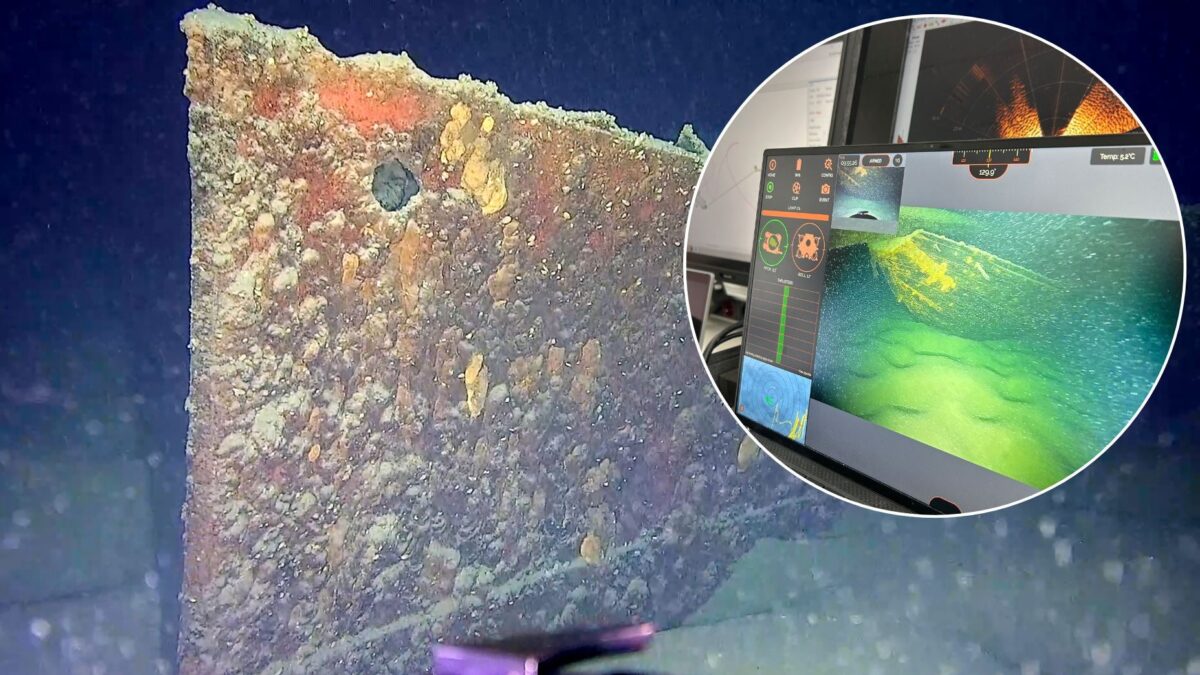
In a groundbreaking underwater archaeology project, researchers have discovered 31 previously unknown shipwrecks lying silently on the floor of Lake Constance (Bodensee). The ambitious “Wrecks and Deep Sea” project, launched in 2022 by the State Office for Monument Preservation (LAD) in Baden-Württemberg, is the first systematic exploration of the lake’s submerged cultural heritage.
Over the past two years, scientists have used cutting-edge geophysical surveys, diver teams, and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) to uncover a remarkable collection of finds — from 19th-century paddle steamers to a rare, fully intact historical cargo sailing ship.
Mapping the Depths
Lake Constance (Bodensee) plunges to a maximum depth of 251 meters, and much of its underwater world has remained unexplored — until now. By the end of 2024, the team had identified over 250 “anomalies” — unusual shapes or features on the lakebed — using high-resolution bathymetric data from the Institute for Lake Research (ISF) and advanced side-scan sonar imaging.
Of these anomalies, 186 were systematically examined. The majority turned out to be natural formations or modern debris. However, 31 were confirmed as genuine shipwrecks — vessels that once carried passengers, cargo, and stories across the lake.
