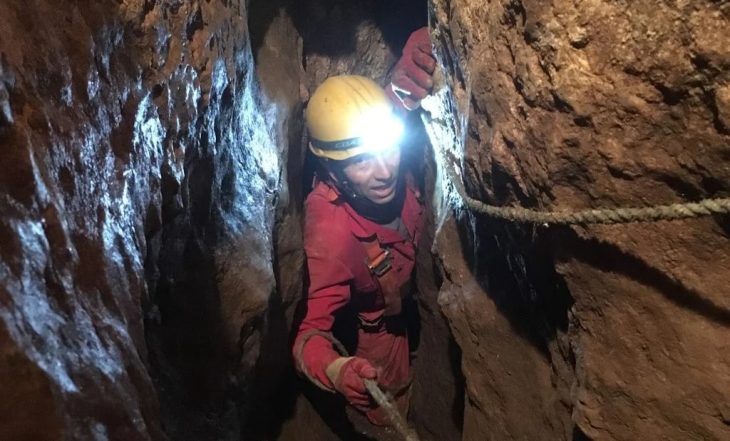
A remarkable archaeological find in the rugged terrain of West Texas is transforming our understanding of the region’s prehistoric inhabitants. Deep within the San Esteban Rockshelter cave system, researchers have uncovered a well-preserved hunting kit, believed to be approximately 6,500 years old. This discovery is being hailed as one of the oldest intact weapon systems ever found in North America.
The excavation was conducted by a team from the Center for Big Bend Studies (CBBS) in collaboration with the Odyssey Archaeological Research Fund at the University of Kansas. While it has long been theorized that ancient hunter-gatherer societies in the area utilized atlatl-based hunting tools, the discovery of this complete and untouched cache allows scientists to move from speculation to a vivid reconstruction of these early technologies.
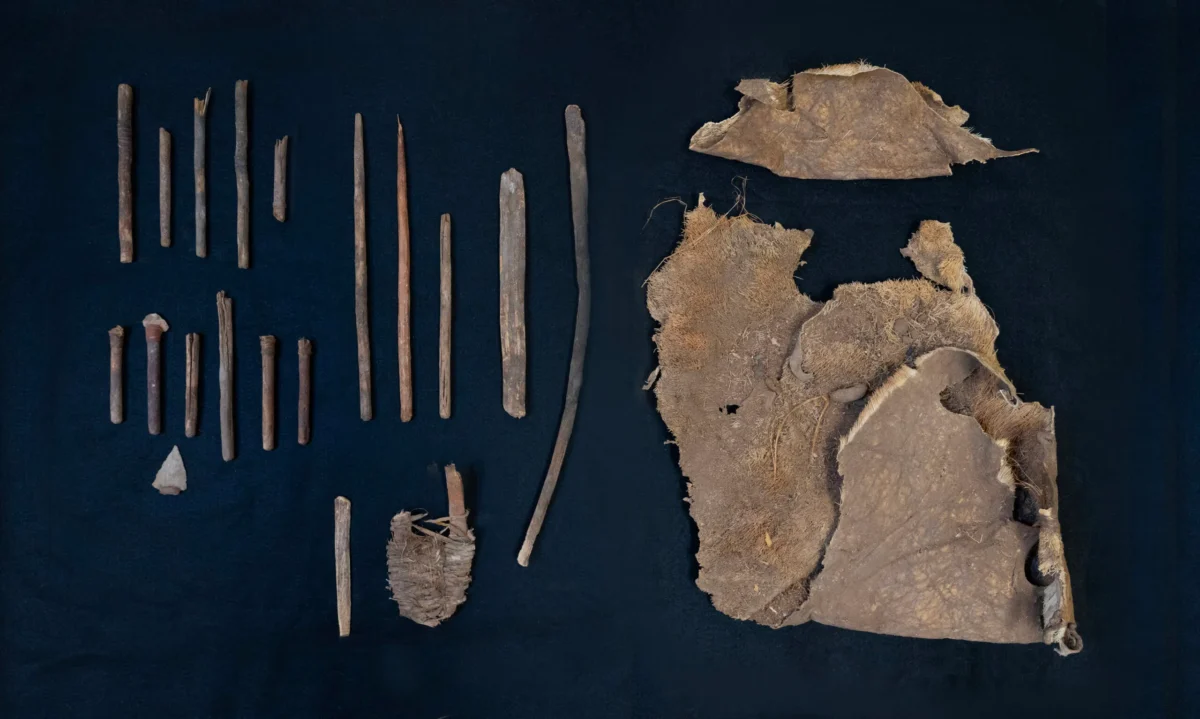
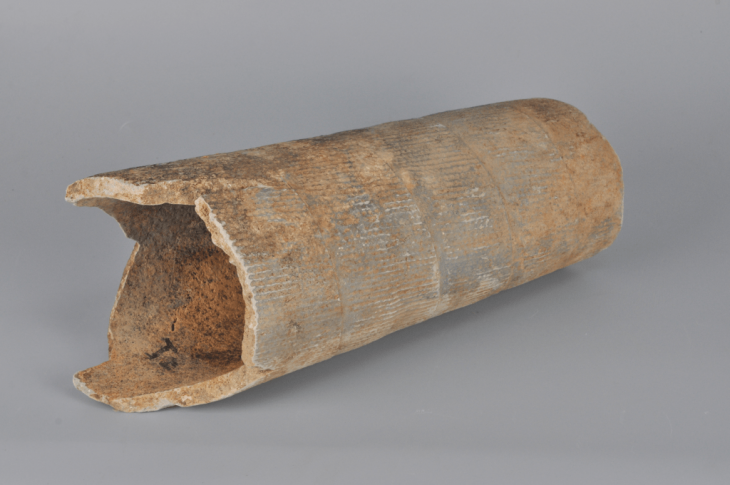
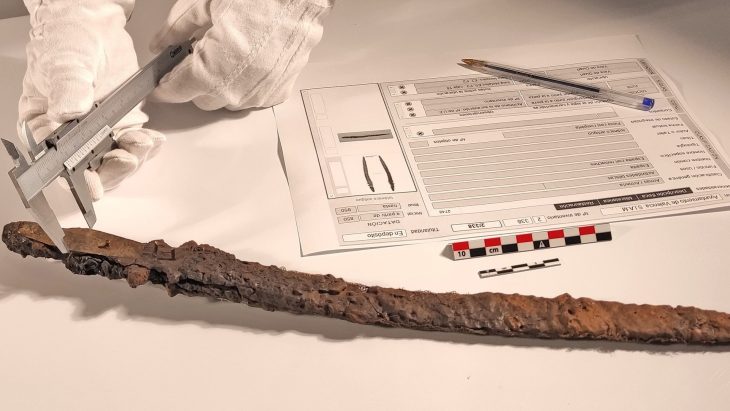
Among the significant artifacts recovered were six stone-tipped foreshafts, which were used to connect darts to an atlatl—a spear-throwing lever. Additionally, four hardwood foreshafts, likely intended for poison delivery, were found alongside four damaged dart nock ends and a rare, straight-flying boomerang. A partial atlatl was also recovered, although one end of its handle had deteriorated over time.
Devin Pettigrew, a weapons expert and assistant professor at CBBS, noted, “We’re also missing the proximal handle end of the atlatl, but we know enough about this type to reconstruct what it may have looked like.” The preservation state of these ancient Native American hunting tools is exceptional, particularly given their age. Most archaeological finds from this era are fragmented, making full reconstructions difficult. However, this discovery allowed researchers to piece together nearly the entire weapon system, enabling them to visualize how these components functioned together in actual hunting scenarios.
Beyond the weaponry, the cache provided intriguing insights into the lives of the people who once inhabited the region. Archaeologists discovered a folded, tanned pronghorn hide still retaining its original hair, along with human feces—evidence that adds a uniquely human context to the find. The hide, featuring spaced holes around its edges, suggests it was tied to a frame for softening, reflecting techniques known from Plains Native traditions.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
