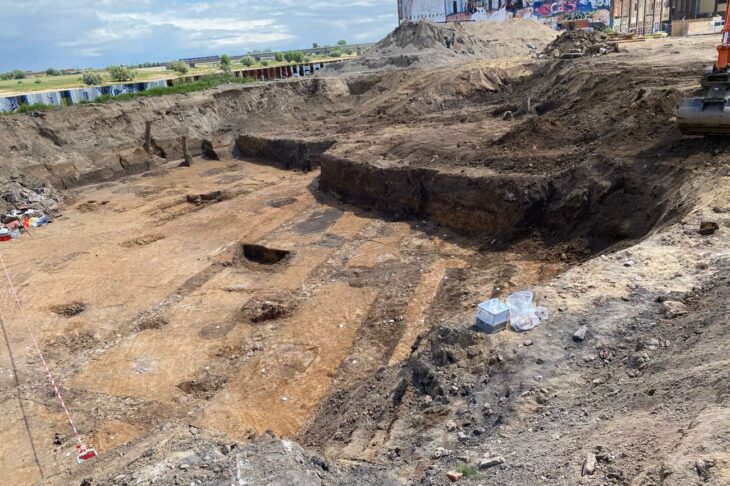
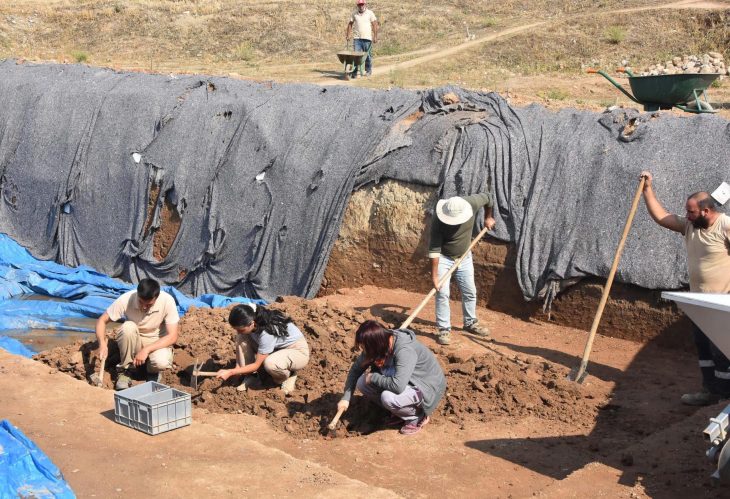
Several electoral inscriptions, the ancient equivalent of today’s electoral posters and pamphlets, have appeared on the walls of the room that housed the Lararium, the domestic altar of the house, inside a house on the Via di Nola, in the central area of ancient Pompeii.
It turns out that there was already an exchange of votes back then as reported in the online scientific magazine of the Pompeii Archaeological Park, the E-Journal of the Pompeii Excavation. Not only that, the excavations also revealed the last sacrifice on the domestic altar which probably occurred before the eruption.
The fact that they were found inside the house was surprising because normally these inscriptions were placed on the exterior facades of buildings, where citizens could read the names and qualifications of the candidates for the city’s magistracies.
Archaeologists explain the presence of electoral propaganda inside the house because the practice of organizing events and dinners inside the homes of the candidates and their friends to promote the electoral campaign was common.