The Stars of the Find: Paddle Steamers and a Time-Capsule Cargo Ship
Among the most striking discoveries are the remains of two large metal hulls, which preliminary analysis suggests could belong to the paddle steamers “SD Baden” (originally the Kaiser Wilhelm, launched in 1871) and “SD Friedrichshafen II” (in service from 1909). These majestic vessels once carried up to 600 passengers each, but both met tragic ends. The Friedrichshafen II was destroyed in a World War II air raid and later scuttled in 1946; the Baden was decommissioned in 1930 and eventually sunk.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
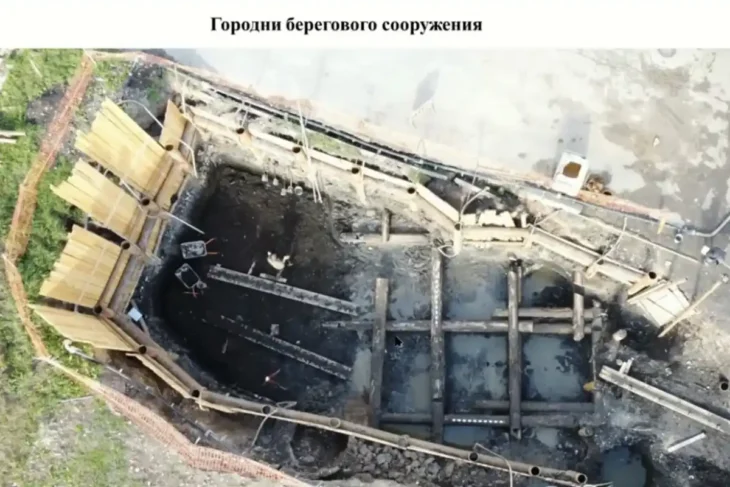
The crown jewel, however, is a nearly intact historical cargo sailing ship — complete with mast and yardarm still in place. Such preservation is rare in freshwater archaeology. Minimal colonization by invasive quagga mussels means that intricate details — including bow fittings, belaying pins, and a toothed ratchet wheel — remain visible.
“The find offers unique insights into the sailing technology and shipbuilding of historical Lake Constance vessels,” said Alexandra Ulisch, scientific associate on the project. “It is a significant reference object for research.”
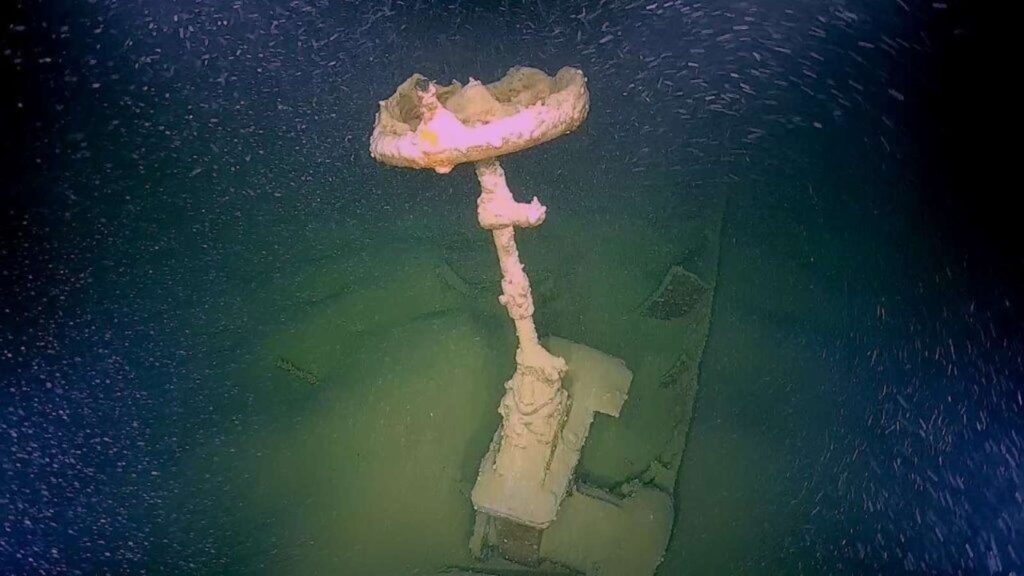

Lost Cargo and Forgotten Journeys
In another location, the team found a scattered debris field of at least 17 wooden barrels, some with intact lids and potential branding marks. Without an associated shipwreck, the origin of this cargo remains a mystery. Plans for further investigation are underway.