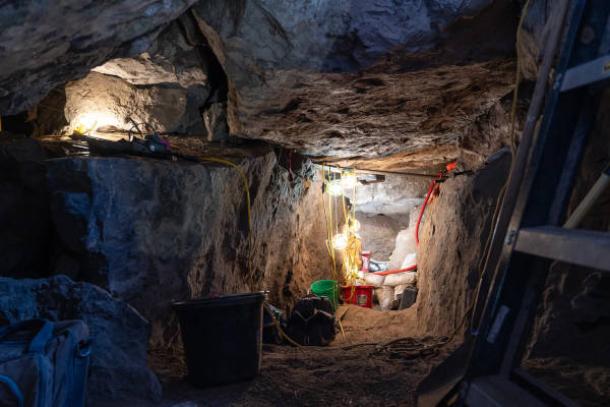

The moment of discovery left a profound impact on the excavation team. “We just sat there and stared at it in wonder. That’s a moment in time,” Pettigrew expressed. “It’s akin to holding dish gloves that somebody put over the sink after doing the dishes. Somebody folded that hide up and sat that right on top of this rock, and nobody touched it for 6,000 years.”
The arrangement of the broken dart nocks and the deliberate positioning of the weapon parts imply that the cache may have held symbolic or spiritual significance. “Interpretations like this, based on more recent cultures, are more difficult the further back in time you go,” Pettigrew noted. The possibility that this was more than a mere utilitarian stash adds a deeper dimension to our understanding of prehistoric lifeways.
Louie Bond of Texas Parks and Wildlife Magazine explained the technical aspects of the artifacts: “The nock ends of the darts fit against the atlatl spur; the dart flexed when thrown to maintain straight flight. The dart foreshafts fit into sockets or sleeves in the end of a dart main shaft.” This construction allowed ancient hunters to maximize power and accuracy, enhancing their chances of success in the challenging environment of ancient Texas.
These technical insights not only deepen our understanding of prehistoric engineering but also illuminate how early peoples interacted with their ecosystem—tracking, targeting, and hunting large game with complex, reusable tools.

Bryon Schroeder, Director of the Center for Big Bend Studies, described the find as “monumental,” emphasizing its role in filling critical gaps in the archaeological record. “We get these incredible snapshots of life, vignettes of how they lived, what the environment was, and how they responded to it,” he stated. The meticulous excavation process, where each artifact was uncovered piece by piece, brought renewed excitement with every discovery.
What may have initially appeared as a single hunter’s gear stashed away for later use is now viewed as a window into an entire way of life—one shaped by innovation, adaptation, and possibly ritual. As the research team continues to study the cache, they anticipate that this singular discovery will have a lasting impact on archaeological research in North America for years to come.
Texas Parks & Wildlife Magazine
Cover Image Credit: Robert Greeson- Center for Big Bend Studies