As part of a Jewish heritage project in Izmir, Turkey, nine historic synagogues will be reopened as museums.
Built by Sephardic Jews who immigrated from Spain to Anatolia, nine synagogues in the Kemeraltı quarter of the Aegean province of Izmir will soon welcome visitors as an open-air museum.
From June, visitors to the old bazaar of Kemeralti can get a taste of life as it was when this buzzing area on Turkey’s Aegean coast was home to 30,000 Jews.
Izmir is one of many Turkish cities that have housed a variety of cultures and faiths over time. Izmir’s texture still exhibits signs of historical diversity, where Jews, Greeks, Armenians, Levantines, and Turks have all resided.
There is no doubt that the Jews came first among the peoples to contribute to the cultural structure of Izmir in history. With the support of the Ottoman Empire, which embraced the Jews fleeing the Inquisition, Jews came from Spain and Portugal in 1492 and settled, building important cultural riches in Anatolian lands since their arrival. In Izmir, which houses synagogue ruins dating back to ancient times, this Jewish community also played a major role in the city’s multicultural identity and constructed spellbinding synagogues for worship here.
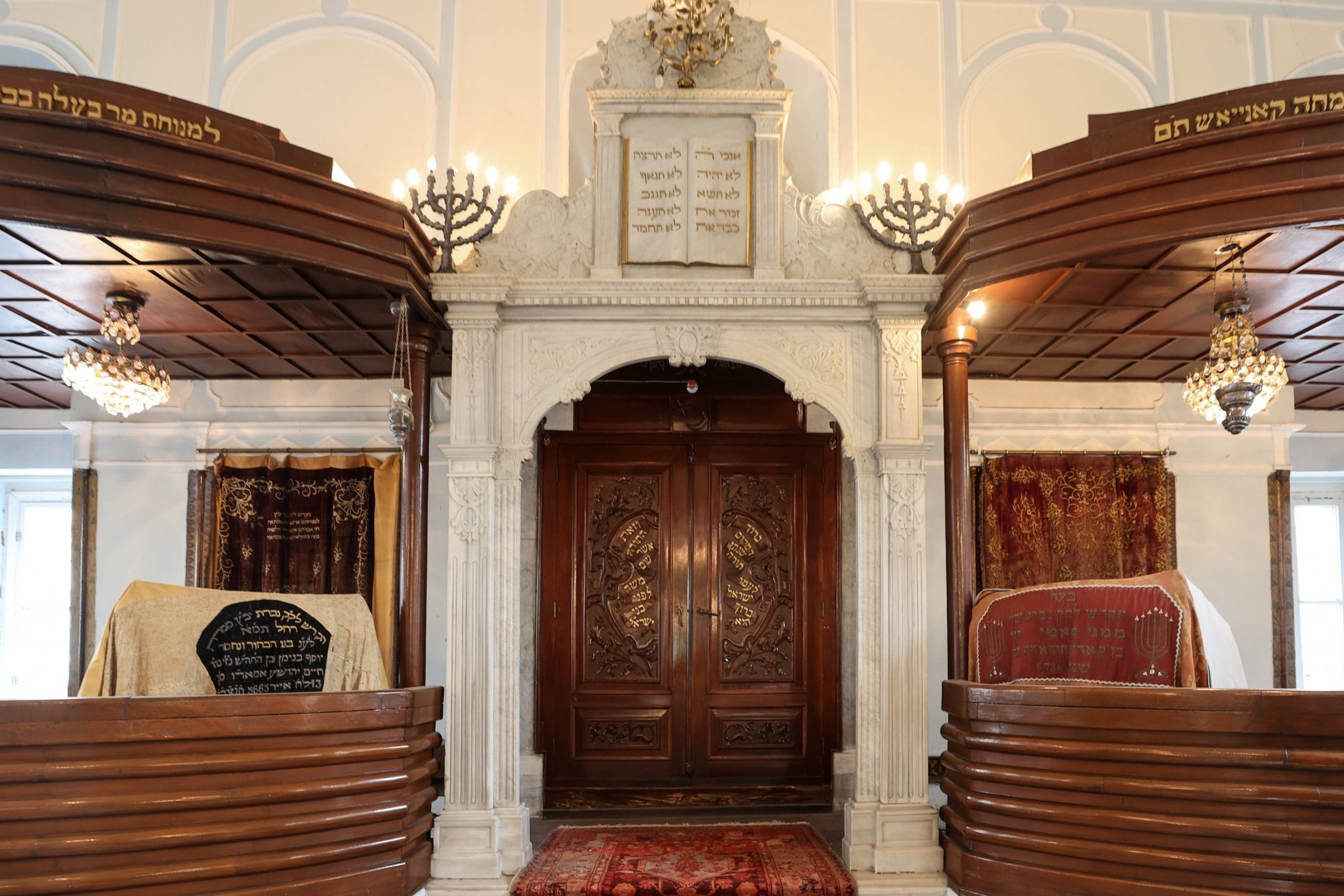
The Jewish people reportedly constructed 34 synagogues in Izmir over the course of history, nine of which can be found in the Kemeraltı quarter. These synagogues will soon serve as cultural centers and host visitors following preservation and restoration work. Among them are the Bikur Holim, Bet Hillel, Portekiz, Etz Hayim, Hevra, Şalom, Algazi, Forasteros and Sinyora synagogues.
