A 5,500-year-old (that is around 3500 BC) menhir has been discovered in the town of São Brás de Alportel in the District of Faro, Algarve region, in Portugal.
A menhir is a single upright prehistoric stone monument, similar to a stele, and often buffed to create a phallic shape. They are one of the first stone monuments in human history, and in Europe, they are the first to have a religious function. In practice, they symbolized fertility, whether of animals, people or land, hence their form.
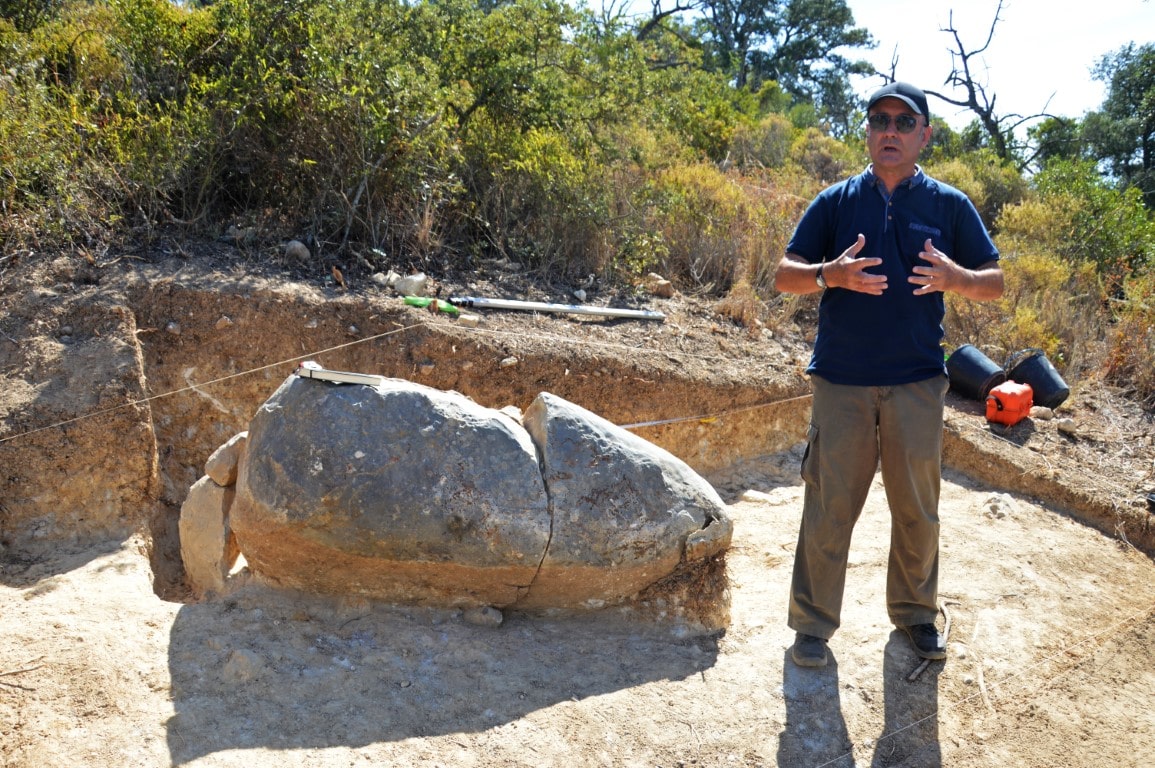
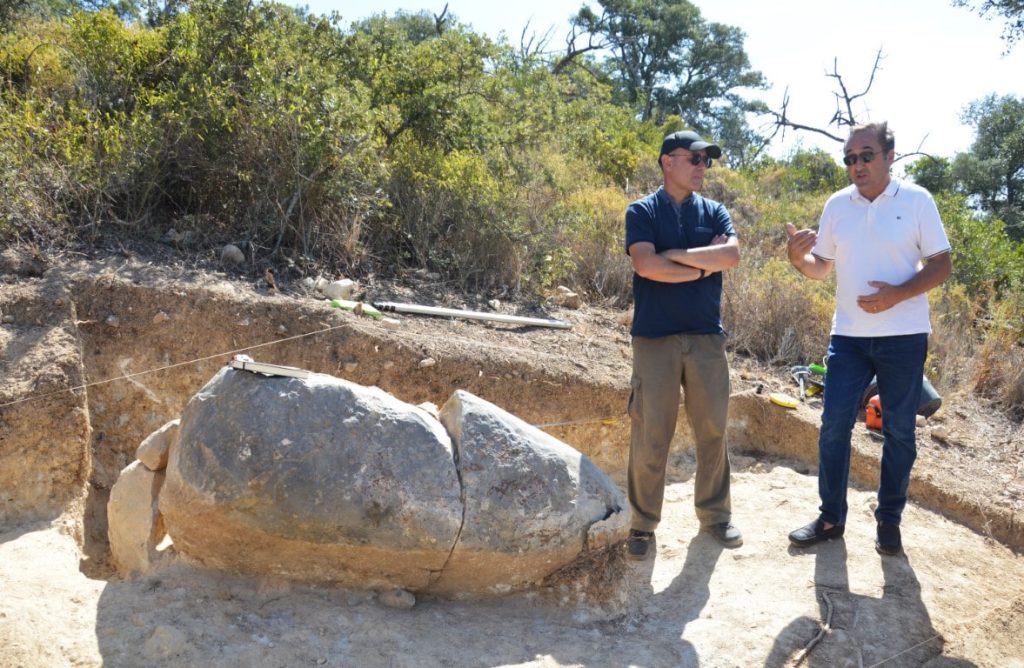
Archaeologist António Faustino de Carvalho made the announcement in front of the now-named menhir of Monte do Trigo, which was the focus of excavations he oversaw for a week in August. This is the first archaeological excavation in the history of the municipality of So Brás de Alportel.
