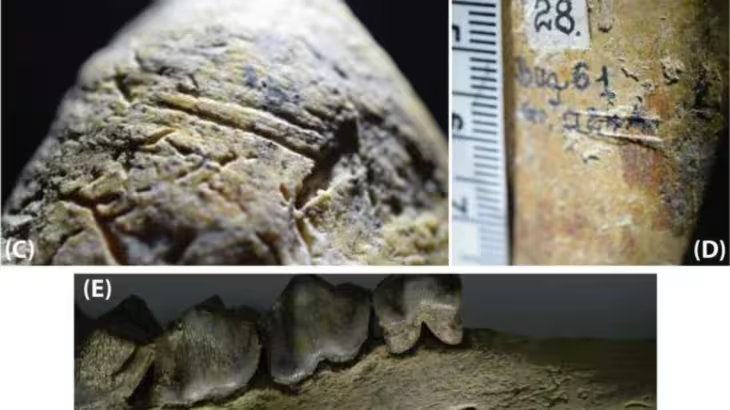
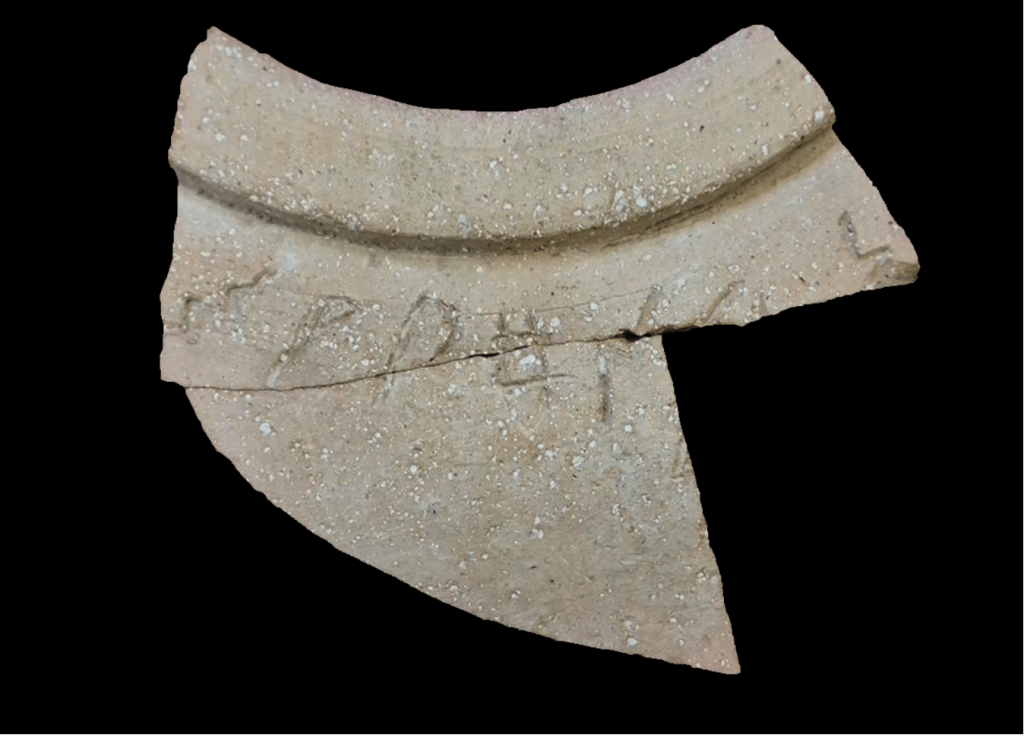
Archaeologists deciphered a partially preserved inscription that was found on the neck of a large jar dated back to the time of King Solomon.
Dr. Daniel Vainstub of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HU) was able to decipher an ancient South Arabian script used at the time in the southern Arabian Peninsula (current-day Yemen region) when the Kingdom of Sheba was the dominant kingdom.
