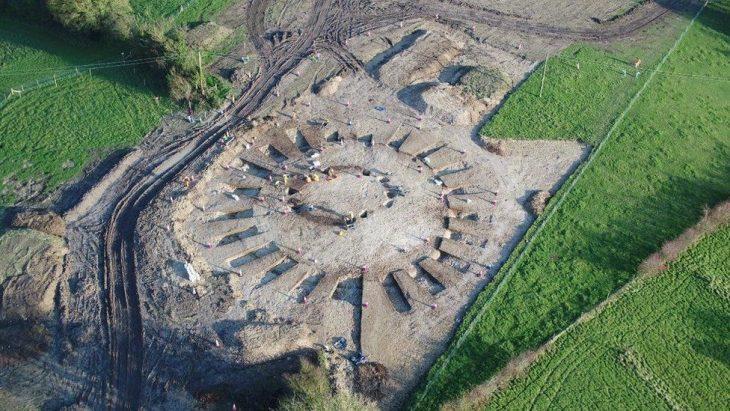
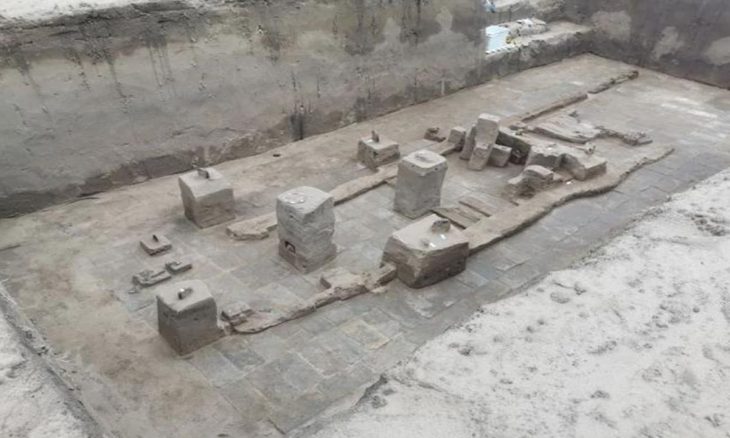
The temple was discovered during excavations in Spello, an ancient hilltop town located more than 70 miles north of Rome. The structure is thought to have been built in the fourth century during the reign of Emperor Constantine, who ruled Rome from A.D. 306 to A.D. 337. Constantine was the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity.
Their findings offer a profound glimpse into a time of cultural and religious flux, revealing a society that was more “multicultural” than previously thought.
A rescript—a fourth-century letter from Emperor Constantine to the townspeople—drew Boin to Spello, a renowned medieval hilltop city. This 18th-century letter revealed an intriguing aspect of multicultural Roman society. It allowed the people of Spello to hold a religious festival in their own town, but there was a catch: they had to erect a temple to Constantine’s divine ancestors, the Flavian family, and worship them.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The discovery of the temple provides concrete evidence of religious continuity between the Roman and early Christian worlds, challenging the notion that societal changes were abrupt.