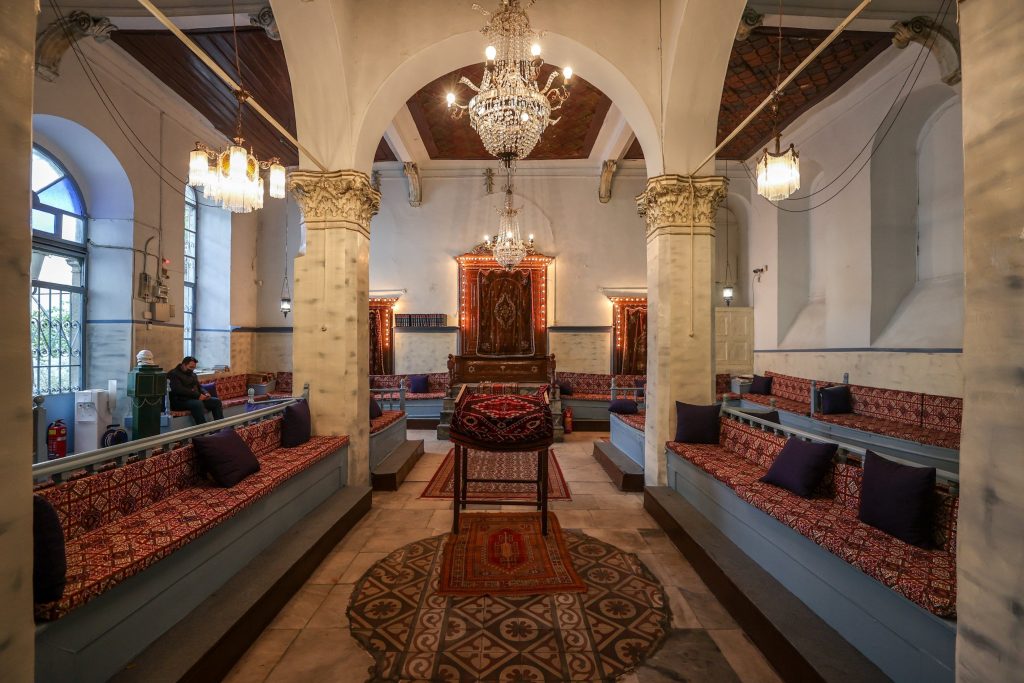

While some of these synagogues remained open to worship uninterruptedly for 300-400 years, others became unusable due to earthquakes, fires, and neglect. To remedy the situation, the Izmir Jewish Community set to work to protect the places of worship. Conservation and restoration are being carried out within the framework of the Izmir Jewish Heritage Project, which is being executed in cooperation with local governments, national and international organizations, and various nongovernmental organizations (NGOs).
Six of the nine synagogues being restored are grouped together “practically wall to wall” around a courtyard. Work is also ongoing to restore the former office of the city’s chief rabbi and a building that once housed a kosher winery.
Kemeraltı synagogues
The building of the Bikur Holim Synagogue was donated by Salomon de Ciaves, who was a Portuguese-born Dutch immigrant from Izmir, in 1724. De Ciaves also ensured that all the books and sacred objects needed for a synagogue were purchased, in addition, he donated some of the adjacent houses and shops to the synagogue to generate income. This basement of this synagogue was used as a hospital during one of the frequent epidemics in the city. Therefore, it was named “Bikur Holim,” meaning patient visitation, from then on.