The first-ever archaeological excavation in the history of the municipality of São Brás de Alportel started on August 14, 2021, following the discovery of a possible menhir by a resident looking for trilobites (fossils) at the top of Monte do Trigo, in the Machados area.
The Regional Directorate of Culture of the Algarve joined forces with the Municipality of São Brás de Alportel and the University of the Algarve (UAlg).
As soon as professor and archaeologist António Faustino Carvalho came across the object, he said he was “immediately 95 percent certain that we were facing a menhir”, he clarified to journalists last Friday, August 18, during the presentation of the preliminary fieldwork results.
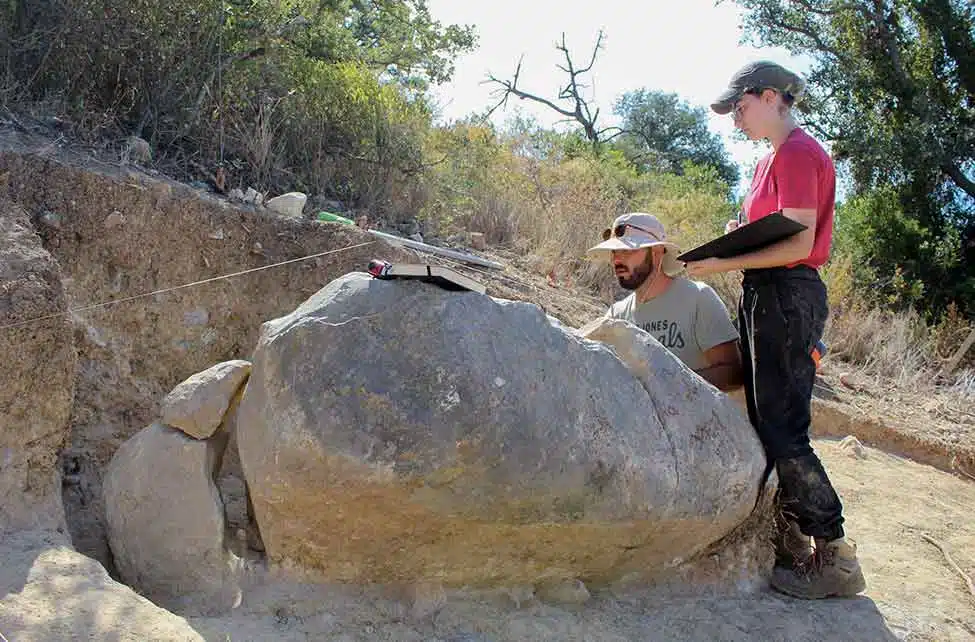

Next to the stone monument, he explained that it is a menhir of particular importance for the Eastern Algarve and of interest on a regional scale. “Its shape, the raw material it is made of (limestone), and its dimensions are the same as the dozens of menhirs from the Neolithic period that we already know of in Barlavento, in Aljezur, Lagoa, Lagos, and Vila do Bispo. Outside these municipalities, we aren’t aware of any”.
But that is not the only particularity of the archaeological find: it is also the first menhir in limestone and with characteristics that attribute it to the Neolithic period (5500 years ago, that is around 3500 BC) to be discovered in the Sotavento Algarvio.
Professor António Faustino Carvalho, “in Sotavento, in Loulé and Salir, for example, there is the menhir of Cerro das Pedras, which was discovered by Estácio da Veiga in the 19th century, in Lavajo, in Alcoutim, there is also a meniric complex, which is also open to the public.”
But “these are the only examples we have in Sotavento of structures similar to this one, but here the key word is “similar” because they are not exactly the same». The Sotaventine menhirs “are made in other rocks, have other configurations, which are more or less truncated conical, prismatic or with irregular morphologies, not with this phallic morphology,” he said.

They are, moreover, from “a later period of Prehistory, from the Chalcolithic period or Copper Age, they are about 5000 years old”, that is, at least five centuries older. new than the menhir of Monte do Trigo.
The menhir of Monte do Trigo “was lucky to be partially covered with earth and, as it is bulky, it will have resisted more to human action and the action of time.”
This menhir is no longer, that is, in the original place where it would have been erected, erect to mark the territory of the people who 5500 years ago would have lived on the slope and in the valley at the foot of the mountain, in the area that is now called Machados, on the edge of the EN2.
Although today it is lying down, originally it was vertical, marking the territory, most likely on top of the hill, perhaps with other menhirs in the vicinity.
As for the future fate of the Monte do Trigo menhir, a report, and topographical study will now be redacted, and the decision on what to do with the monument will be made.
Cover Photo: Elisabete Rodrigues | Sul Informação