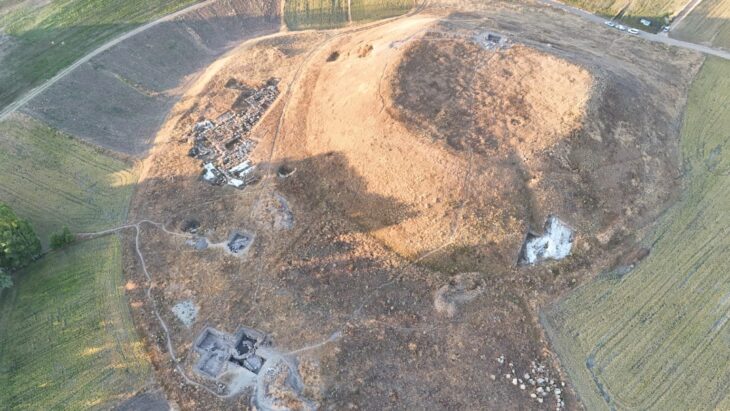
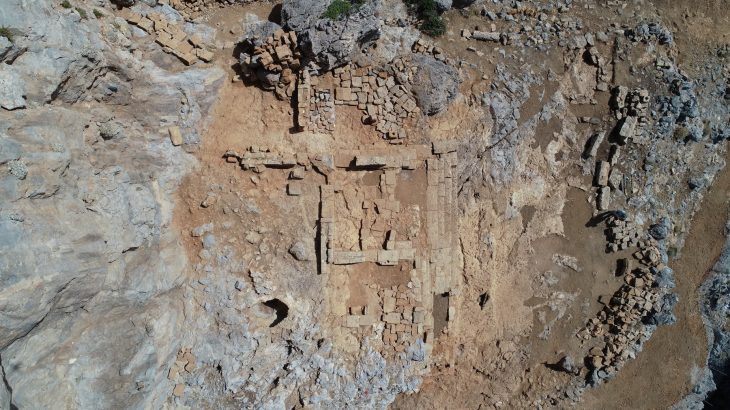
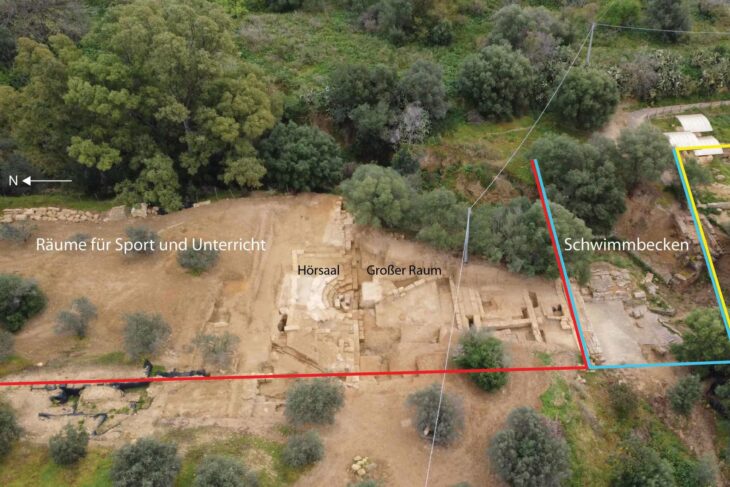
Excavations at the Butkara Stupa, located near Mingora in Swat, Pakistan, have uncovered significant findings, including two-thousand-year-old coins, pottery, and inscriptions in the Kharosthi script, all of which provide valuable insights into the Saka-Parthian period and the rich Buddhist heritage of the region.
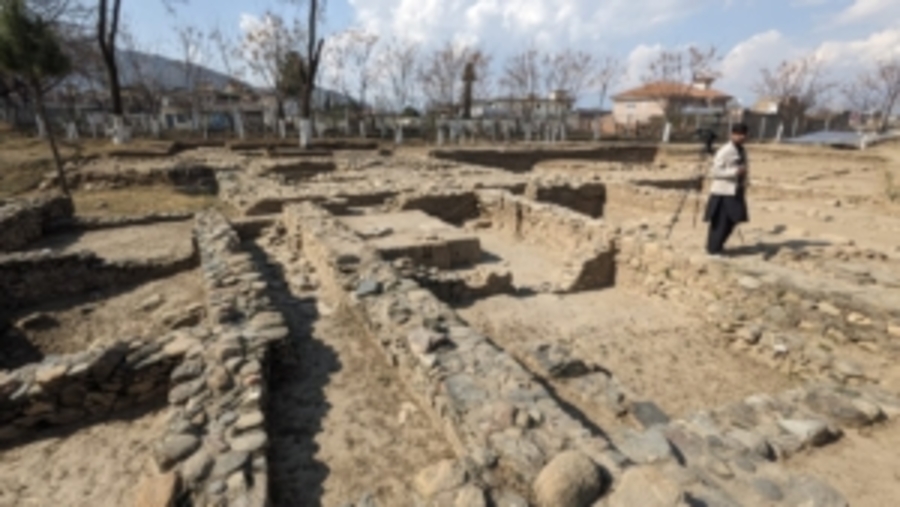
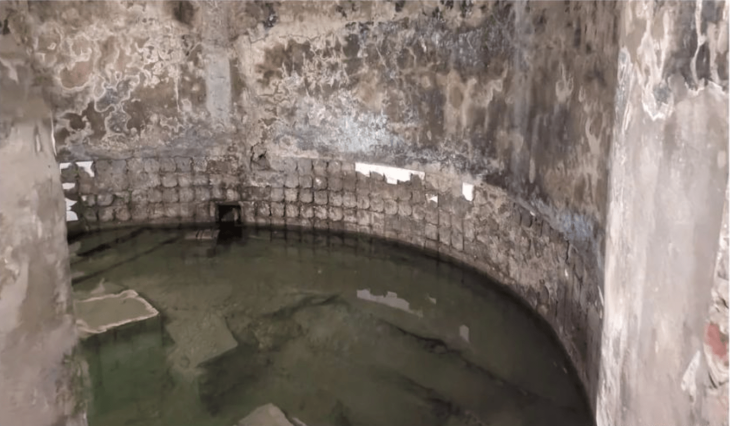
The Butkara Stupa, located near Mingora in Swat, Pakistan, is an ancient Buddhist site that dates back to the 2nd century BCE. It is one of the most significant stupas in the region, reflecting the rich Buddhist heritage of Swat. The stupa serves as a pilgrimage site for Buddhist followers.
