Findings on settled village life in the ongoing excavations in Karahantepe will profoundly change our knowledge of the Neolithic Age.
Karahantepe excavation head Professor Necmi Karul, who participated in the “42nd International Symposium on Excavations, Surveys, and Archaeometry” held in Denizli, said that “the artifacts unearthed or to be reached will provide important information to the scientific world, especially about the Neolithic Age.”
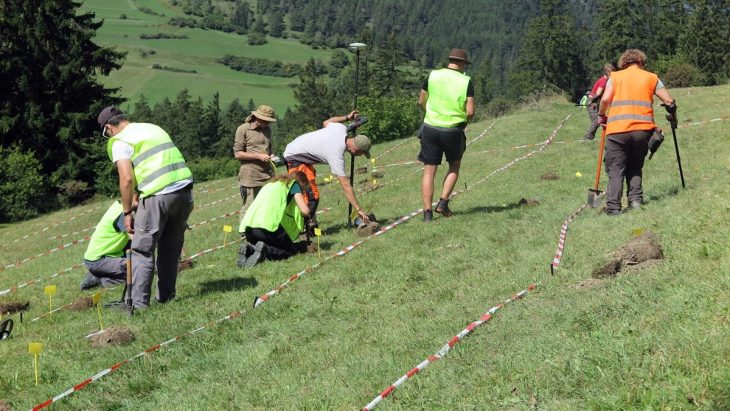
Pointing out that many unanswered questions have been clarified with the Karahantepe and Göbeklitepe excavations, Professor Necmi Karul stated that during the long working period they spent in Karahantepe, they obtained data about the buildings and lifestyle of the period with aspects they did not know before.
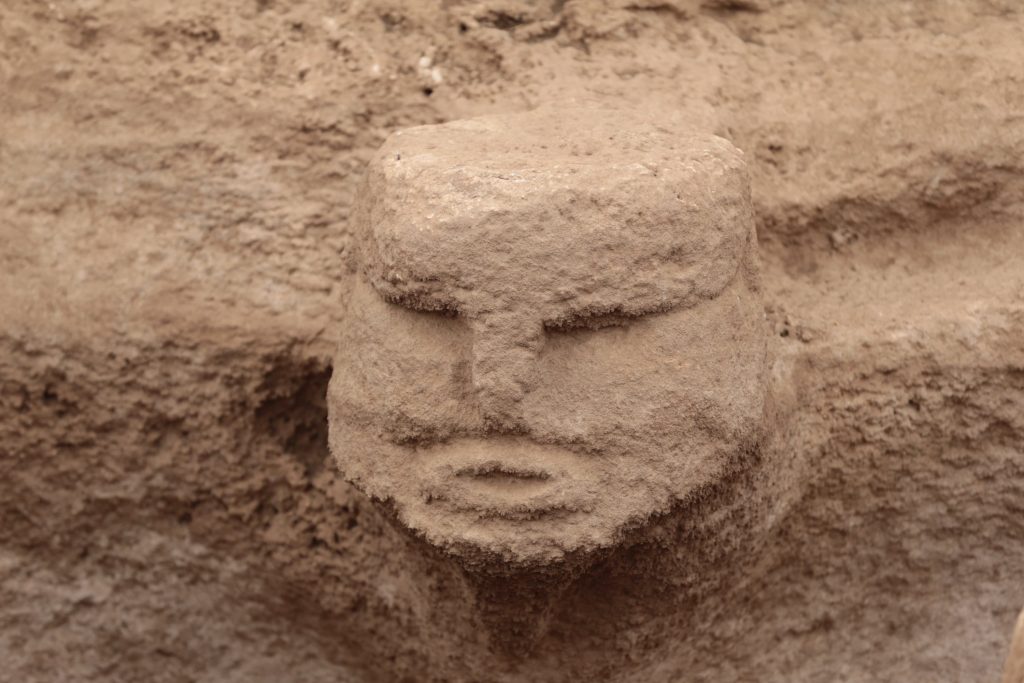

Karul gave information about the studies to the AA correspondent and said the following.
