Archaeologists uncover a unique Roman-era Association Building in Sagalassos, Türkiye, revealing ancient social life, guilds, and family gatherings.
Archaeologists in southwestern Türkiye have uncovered a remarkable communal building in the ancient city of Sagalassos, shedding new light on the social and economic fabric of the Roman world nearly 1,800 years ago. Excavations show that the structure, located near dozens of craft workshops, was used by professional and religious associations—similar to guilds—for gatherings, banquets, weddings, and community events.
The discovery, described by researchers as unique in the Roman world, provides a rare glimpse into the lives of artisans and their families, revealing how communal traditions and everyday meals shaped the identity of this once-thriving city in Pisidia.
A City of Craftsmen in the Heart of Pisidia
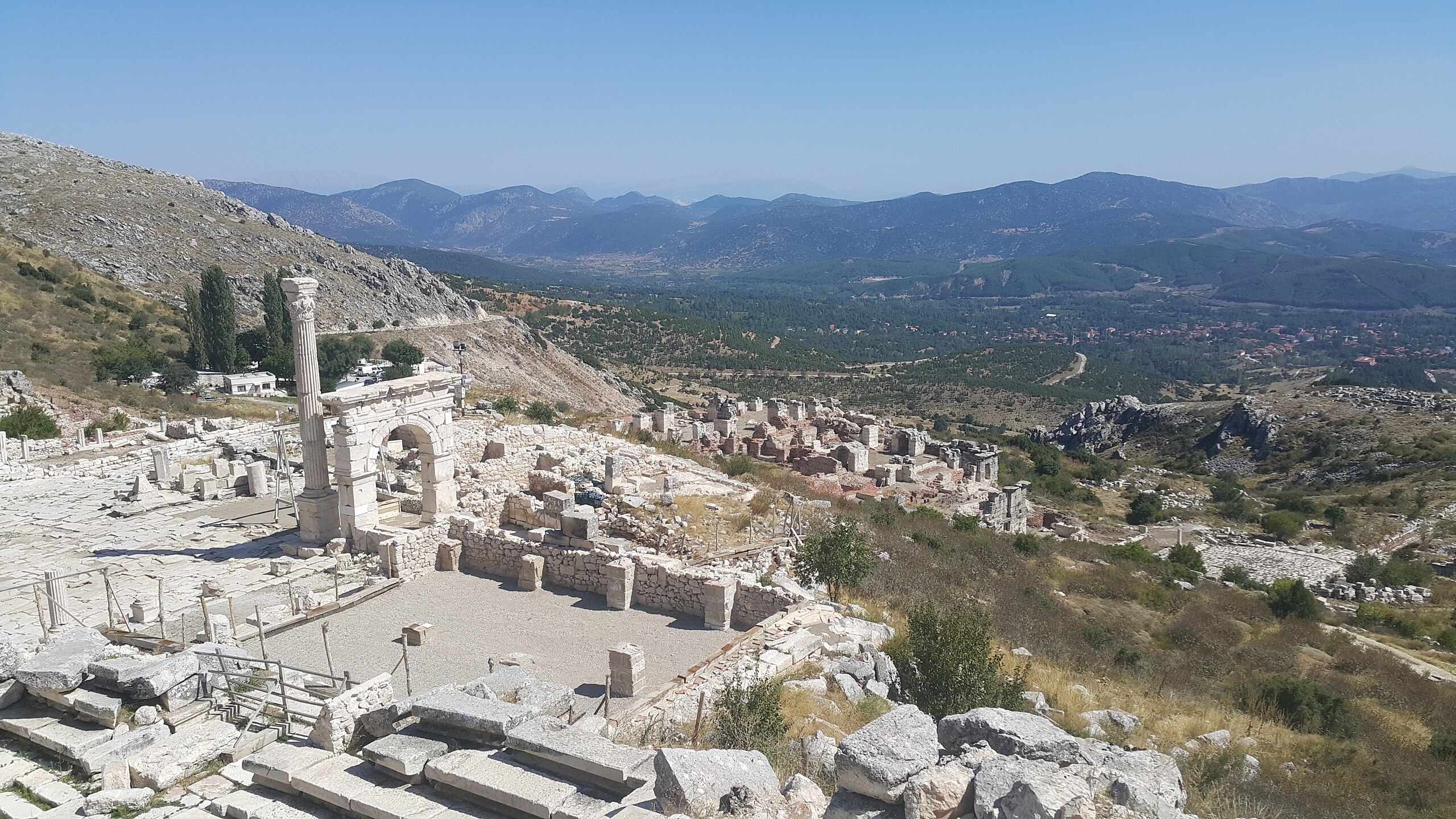
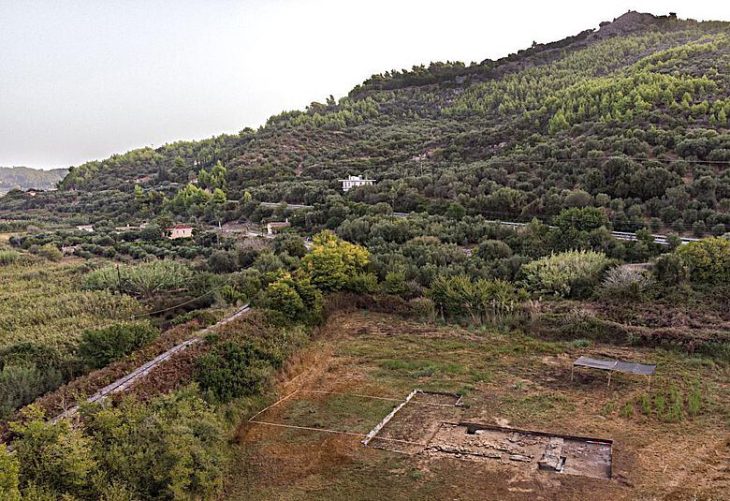
Sagalassos, situated in modern-day Burdur’s Ağlasun district, was one of the major urban centers of ancient Pisidia, a mountainous region that played a strategic role in Anatolia. The city flourished under Roman rule from the 1st century BCE until late antiquity, known for its theaters, temples, baths, and vibrant artisan quarters. Today, it is listed on UNESCO’s Tentative World Heritage List, recognized for both its urban planning and cultural heritage.
