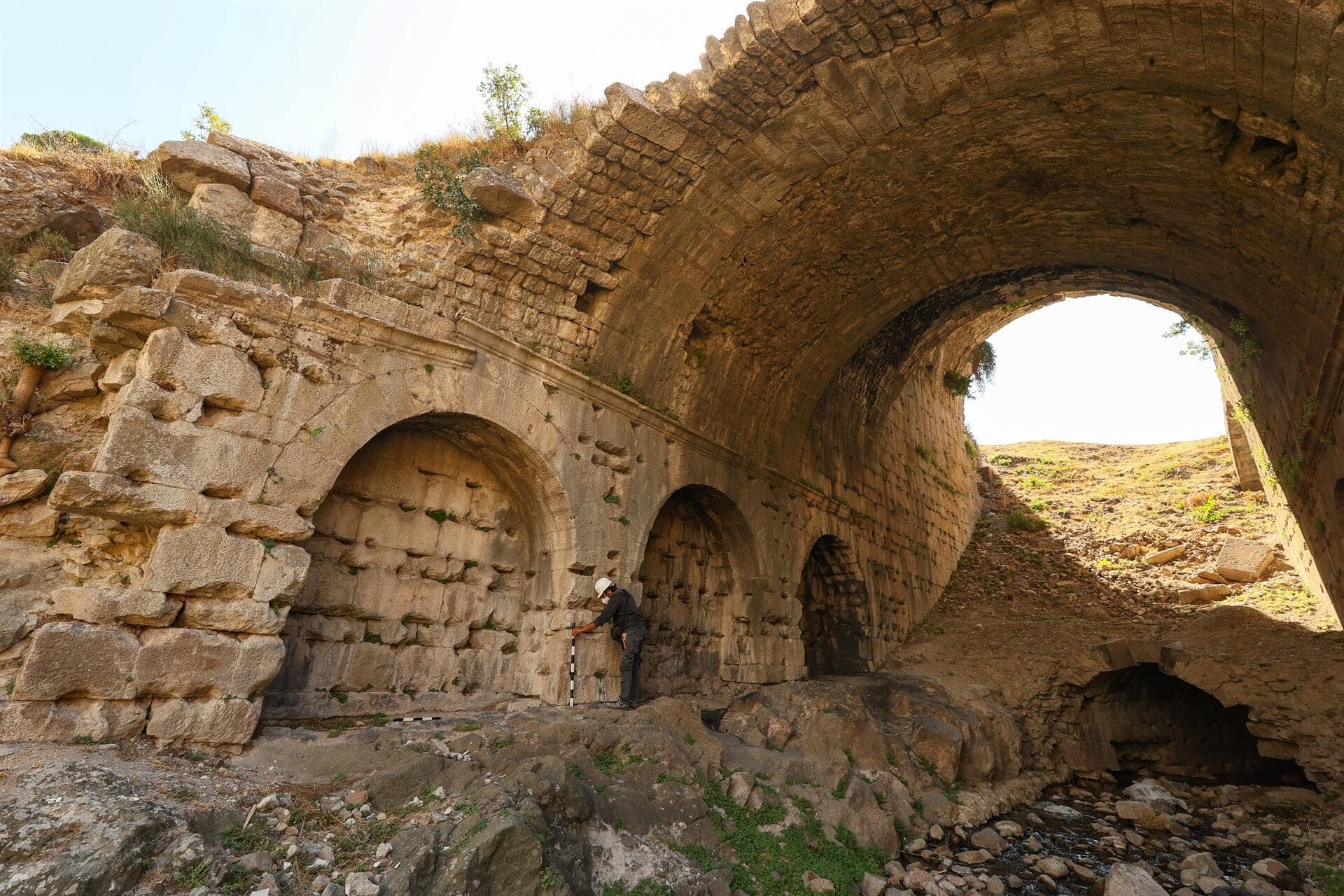
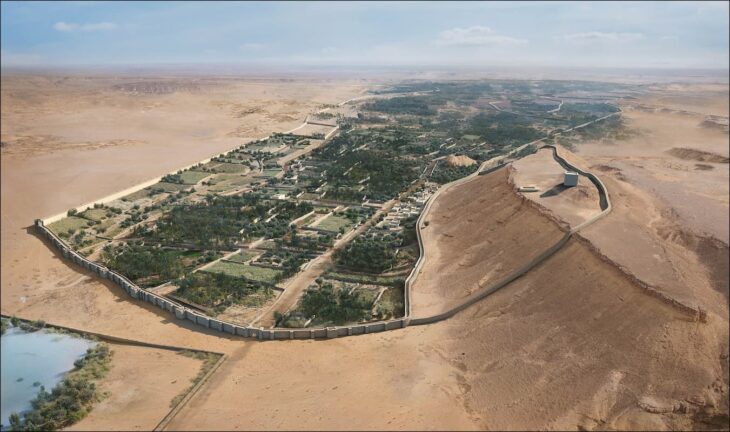
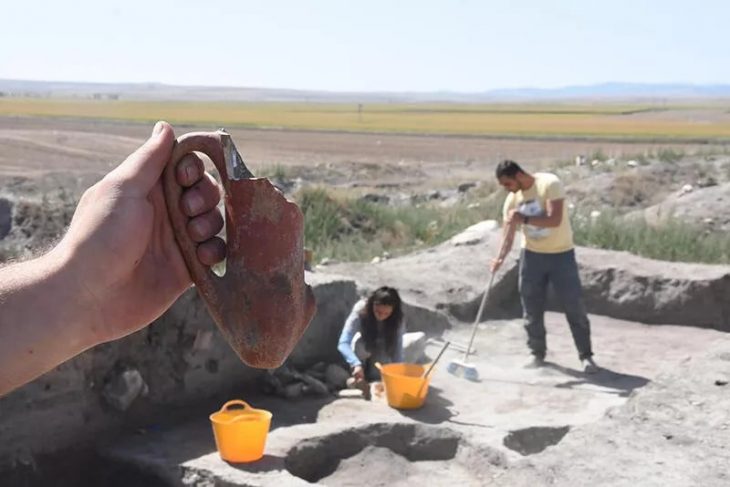
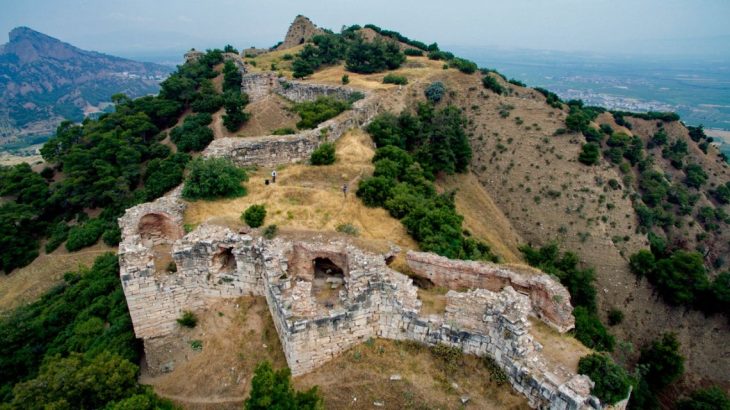
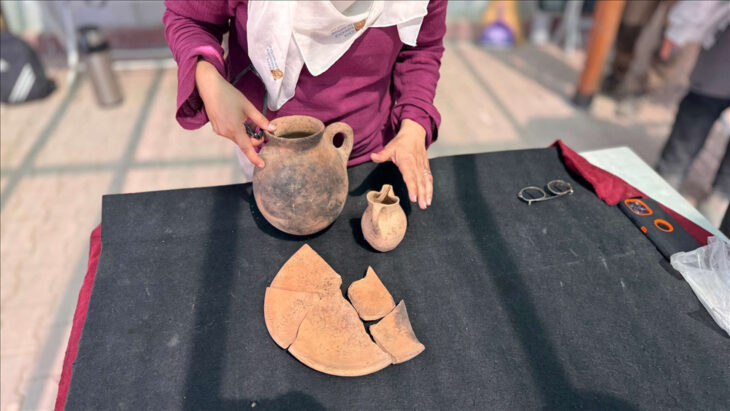