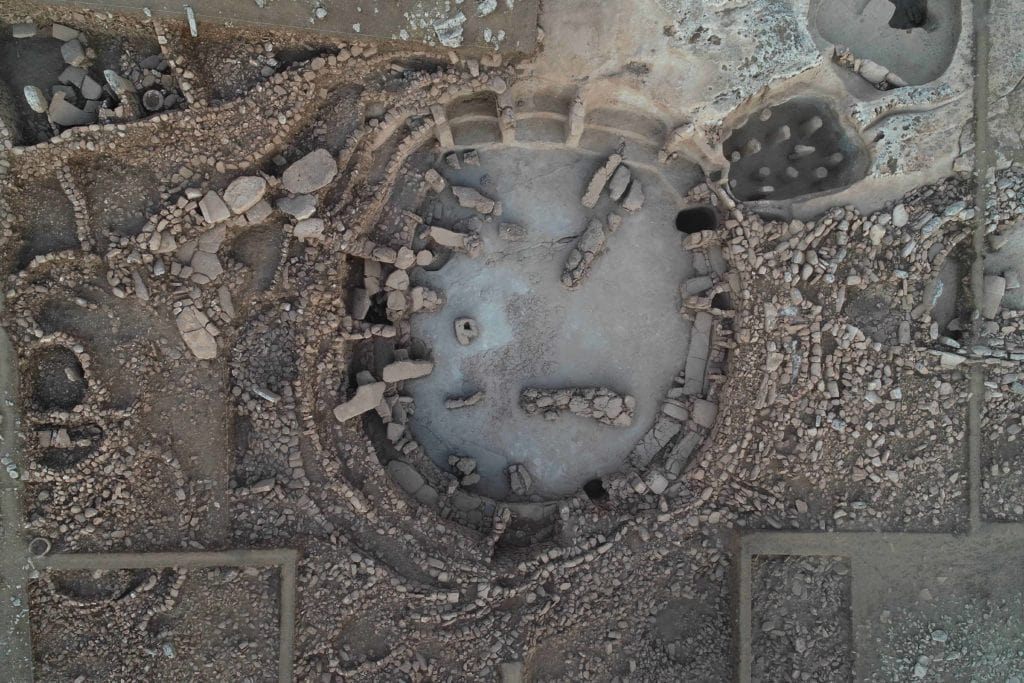
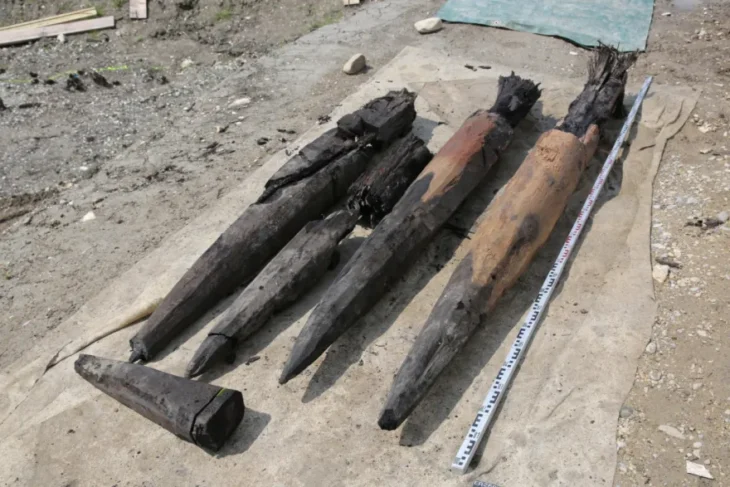
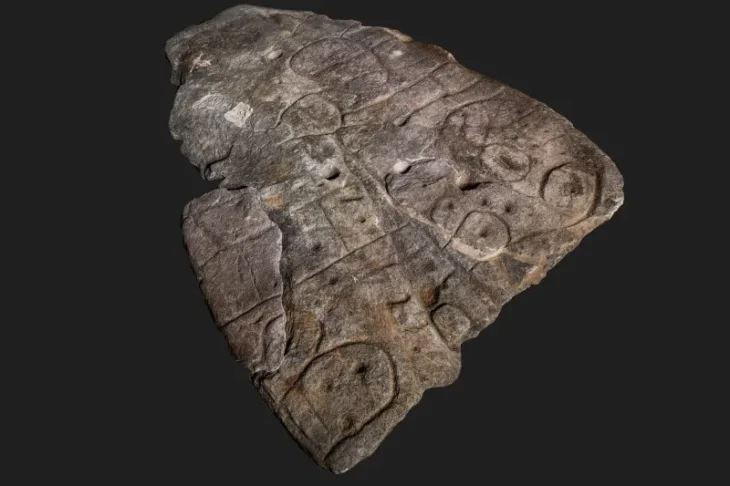
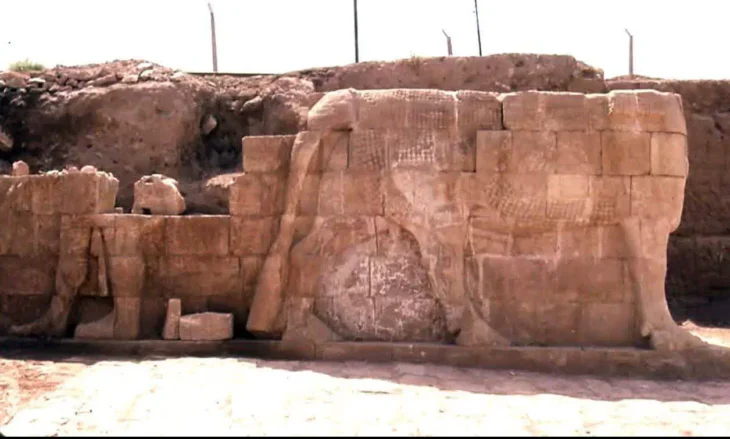
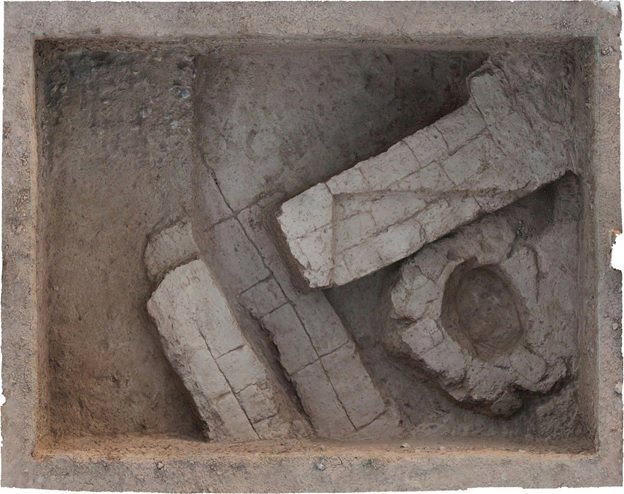
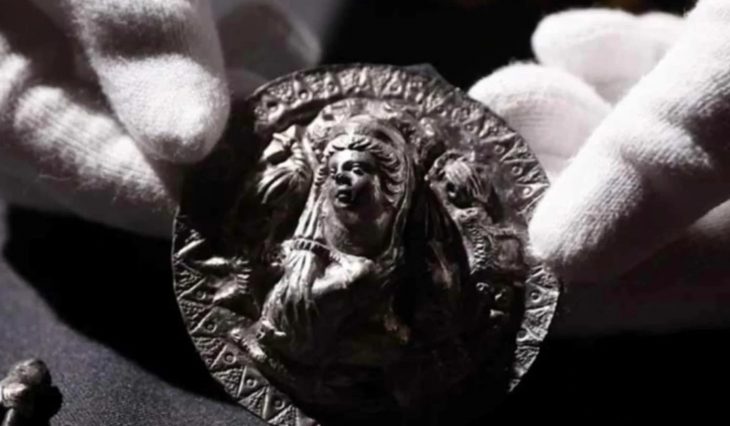
“There is a complex in Karahantepe with a monumental building with a diameter of 23 meters at its center and structures that are articulated to it and built by thinking together. Among them, there are places too with features that we did not know before. We came across a variety of artifacts, from composite sculptures that bring humans and animals together, to a human head sculpted from bedrock.