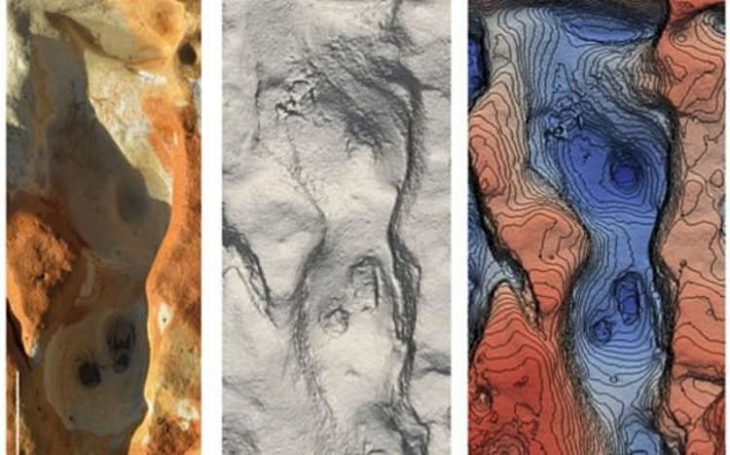
Recent geophysical surveys over an 8-hectare zone identified nearly 80 workshops, primarily devoted to pottery, but also textile production and copperworking. These findings suggest that Sagalassos was a hub of craftsmanship and trade, where family-run workshops formed the backbone of the economy.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Association Building: A Hall for Banquets and Agreements
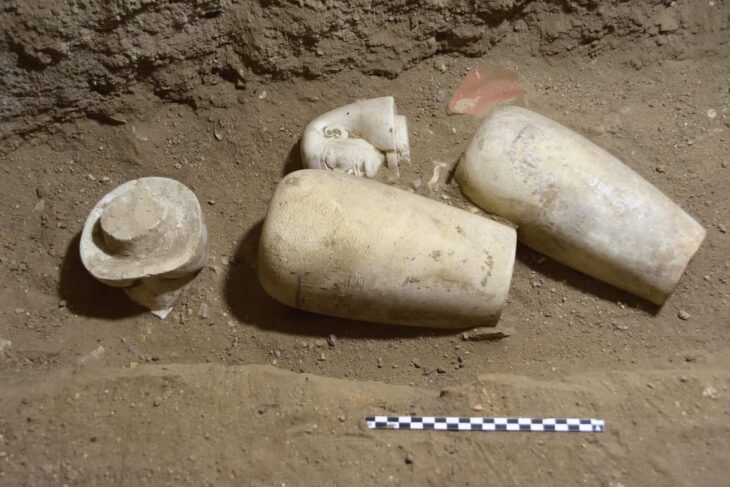
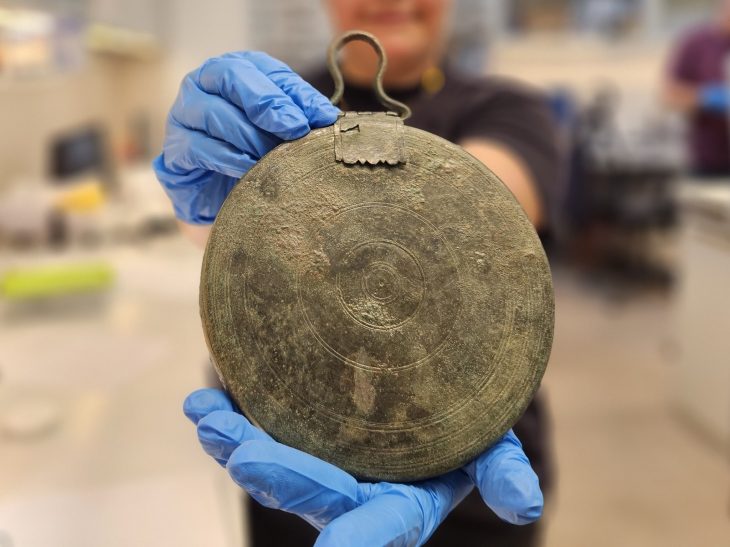
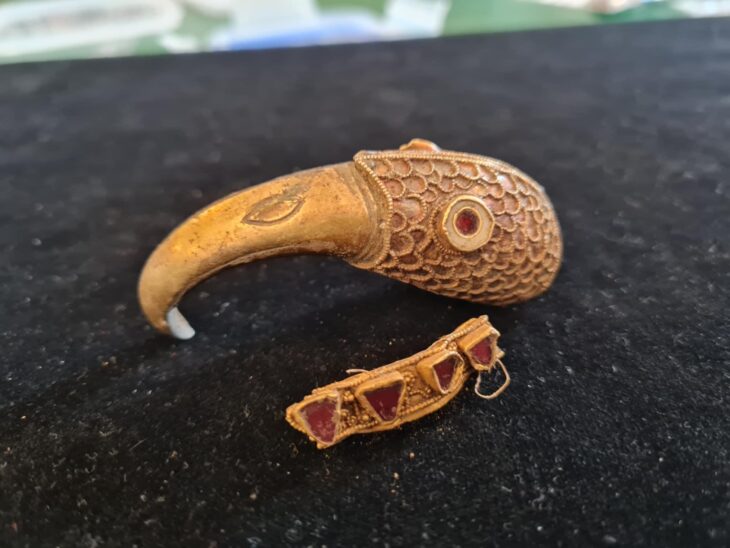
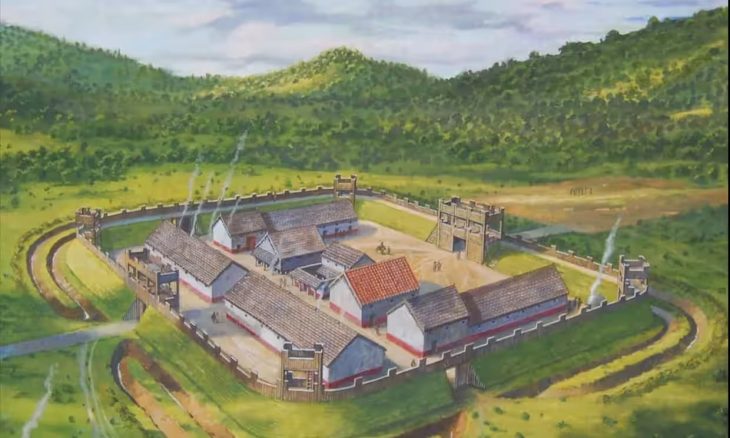
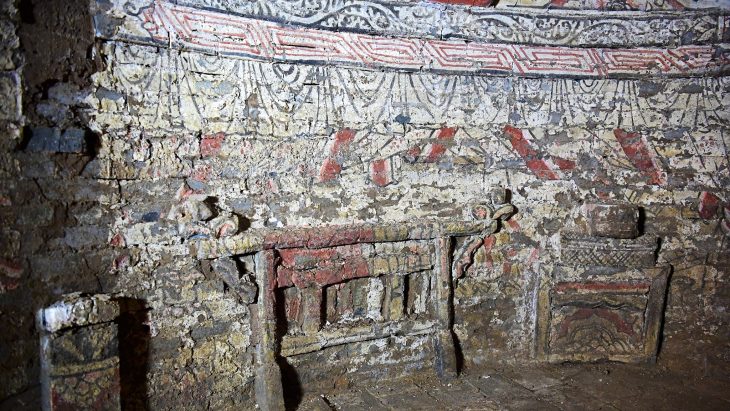
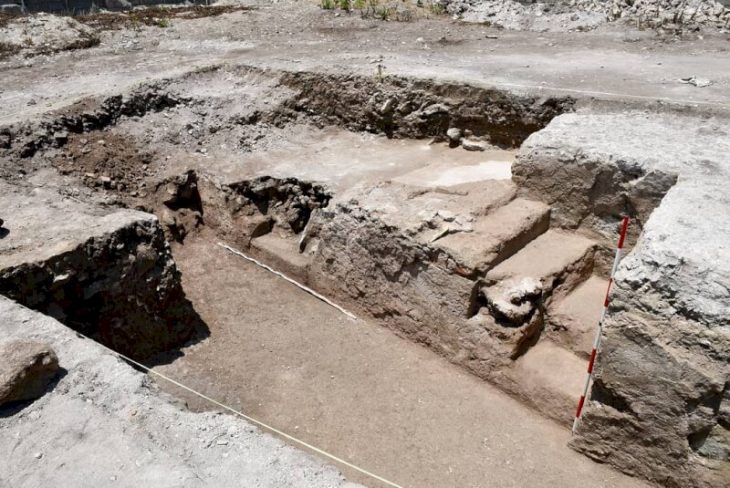
Next to these workshops, archaeologists unearthed part of a monumental structure dated to the 3rd century CE. Unlike the surrounding workshops, the building contained no kilns or furnaces, indicating it was not a production site. Instead, excavation layers revealed food scraps, discarded ceramics, and personal items such as hairpins, pointing to communal meals and family gatherings.
Professor Jeroen Poblome of KU Leuven University, who has led research at Sagalassos for decades, explained:
“What we uncovered was not a workshop, but a large communal building with refuse piles nearby. These heaps told us what people ate—simple meals, cow hooves, pig ears—not elite banquets, but food shared at communal gatherings.”