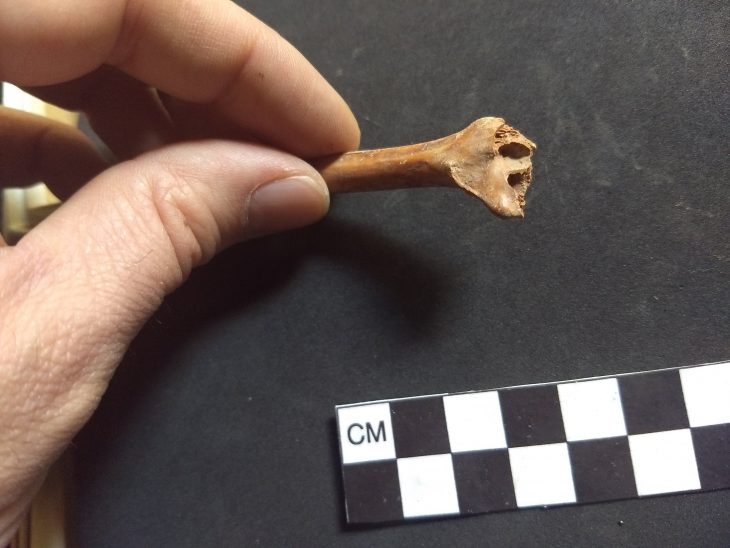
Private lodges built for the elite-class people to watch gladiator or wild animal fights shows have been unearthed in the amphitheater in the ancient city of Bergama (Pergamon).
