Archaeologists discovered the 3,800-year-old burial of a woman who died when she was around 20 years old in what is Tübingen, Germany.
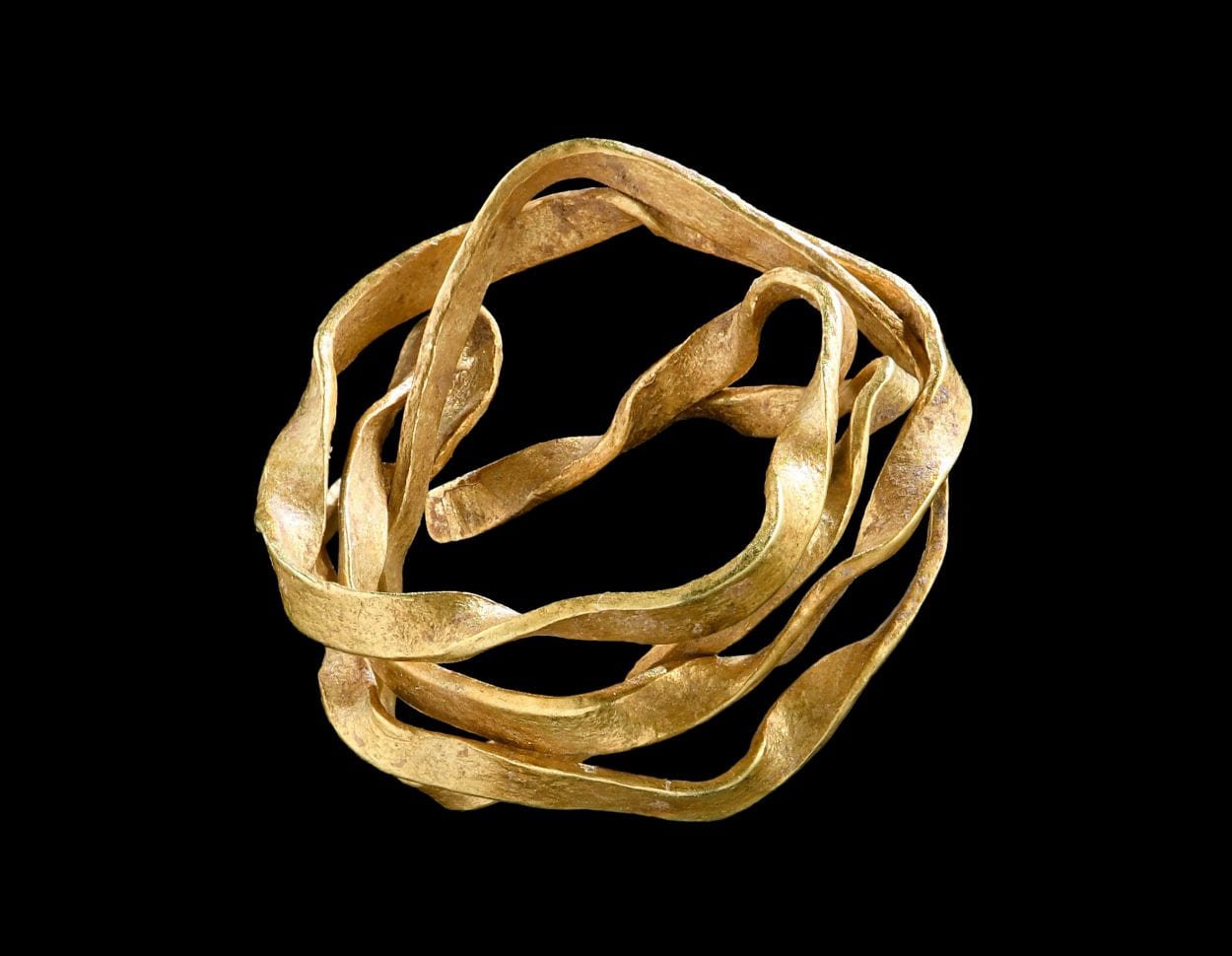
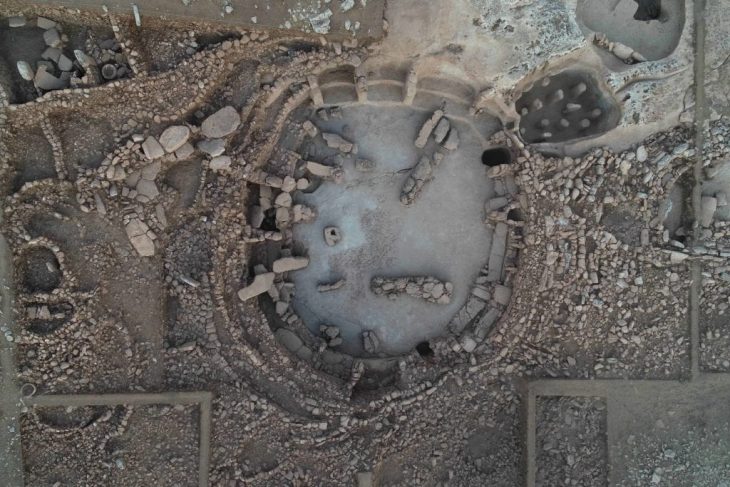
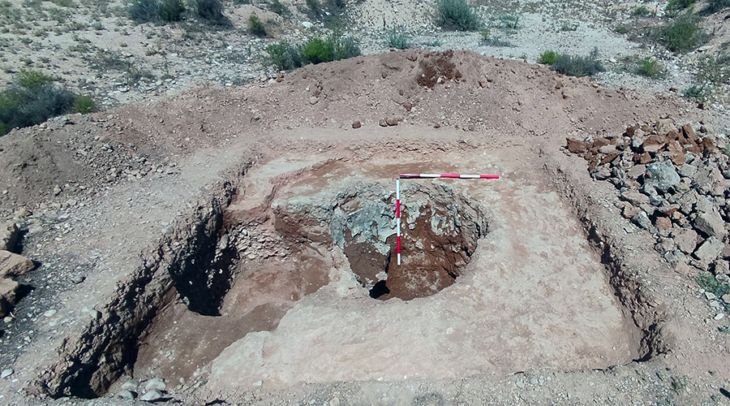
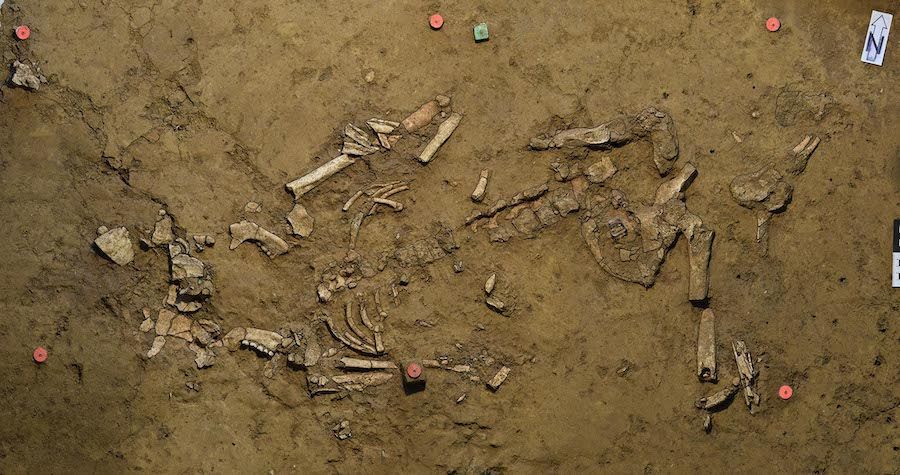
In autumn 2020, researchers from the Universitaet Tübingen excavated a late Neolithic burial site that contained the remains of a young woman. Inside her tomb, archaeologists found only one burial item: a coiled gold wire that could have been used as a hair ornament.
At the same time, archaeologists have discovered the oldest known gold artifact in the region with the discovery of this spiral wire.
The excavation was directed by Professor Raiko Krauss of the University of Tübingen’s Institute of Prehistory and Medieval Archaeology and Dr. Jörg Bofinger of the Baden-Württemberg State Office for Cultural Heritage Management in Esslingen.
The golden spiral is composed of around 20% silver, less than 2% copper, and traces of platinum and tin. This composition suggests a natural gold alloy, similar to gold washed down rivers. The trace element pattern is similar to that of gold from deposits in Cornwall, notably the Carnon River region.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

“Precious metal finds from this period are very rare in southwestern Germany,” the researchers said in the statement. “The gold finds from the Tübingen district [is] evidence that western cultural groups [such as from Britain and France] gained increasing influence over central Europe in the first half of the second millennium [B.C.],” researchers said.
The gold discovery in the Tübingen area is viewed by the study team as proof that western cultural groups gained growing dominance over central Europe in the first part of the second millennium BC. The woman’s grave was discovered in a cluster of other Early Bronze Age remains and appears to be linked to the prehistoric hilltop village on the adjacent Kirchberg.
The fact that the artifact is made of gold shows that the woman may have had a high social status, according to the experts. They used radiocarbon dating on the woman’s remains and discovered she died between 1850 and 1700 B.C. Because writing had not yet extended to southwest Germany at the time, there are no written documents that may assist determine who she could have been.
The grave was excavated in autumn 2020 and the team’s findings were published May 21 in the journal Praehistorische Zeitschrift.
Source: Universitaet Tübingen
Cover Photo: Yvonne Mühleis, LAD Esslingen