Since 1956, the Italian Archaeological Mission has been conducting excavations in Swat, and during their third season at the Butkara site, important discoveries were made under the leadership of Dr. Elisa Lori, an assistant professor at the University of Venice and the deputy director of the mission, with support from the KP government.
In a statement to Minute Mirror, Alisa Lori expressed, “These findings are especially exciting because we have successfully reached the early stages of this site. Butkara holds great significance in Buddhist heritage as it is a sacred site for Buddhist followers.”
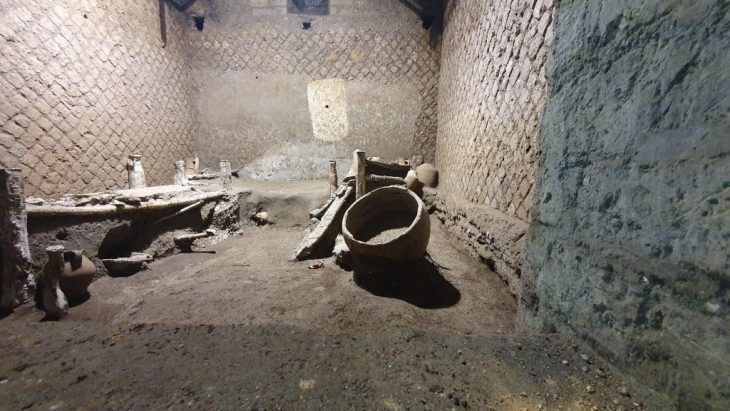
Dr. Alisa Lori further explained that during the recent excavations, they discovered a residential unit, a workshop or production area, and a major road that once connected the ancient capital of Swat, Massagana (Mingora), to the Butkara site. “We have uncovered a significant amount of material from the rooms, including coins linked to the first century BC.,” she stated.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
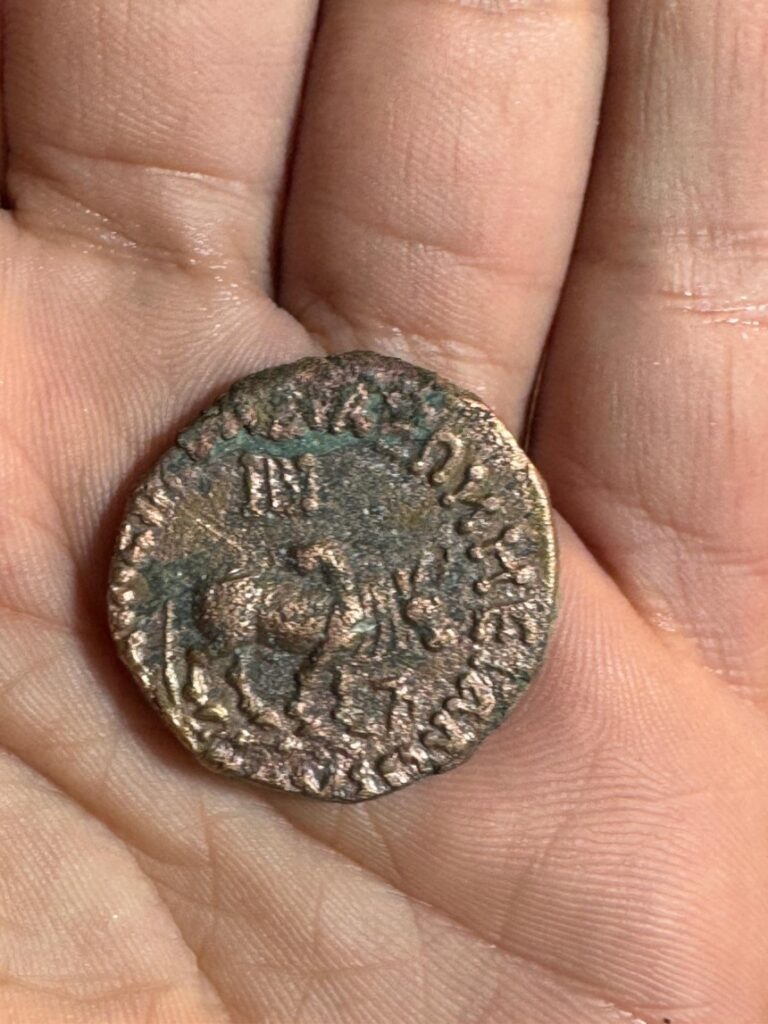

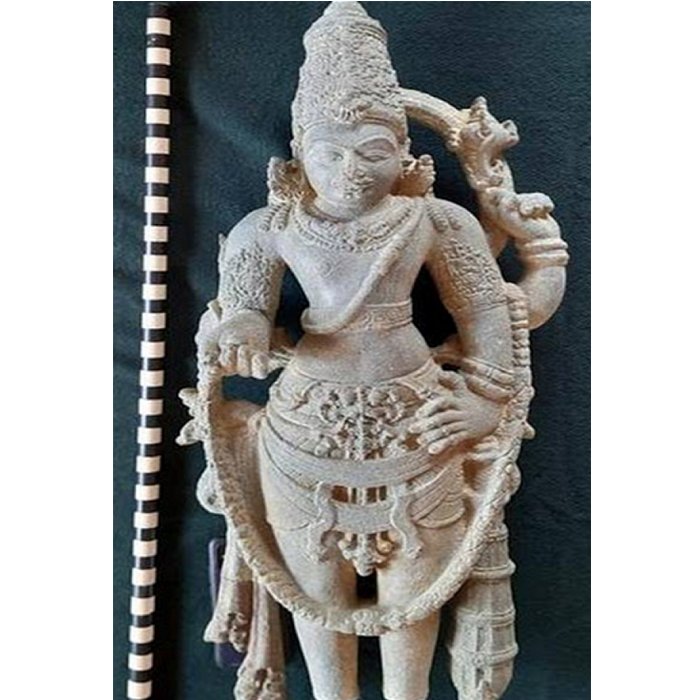
Among the significant discoveries at the Butkara site was an amulet shaped like a foot, inscribed with the Kharosthi script, which adds a fascinating layer to the historical understanding of the area. In addition to the amulet, the excavation team uncovered Saka-Parthian-era coins dating back to the first century CE, along with artifacts from the Mauryan dynasty.