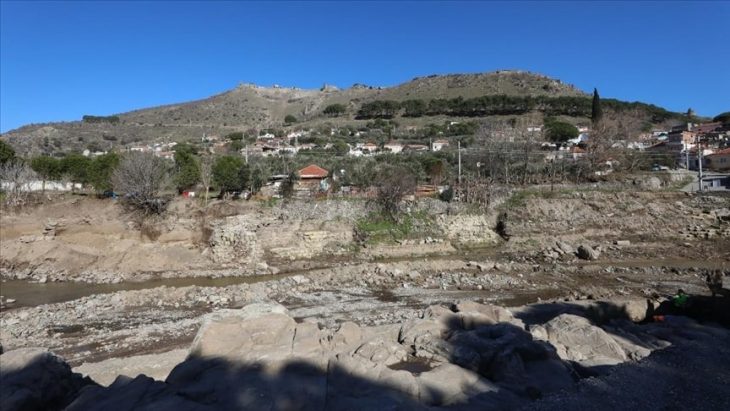
Pergamon is an ancient city located near Izmir, the gate to history with its ancient temples, theatres, library, cultural heritage, and richness. Pergamon rises high above the Bakircay Plain in the Aegean region of Turkey.
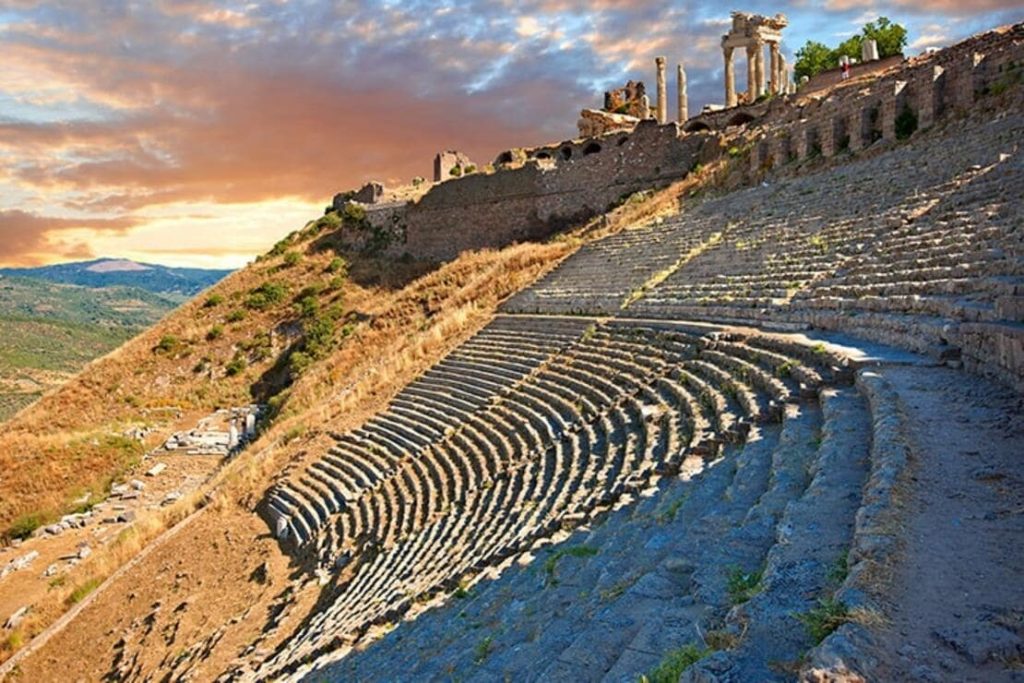
Archaeological investigations at the Bergama Amphitheater, which has piqued the interest of the archeology world due to its resemblance to the Colosseum, the world-famous icon of Rome, Italy’s capital, have been ongoing since 2018.
New finds that shed light on history were obtained with the permission of the Culture and Tourism Ministry during work carried out as part of the “TransPergMikro” project by the German Archaeology Institute and the Berlin Technical University Architecture Institute’s Department of Historical Building Research and Monument Conservation.