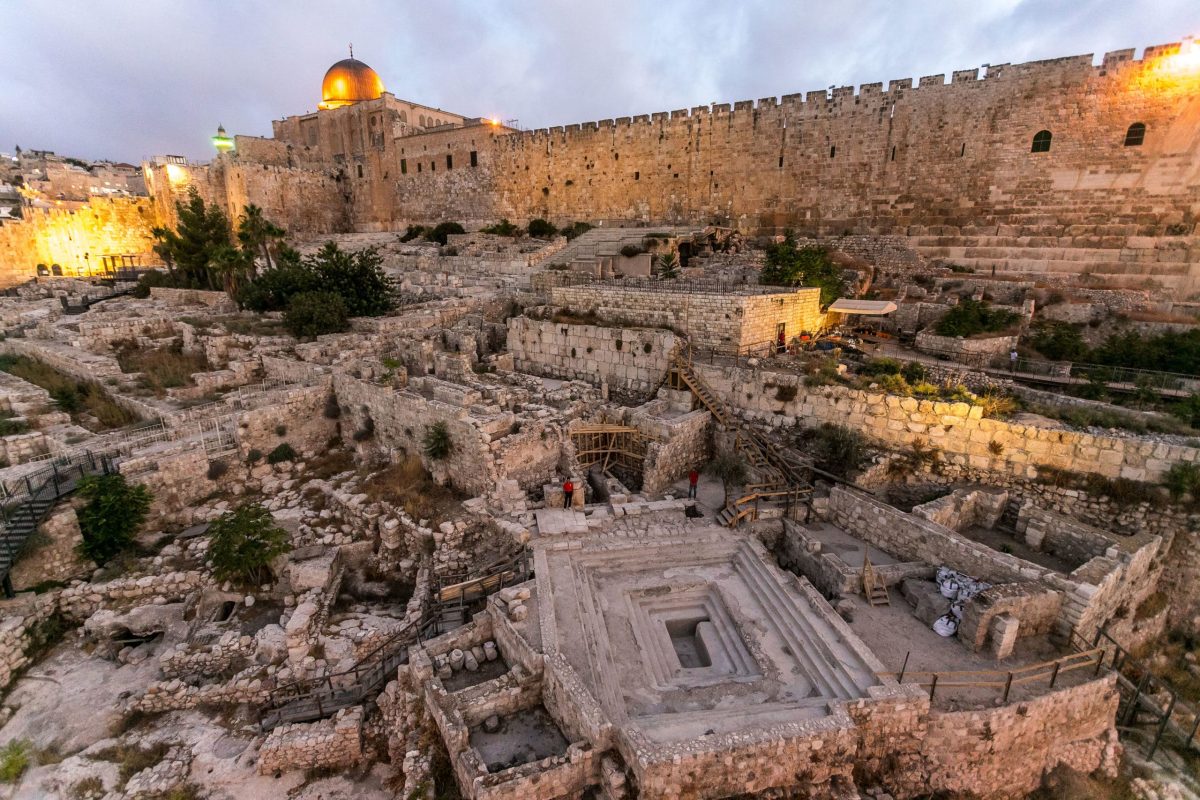
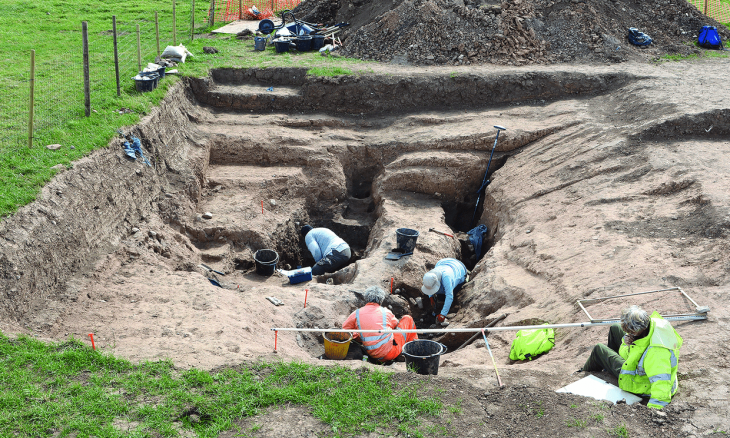
The jar was originally discovered together with the remains of six other large jars during excavations carried out in 2012 in the Ophel area south of the Temple Mt., led by the late Dr. Eilat Mazar from the Institute of Archeology of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
There were only seven letters left from the original inscription. The inscription is written in Canaanite script, from which the ancient Hebrew script used during the First Temple era was developed. Over the course of the last ten years, more than ten researchers have proposed various readings without coming to a consensus. In the study, Dr. Daniel Vainstub determined the script is “Ancient South Arabian,” the script that was used in the south-west part of the Arabian Peninsula (the Yemen region of today), where the Kingdom of Sheba was the dominant kingdom at that time.