Thousands of ceramic fragments from serving vessels were discovered, many of which are now being painstakingly reassembled. The evidence suggests that associations hosted organized banquets, celebrations, and possibly even commercial negotiations inside the building, reinforcing the role of such spaces as the heart of social and economic life.
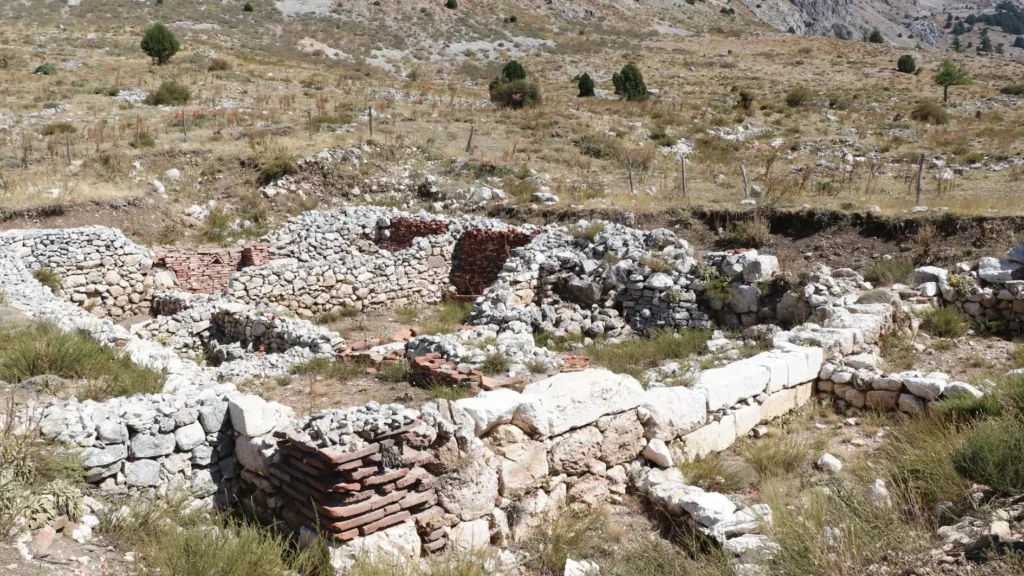

Women and Families in Roman Associations
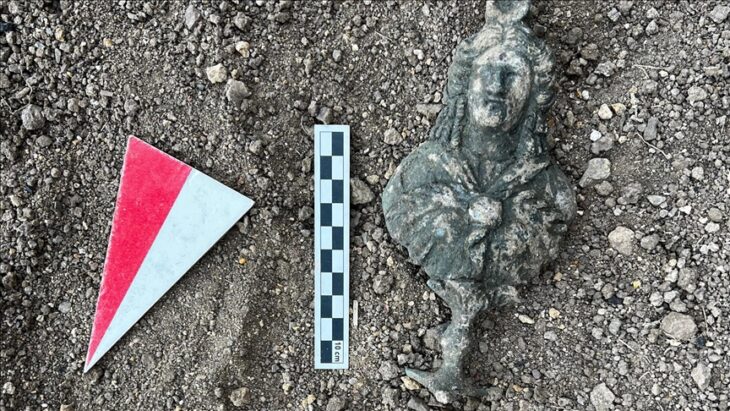
One of the most striking discoveries was the presence of female hairpins, suggesting that women participated in these gatherings. This is especially significant, as Roman associations were often thought to be male-dominated.
The find aligns with evidence that workshops in Sagalassos were often family enterprises, run across generations. When guilds or trade groups organized events, entire households—including women and children—would attend. Poblome likened the building to a Roman-era wedding hall:
“When there was a party, everyone came. It was like a wedding hall, heavily used, as shown by the many refuse heaps we uncovered. Being together has always been important, and this is a typical example of that from the ancient world.”
Inscriptions and the Search for Guild Identity
Among the artifacts, archaeologists found an inscription referring to a textile association, though pottery clearly dominated local production. Potters’ guilds were common in the Roman world, but a direct inscription for a Sagalassos pottery association has not yet been unearthed. Researchers continue to excavate the city’s so-called “potters’ quarter,” located just behind the ancient theater, in hopes of confirming this connection.