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Expressing that there are many question marks about the excavated areas, Karul continued his words as follows:
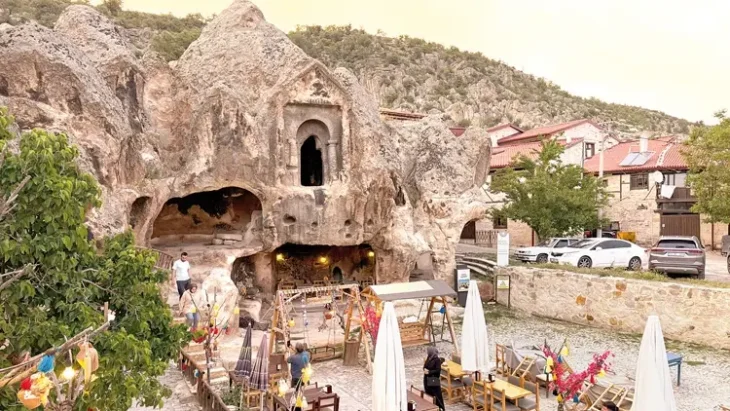
“For example, it was a matter of debate whether there was housing in these settlements! There were discussions about people coming together and using them as places of worship. During the excavations, we found data on settled village life. In Karahantepe, we uncovered many hut-style shelters around specially built structures. We understand from the finds inside these structures that they were used as residences. The new excavations are capable of radically changing the way we look at the region and the Neolithic.”