The team discovered electoral inscriptions in support of Aulus Rustius Verus, a candidate for the position of aedile. Aediles were in charge of maintaining public buildings (aedēs) and regulating public festivals. The office of the aediles was typically held by young men aspiring to high political office, traditionally after their quaestorship but before their praetorship.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
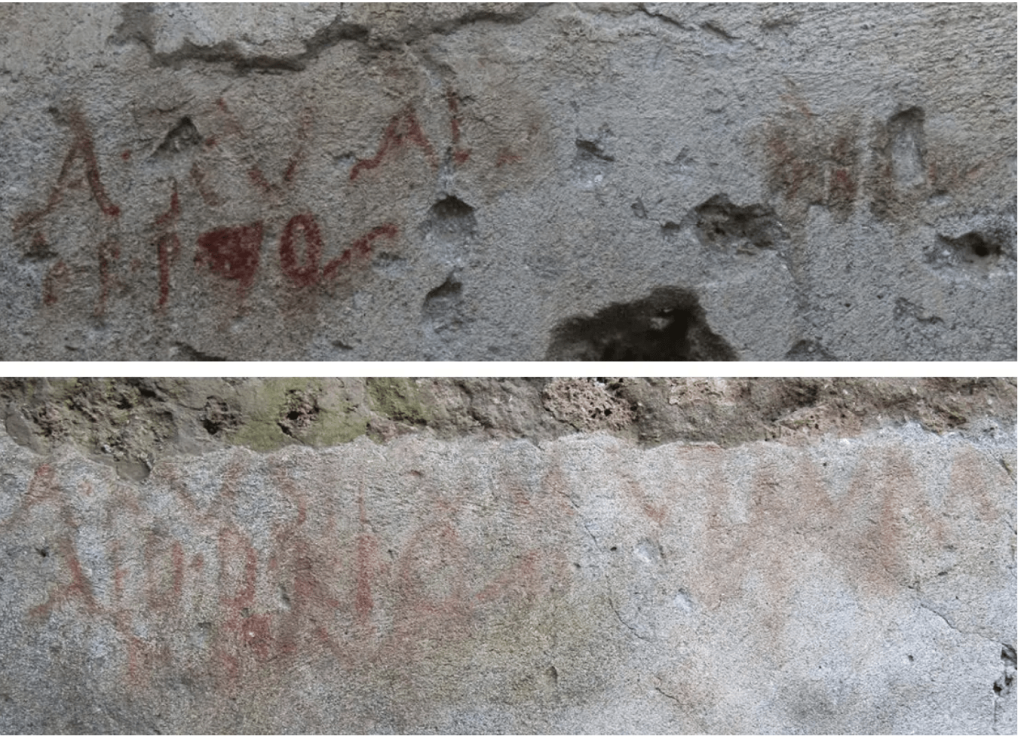

In this case, the signs encourage voting for a certain Aulus Rustius Verus for the position of aedile, in ancient Rome a type of councilor who was in charge of public works.
Aulus Rustius Verus’s name appears in other inscriptions and is known in Pompeii for having held the highest public office in the city in the seventies of the 1st century AD, along with Giulio Polibius, owner of a splendid house on the Avenue of Abundance. , that of duovirea degree that was accessed after having been aedile, so archaeologists deduce that the newly discovered inscriptions are ancient and that Aulus Rustius Verus probably won those elections.
The house apparently belonged to a supporter of Aulus Rustius, perhaps one of his freedmen or a friend, and houses a detail that has not gone unnoticed by archaeologists: a bakery with a large oven, near which the bodies of three victims, two women, and a child, killed by the attic collapse during the first phase of the eruption.