To the LAD researchers, shipwrecks are not just lost vehicles — they are “time capsules preserving craftsmanship and stories from long-forgotten days,” as Ulisch notes. From the Titanic to local legends like the Säntis or Lady Jay, the fascination with shipwrecks spans cultures and centuries.
A Methodology That Sets New Standards
The “Wrecks and Deep Sea” project represents a methodological milestone in inland water archaeology.
The process involves: Bathymetric mapping to detect anomalies.
Side-scan sonar surveys to create near-photographic images of the lakebed.
ROV or diver inspections for confirmation and documentation.
This approach allows archaeologists to distinguish natural features from human-made objects with precision, ensuring that only genuine cultural heritage sites are recorded.
Project leader Dr. Julia Goldhammer emphasized that the initiative is about more than just spectacular finds:
“The insights gained will form the basis of an archaeological inventory of Lake Constance wrecks, providing critical data on their condition and threats.”
No salvaging is currently planned, as recovery and conservation costs are high. Instead, the focus remains on thorough documentation and long-term preservation through research.
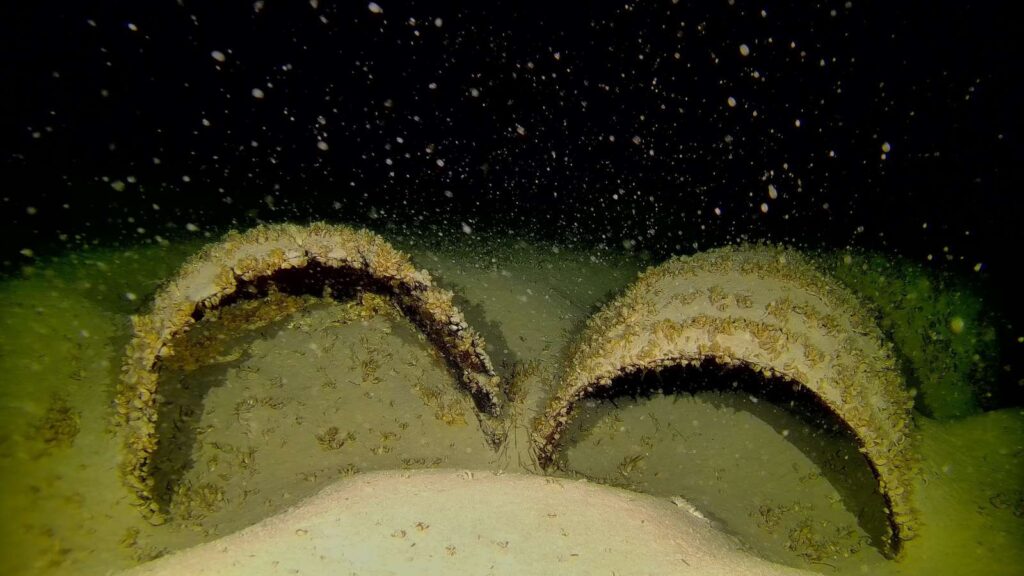

Why It Matters
Beyond their historical intrigue, these wrecks tell a broader story about trade, transportation, and daily life on Lake Constance across centuries. Scientific analysis of preserved materials can reveal the origins, processing methods, and quality of goods transported — from building materials to raw resources.
As the project continues, researchers expect more revelations before its scheduled conclusion in 2027. Until then, the silent fleet beneath Lake Constance will continue to guard its secrets — at least, until the next sonar sweep.
State Office for Monument Preservation (LAD)
Cover Image Credit: LAD at RPS/ISF of LUBW/picture alliance/dpa