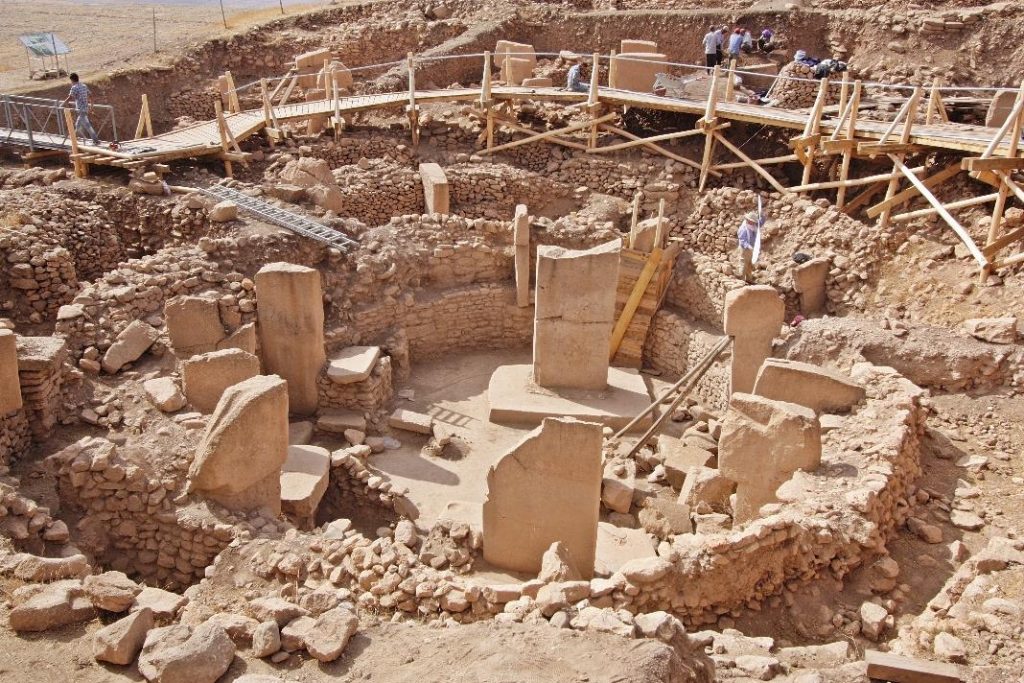

Expressing that the hunter-gatherer life, which lasted for about 3 million years, ended 12 thousand years ago, and that they are trying to understand the contributions of this region, where the first villages were established, to the history of humanity, Karul said, “It is difficult to predict what we will achieve in Göbeklitepe and Karahantepe. This is inherent in archeology. Therefore, it is certain that what we will encounter in the excavations will be a surprise for us as well as you,” said.
Emphasizing that the Göbeklitepe excavations are important for everyone, Karul said, “The beginning of settled life is actually an issue that concerns the whole world. The fact that humanity lives in the same place and establishes villages for the first time throughout the year means the construction of a new social order. Wherever you live in the world today, here you can see a piece of your distant past and find answers to many questions. This must be one of the reasons for the interest in the Taş Tepeler Project.”