According to experts, the presence of the bakery reveals that political clientelism, which consisted of promising favors in exchange for votes in ancient times, was the order of the day.

Maria Chiara Scappathiccio, professor of Latin at the Federico II University of Naples and co-author of the study of the new findings, explained that the councilors and the bakers “collaborated to the limits of legality” and that Aulus Rustius Verus “was able to realize very “soon, when he was still in the middle of the electoral campaign to become mayor, that the voter lives above all on bread.”
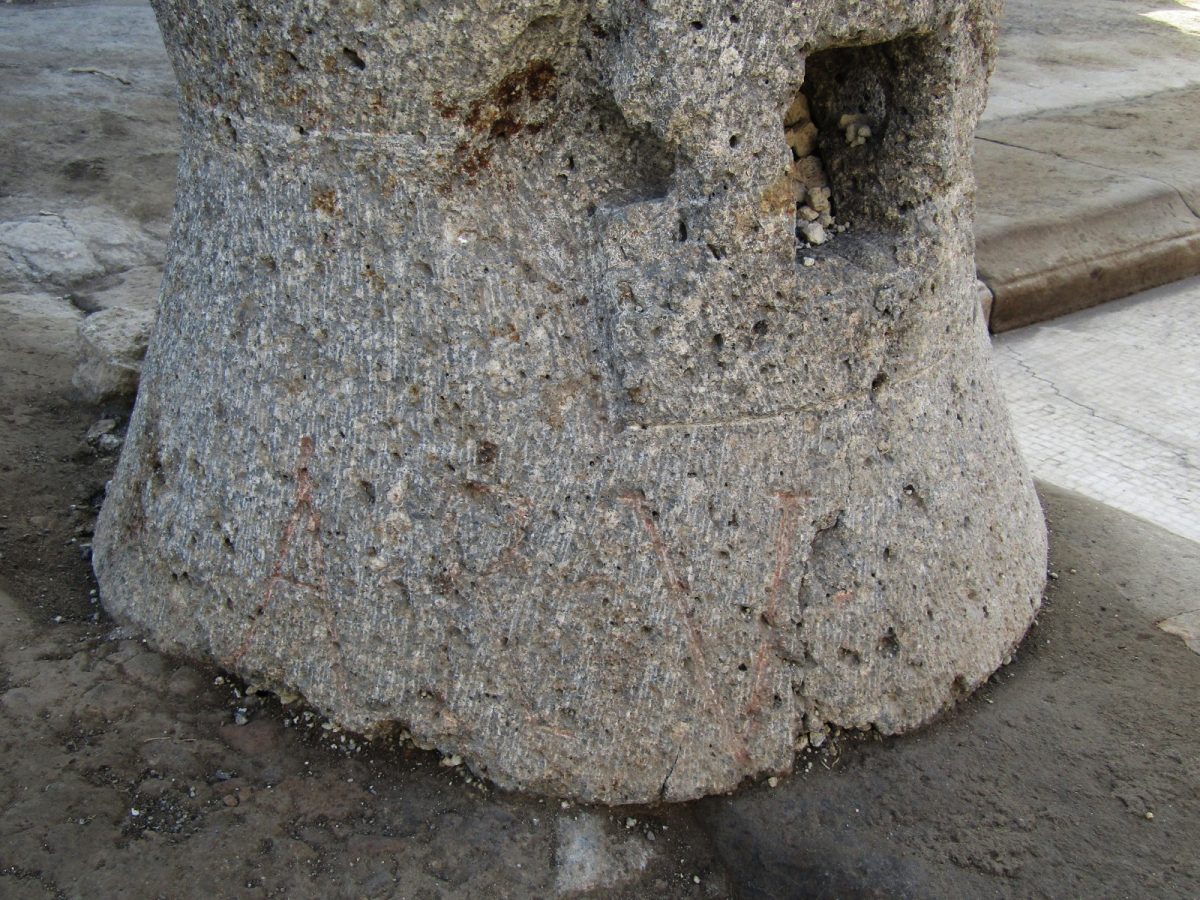
The discovery of the candidate’s initials, ARV, on a volcanic stone millstone, resting in the hall of the house, where renovation work was taking place at the time of the eruption, supports this thesis. “Aulus Rustius Verus probably directly financed the bakery’s activity, both for economic and political purposes,” said Maria Chiara Scappathiccio.
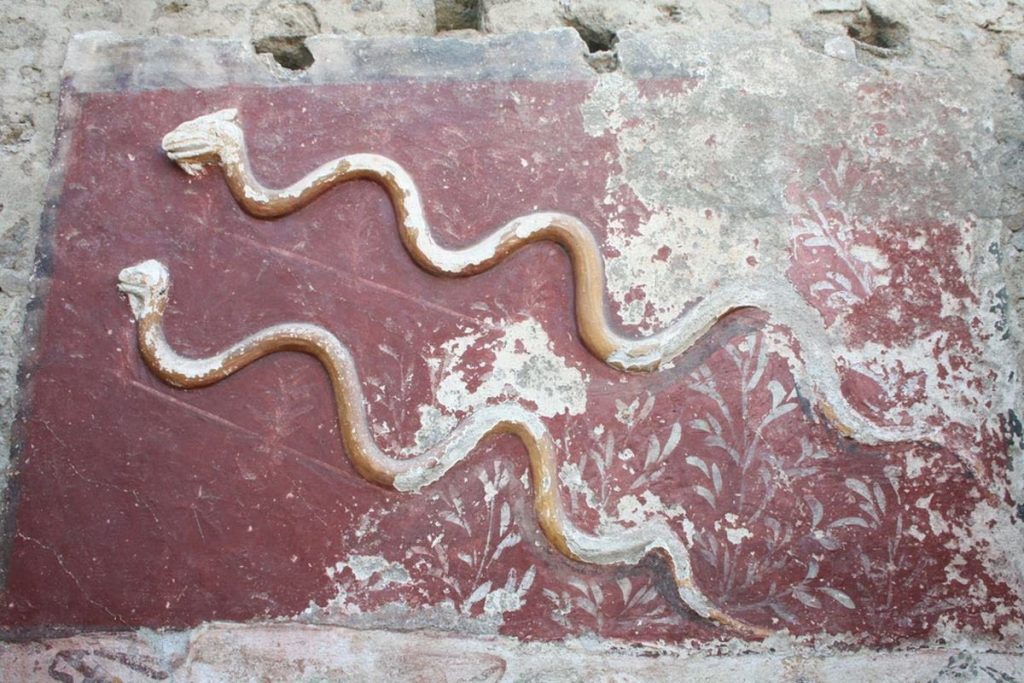
Furthermore, on the altar of the great Larario, decorated with two stucco snakes, the remains of a last votive offering have been found, probably occurring shortly before the eruption. Scientists have analyzed the remains and discovered that the ritual consisted of offering figs and dates that were burned in front of the altar. To close the rite, a whole egg was placed directly on the masonry altar of the lararium. The altar was then covered with a tile. Remains of previous offerings were also found, which also included vine fruits, fish and mammal meat.
Cover Image Credit : POMPEII SITES