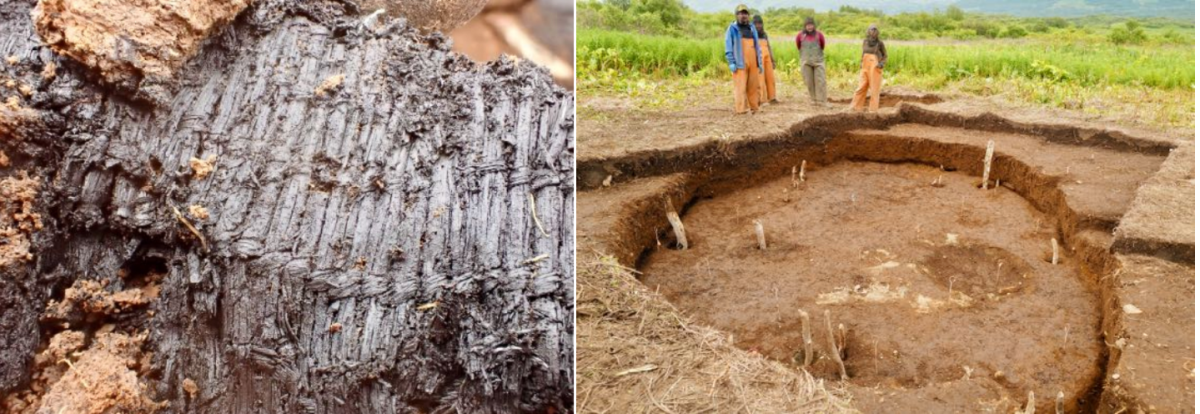
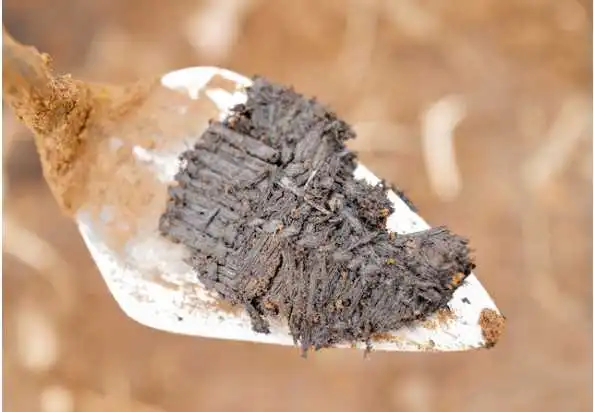
Archaeologists have uncovered fragments of woven grass artifacts estimated to be 3,000 years old during excavations at an ancestral sod house on the shores of Karluk Lake on Alaska’s Kodiak Island.
In a press release by the Alutiiq Museum, it was announced that the fragments, which appear to be pieces of mats, are among the earliest well-documented examples of Kodiak Alutiiq/Sugpiaq weaving.
Weaving is a long-practiced Alutiiq art, but one that is difficult to document archaeologically as fiber artifacts are fragile and rarely preserved.
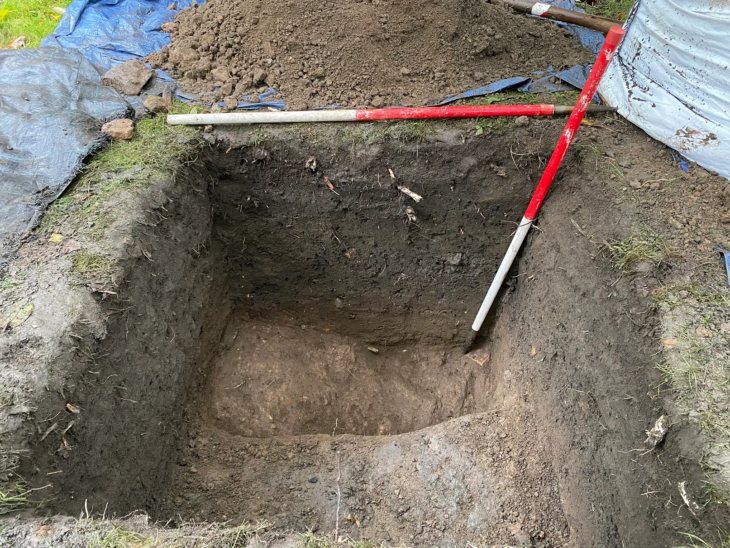
“We were excavating a sod house beside Karluk Lake as part of a broader study to understand how Alutiiq people used Kodiak’s interior,” said Alutiiq Museum Curator of Archaeology Patrick Saltonstall.
“When we reached the floor, we discovered that the house had burned and collapsed. The walls of the structure, which were lined with wood, fell into the building and covered a portion of the floor. This sealed the floor quickly and limited burning. As we removed the remains of the walls, we were surprised and excited to find fragments of charred weaving. It looks like the house had grass mats on the floor. The pieces covered about a two-meter area at the back of the house, perhaps in an area for sleeping.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The extensive archaeological collections of the Alutiiq Museum include grass and spruce root baskets dating back up to 600 years, but nothing older. Radiocarbon dating revealed that the weaving-producing house was about 3,000 years old. This conclusion is supported by the architectural design of the structure and the artifacts discovered nearby.
“It is likely that our ancestors worked with plant fibers for millennia, from the time they arrived on Kodiak 7500 years ago,” said April Laktonen Counceller, the museum’s executive director. “It makes sense. Plants are abundant and easily harvested, and they are excellent materials for making containers, mats, and other useful items. It’s just very hard to document this practice. This wonderful find extends our knowledge of Alutiiq weaving back an additional 2400 years.”
Close inspection of the woven fragments shows that their makers laid down long parallel strands of grass (the warp) and then secured them with perpendicular rows of twining (the weft) spaced about an inch apart. This technique created an open weave also found in historic examples of Alutiiq grass matting. Small fragments of more complicated braiding may represent the finished edge of a mat.
The Alutiiq Museum is a non-profit organization dedicated to preserving and sharing the Alutiiq people’s history and culture. The museum is governed by members of Kodiak Alutiiq organizations and is supported by donations to charities, membership fees, grants, contracts, and sales.
Cover Photo: Alutiiq Museum