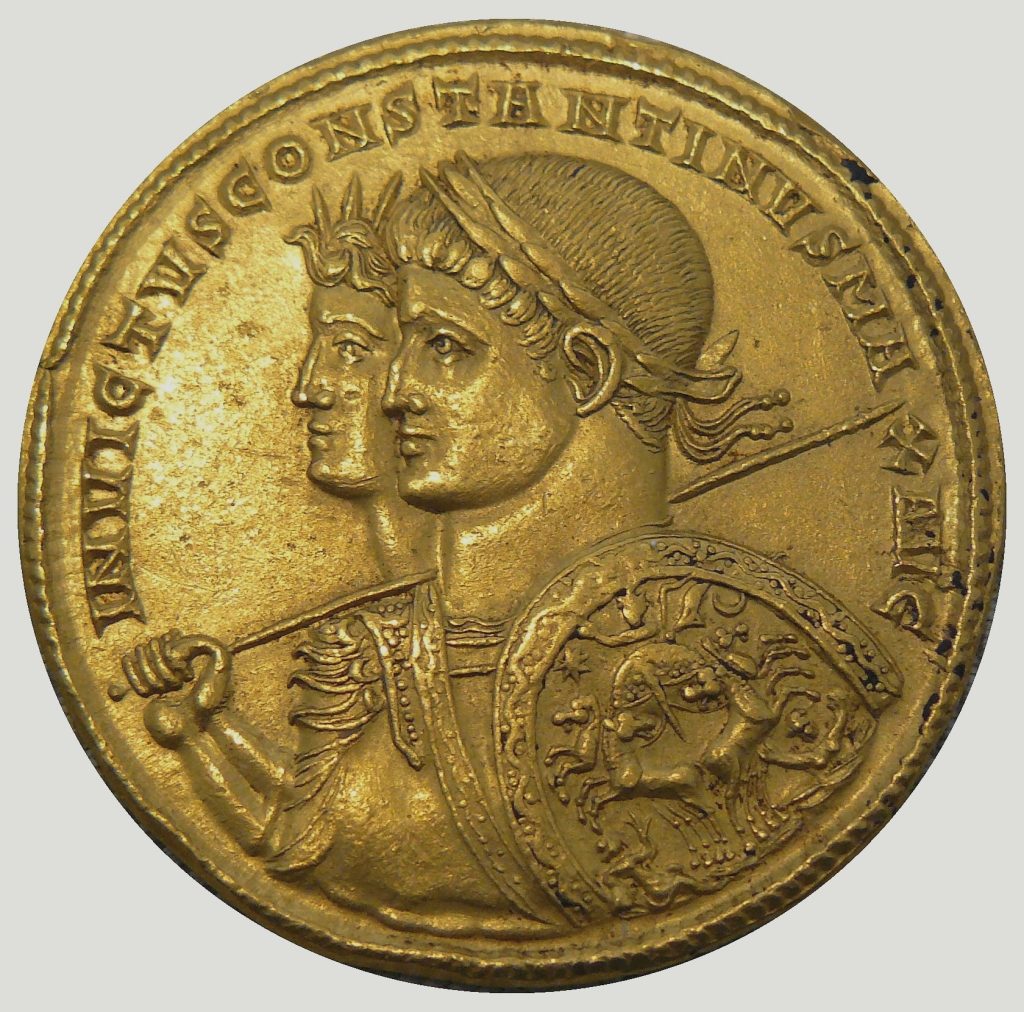

The discovery includes three ancient walls, believed to be part of a temple dedicated to the Imperial Cult. This temple, located in the town of Spello, is now considered the largest evidence of the Imperial Cult practice in fourth-century Italy and the late Roman Empire.
“There was a remarkable religious continuity between the Roman world and the early Christian world,” Professor Boin said. “Things didn’t change overnight. Before our find, we never had a sense that there were actual physical, religious sites associated with this late ‘imperial cult practice.’ But because of the inscription and its reference to a temple, Spello offered a very tantalizing potential for a major discovery of an Imperial cult underneath a Christian ruler.”
This temple immediately became what Boin calls the largest evidence ever of the Imperial Cult in both fourth-century Italy and the late Roman Empire.
“There’s evidence from other places throughout the Roman world that Christian rulers supported imperial cult practices,” Boin said. “We’ve known that pagans worshiped at their temples in the fourth century, but those findings have all been small and inconsequential. And we’ve known that Christians supported the imperial cult, and we’ve known that without any sense of where it would have happened. This temple bridges those two landmarks, and in that respect, it is unlike any temple that I know about from the Mediterranean world of the fourth century Roman Empire. Any study of the imperial cult in the fourth century Roman Empire is now going to have to take account of this temple, which is an incredible discovery to make.”
“We are on the cusp of giving people a very visible piece of evidence that really upends the neat and tidy ways people think about big moments of cultural change,” Boin said “Cultural changes are never as big as we think they are when living through them, and there’s a lot of gray area in between people’s customs and the broader society and culture. And a lot of those can be left out of the story. So to have this temple potentially be a temple dedicated to Constantice’s divine ancestors as a way to worship the emperor in an increasingly Christian world at the time, it’s so weird and I love that we can bring it to light.”
Boin and his team will return to Spello next summer to completely excavate the area to examine the full temple, where he hopes to make even more significant discoveries.
Cover Photo by Douglas Boin.