Researchers found a mass grave in a cave in Spain, now known as Sima de los Huesos, or the Pit of Bones. When they put together 52 fragments of broken skulls, they made a surprising discovery.
No determination could be made regarding the gender or other characteristics of this skull, dating back 430,000 years. But the fractures in the merged skull showed that this person was killed.
Although it is possible that a skull, found deep in a cave, caused a fatal wound from a fall, researchers were sure that the victim was killed.
Scientists compared accidental falls and cases of inter-personal violence with modern data. They found that the only logical explanation should be a face-to-face attack by another person. They saw no evidence that the bones were starting to heal, is showing that the person died immediately or soon after being hit. The almost identical size and shape of the holes led them to believe that the cause of death was repeated blows to the head with the same object.
Researcher Nohemi Sala and colleagues identified the victim and the owners of other found bones as Homo heidelbergensis. Homo heidelbergensis is known as the ancestors of Neanderthals.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
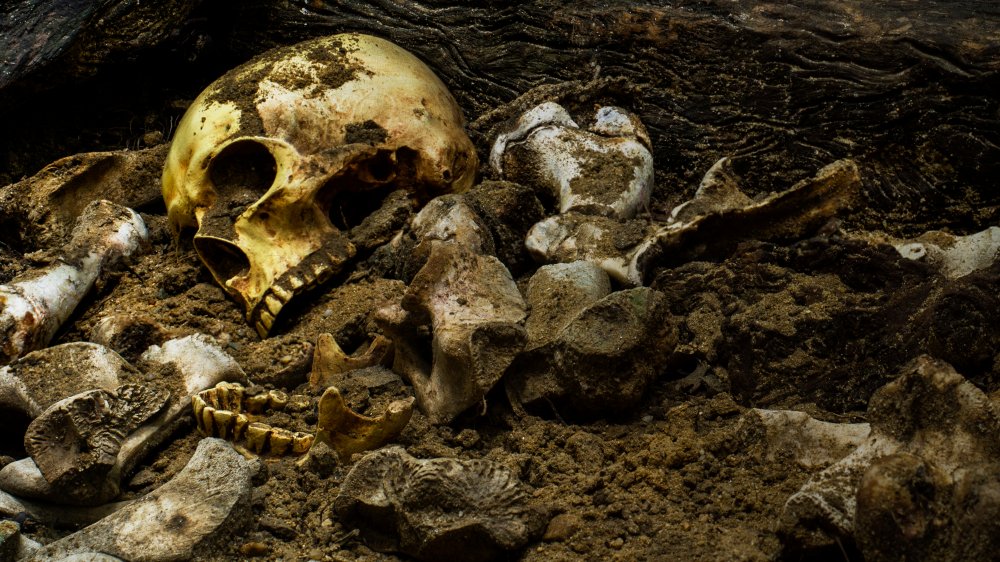

Thus, the “world’s first murder” occurred 430,000 years ago, during the Middle Pleistocene, when the first homo sapiens fossils appeared. The remains of the victim were found in the “Bone Pit” in the Atapuerca Mountains of Spain.
In a research article published in PLOS One in 2015, using three-dimensional analysis, they brought it together with the breaks that occurred at the time of death or after death. Skull recesses indicated that the cause of death was ‘blunt force trauma to the head at the time of death’. It seems that an attacker hit the victim at least twice with the same object. Of course, even if it was murder, it was now impossible to know who the murder suspect was.
While some scientists believe that what has been found in the “bone pit” indicates a mass murder, Researcher Nohemi Sala and colleagues noted that the results did not indicate such a situation. They noted that the area looked more like a ceremonial burial site than a crime scene, that Homo heidelbergensis had a bit of a ritual feel and did not leave the dead to rot on the ground.
Source: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0126589 you can read the full article.