The building and its contents are considered exceptional because they capture a guild-like event frozen in time. Unlike many Roman sites where material was removed or repurposed, here the remains of a feast were simply abandoned, preserving a unique record of everyday social life.
Sagalassos: A Window into Roman Society
Beyond this discovery, Sagalassos is already celebrated as one of the best-preserved archaeological sites in Asia Minor. Its monumental architecture includes a well-preserved theater, a library, a Roman bath complex, and the famous Antonine Nymphaeum, a monumental fountain that still flows with restored water today. Excavations have revealed not only the grandeur of Roman urban life but also the resilience of provincial cities that thrived far from Rome itself.
The newly unearthed association building adds another layer to this story. It shows that Sagalassos was not merely a city of monuments and elites but a place where craftsmen, families, and associations forged community through shared meals and traditions.
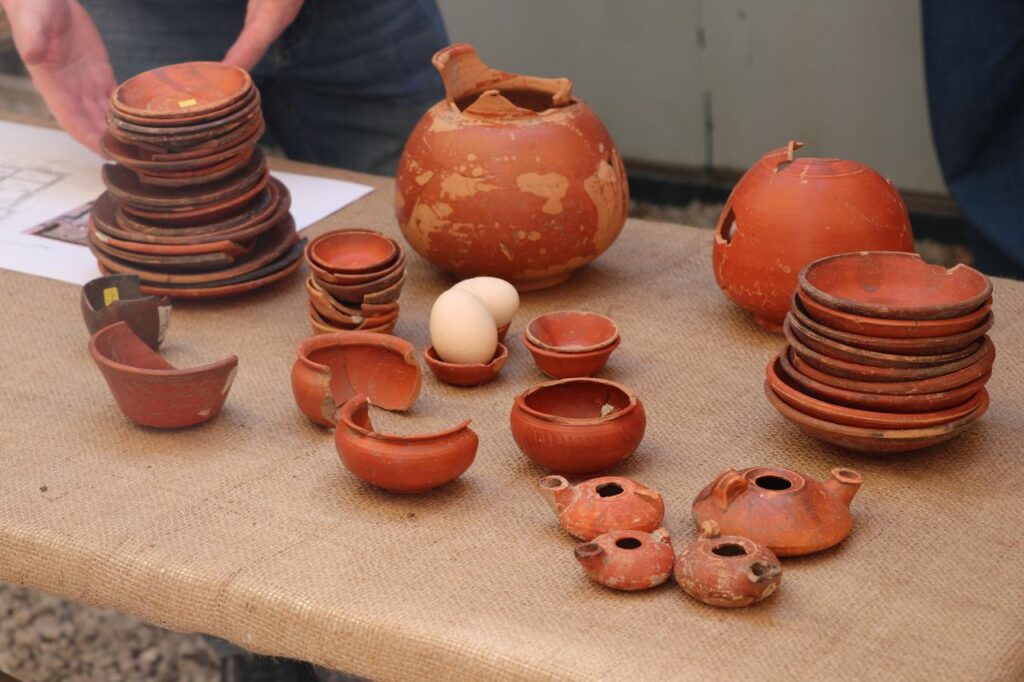

Continuing Excavations and Future Insights
Work at the site is ongoing. Archaeologists are now piecing together thousands of ceramic fragments to reconstruct the sequence of events that took place inside the hall. They hope further finds will clarify how associations functioned, how they supported local trades, and how their members balanced professional, social, and family life.
As excavations continue, Sagalassos is likely to yield more surprises. Its association building, unique in the Roman world, not only enriches our understanding of ancient guilds but also highlights the timeless human need for community.
For travelers, history enthusiasts, and scholars alike, the city remains a living classroom where the daily rhythms of the Roman world come back to life amid the ruins of the Pisidian mountains.
Cover Image Credit: Wikipedia Commons