The Kharosthi language, used primarily in ancient Gandhara, is an important script that provides insights into the region’s cultural and historical context, as it was utilized for writing various languages, including Gandhari, a Middle Indo-Aryan language. Kharosthi has played an important role in the writing of Buddhist texts.
Recent findings indicate that the Butkara sanctuary, constructed in during the Mauryan dynasty (320-185 BCE), served as a significant Buddhist sacred site.
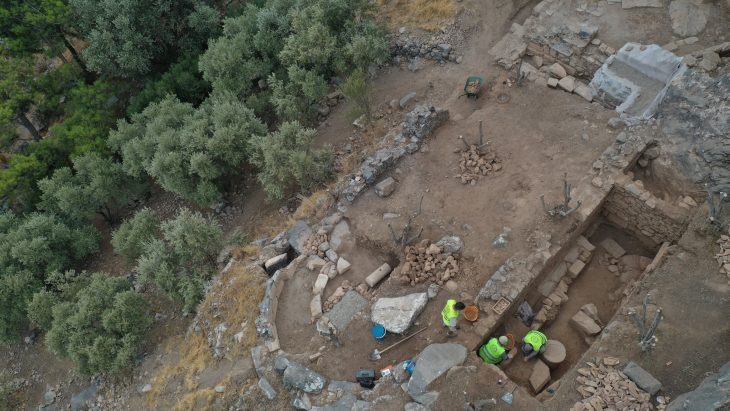
Archaeologists have also uncovered a layer corresponding to the first stupa of the sanctuary, providing new insights into the historical development of the structure. Additionally, a layer confirming a flood event in the Jambil stream has been unearthed, offering vital information about the ancient environmental conditions of the region.
Nasir Khattak, Assistant Curator at the Swat Museum, stated that in addition to the Butkara site, there are 23 preserved sites in the region from which numerous ancient artifacts spanning different eras have been discovered. “The recently uncovered artifacts are extremely rare, including coins and pottery from that time. This site is not only important for tourists but also for archaeology students,” Khattak emphasized.
Swat is rich in relics, ruins, and stupas from various historical periods, including Gandhara, Buddhist, Kushan, Ashoka, Hindu Shahi, and the era of Alexander the Great. Experts believe that if the Department of Archaeology and the provincial government take further steps to promote religious tourism, it could play a vital role in the region’s development.
Cover Image Credit: Minute Mirror