The Kingdom of Sheba was the home of the biblical “Queen of Sheba”, a figure first mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. However, the Bible’s First and Second Books of Kings and Chronicles record her visit to the king with gold, precious stones, and camels carrying spices to see if he was as wise as reputed. According to these accounts, the queen was awestruck by his wisdom and majesty, as well as the Temple he had just finished. She returned home after praising both the king and Israel.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
While competing theories place the kingdom in South Arabia or the Horn of Africa, modern historians associate Sheba with the South Arabian kingdom of Saba, which is located in modern-day Yemen and Ethiopia.
According to the new study, the inscription on the jar reads, “[ ]shy l’dn 5,” means five ” šǝḥēlet,” referring to one of the four ingredients mentioned in the Bible (Exodus 30:34) required for the incense mixture. The ” šǝḥēlet ” was an essential ingredient in the incense that was burnt in the First and Second Temples and was called “tziporen” in Rabbinic literature.
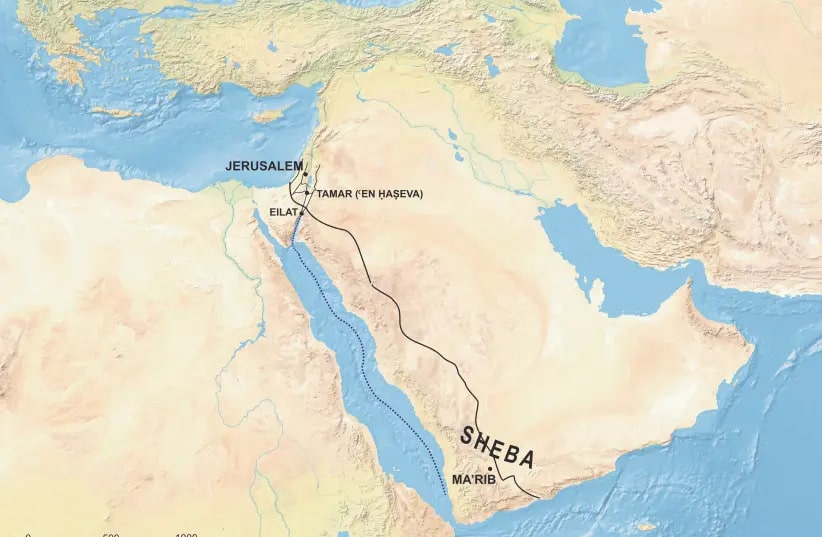
This demonstrates a clear link between Jerusalem in the 10th century BCE (the Kingdom of Solomon’s days) and the Kingdom of Sheba. The pottery jar appears to have been made in the Jerusalem area, and the inscription was engraved before it was fired by a Sabaean speaker who was involved in the supply of incense spices.
Dr. Vainstub said in a statement, “Deciphering the inscription on this jar teaches us not only about the presence of a speaker of Sabaean in Israel during the time of King Solomon, but also about the geopolitical relations system in our region at that time – especially in light of the place where the jar was discovered, an area known for also being the administrative center during the days of King Solomon. This is another testament to the extensive trade and cultural ties that existed between Israel under King Solomon and the Kingdom of Sheba.”
The Ophel site in the Archaeological Park at the foot of the southern wall, within the Jerusalem Walls National Park area, includes a trail that passes between 2,000-year-old mikvahs used by Temple pilgrims. This was also the location of the administrative center of King Solomon’s kingdom.
Cover Photo: Biblical Archaeology