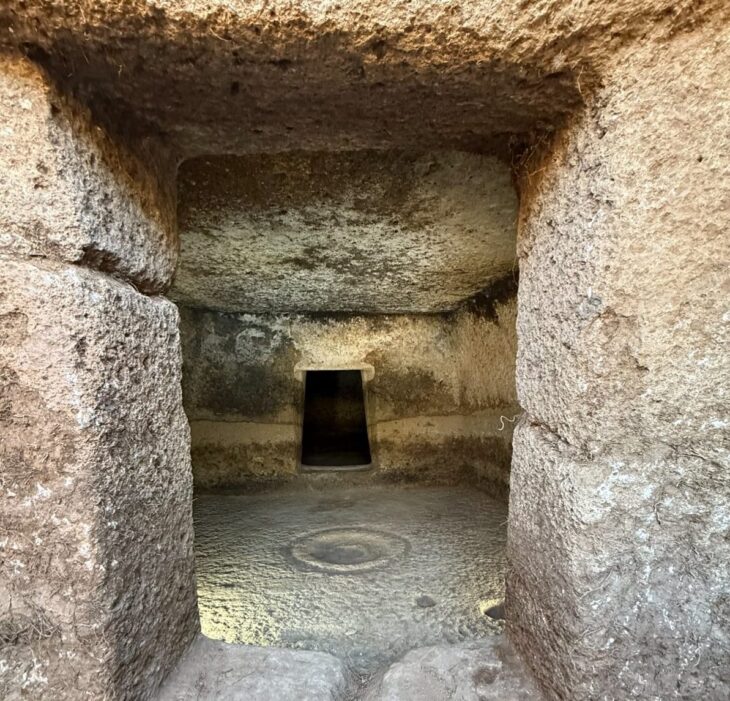
The seating areas, which were once dedicated to the elite class people at the time and look similar to today’s private lodges, were the last finds in the amphitheater, which hosted gladiator and wild animal fights in the second century B.C., witnessed the execution of the first Christians from Pergamon and where sea battles were reenacted.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
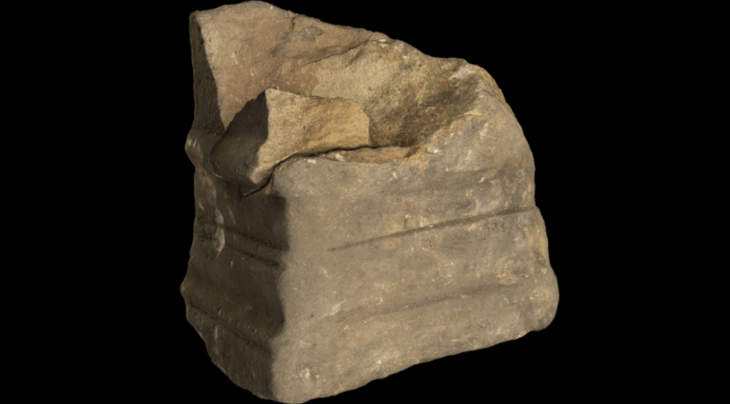
It is believed that the stone seats, on which the names of the elites were engraved, were purchased or rented for periodical use.

Latin names written in Greek letters
Speaking to the state-run Anadolu Agency, Professor Felix Pirson, the director of the German Archaeological Institute, said that the amphitheater, built during the Roman period, had a very large arena.
Stating that the amphitheater in Bergama was built to be one step ahead of the cities of Ephesus and Smyrna, which they competed against each other, Pirson said: “They wanted to build a replica of the Colosseum here, and the people of classes came here. There were also differences within the society. Very rich, very important families had special sections. They found these sections, the seats, by their names engraved on them. Another issue that caught our attention was the writing of Latin names with Greek letters. We think that some people from Italy had a special place in the Bergama Amphitheater.”
Pirson informed that the sitting blocks that were found during the archaeological excavations would be exhibited in the Pergamon Museum.

Noting that they will finish the 2021 season soon, Pirson stated that they would close the area after they remove the finds and deliver them to the museum.
Pirson also stated that after the studies, they would make a new publication on the finds in the amphitheater and that the universities and scientists would continue to work with new information.
The capacity of at least 25,000 people
İhsan Yeneroğlu, an archaeologist and historical building researcher from the Technical University of Berlin, stated that they found five lodges so far in the seating areas, called “cavea.”
Yeneroğlu stated that the sitting blocks that were found during the drilling works on the slopes had the names of the elite people, adding, “The areas we call lodges today were reserved for a certain period of time and their [elite people’s] names were engraved on the stone.”
While explaining the purpose of the amphitheater, Yeneroğlu said: “The amphitheater was built in the Roman era for gladiator fights. We also think that animal fights were also organized there. It is known that some animals and gladiators also fought. In some cases, criminals were thrown in front of animals and executed. On the other hand, we think that naval wars called ‘naumachia’ were reenacted here. Although we cannot determine the exact formation of Cavea yet, we can say that it has a capacity of at least 25,000. This number may rise to 50,000.”