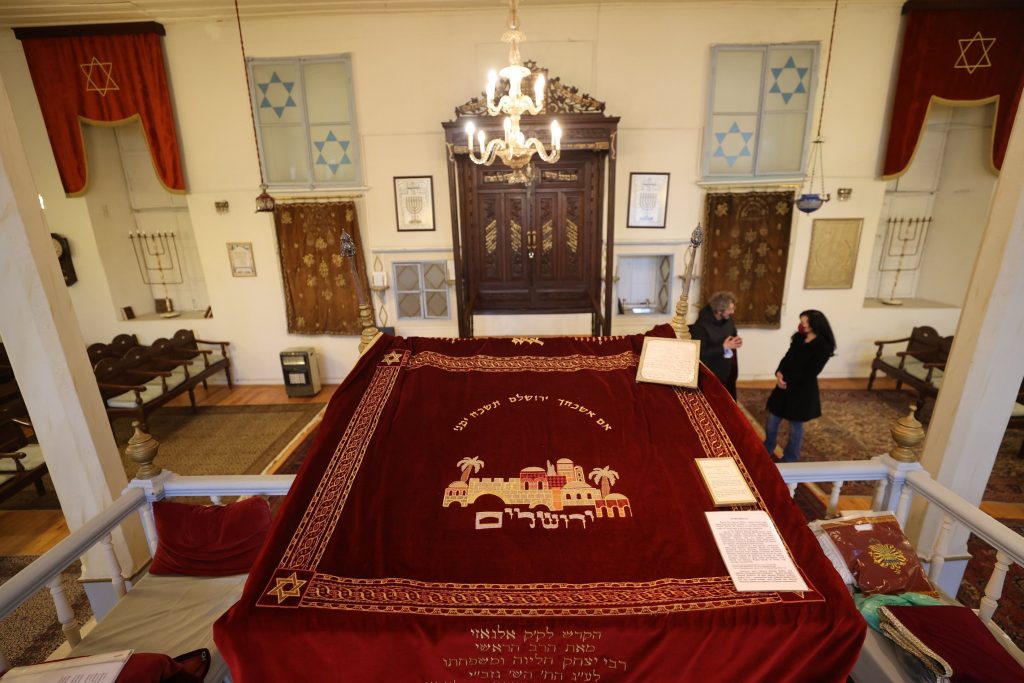

Bet Hillel Synagogue was established by the Palaçi family. Rabbi Hayim Palaçi and his son Rabbi Avraham Palaçi were the greatest religious scholars of their period. It is said that their fame crossed the borders of Turkey and even Jewish religious figures came to Izmir to consult these two rabbis. Rabbi Hayim Palaçi was awarded the order of “religious man in charge of justice” by Sultan Abdülmecid. After the restoration by Izmir Metropolitan Municipality, the synagogue was opened to visitors as Hayim Palaçi Memorial House.
The Portekiz (Portuguese) Synagogue reflects where its founders immigrated from with its name. The synagogue was used as a center by those who were against the Sephardic Jewish mystic and Rabbi Sabbatai Zevi. But Sabbatai Zevi and his supporters broke into the synagogue, expelled the rabbis, and began to use it for their own purposes. The synagogue was also damaged during a fire in 1976.
The oldest of the restored synagogues, Etz Hayim, dates to the 1600s, the Byzantine Empire. The synagogue has survived many fires and earthquakes over its history. After being damaged by a fire in 1841, a philanthropist named Daniel De Sidi repaired the building in 1851.
Hevra Synagogue is also known as the Talmud Tora Synagogue. This synagogue was also suffered a lot of damage in several incidences and was rebuilt. Although it was reconstructed by the brothers Çelebi and Menachem Hacez after a fire in September 1838, it burned in another fire once again in 1841.
Şalom Synagogue, which is also known as El Kal de La Tromba, was allocated to Jews arriving from Aydın in the 1930s. The building was started to be called Aydınlılar Havrası (The Synagogue of Those from Aydın). As one of the most authentic synagogues in Izmir, the construction bears engraving-like decorations called “kalem işi.” In the decoration of the synagogue, the Jews were inspired by the Ottoman galleons that brought them from Spain in the 15th century.

The Algazi Synagogue was commissioned by Ishak Algazi from the Algazi family, who raised important religious scholars in their period. After Beth Israel Synagogue, it is the largest Jewish place of worship in Izmir. The synagogue, also known as Algaze, differs from the others as it does not have an area just for women known as the “azara.”
It is thought that the Forasteros Synagogue, which literally means “foreigners,” was founded by foreigners who immigrated to Izmir from the Aegean islands, Greece and various European countries, but its date is unknown. According to another argument, the synagogue was built in the 17th century by foreign traders (Los Frankos). The synagogue, which was thought to have been completely destroyed and rebuilt in the 1688 earthquake, was renovated once again after 1841, following various outbreaks of fire.
According to popular belief, the Sinyora Synagogue was built with donations of Dona Gracia Nasi, famously known by her nickname La Senora, who held an important position in the Ottoman Empire with a role of leadership in the Sephardic world. Burned several times in the 16th and 17th centuries, the building was completely destroyed in the fire of 1841 and was rebuilt with the contributions of Moiz Bengiat Yerushalmi.
In 2004, the World Monuments Fund added ‘Central Izmir Synagogues’ to its World Monuments list, calling them “an unparalleled testament to the city’s rich Jewish heritage”.