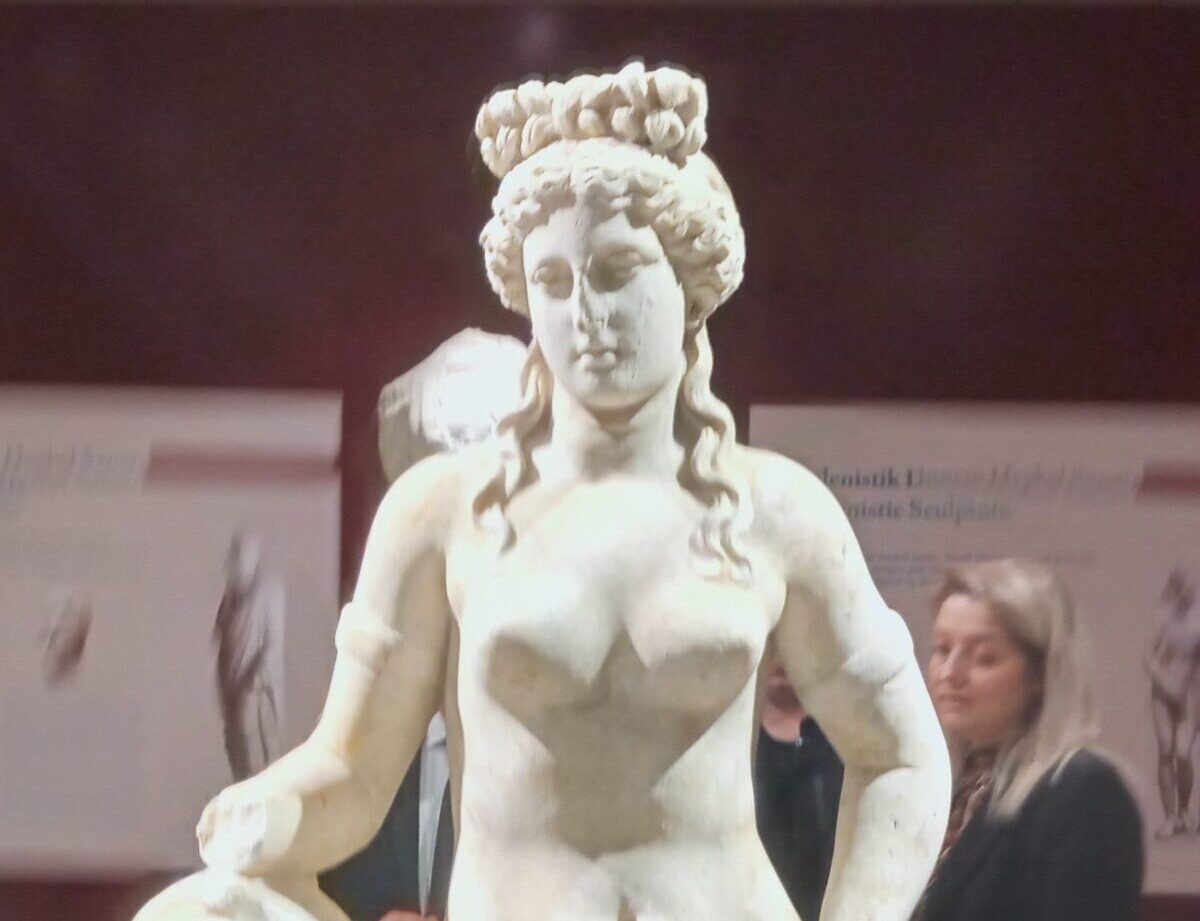
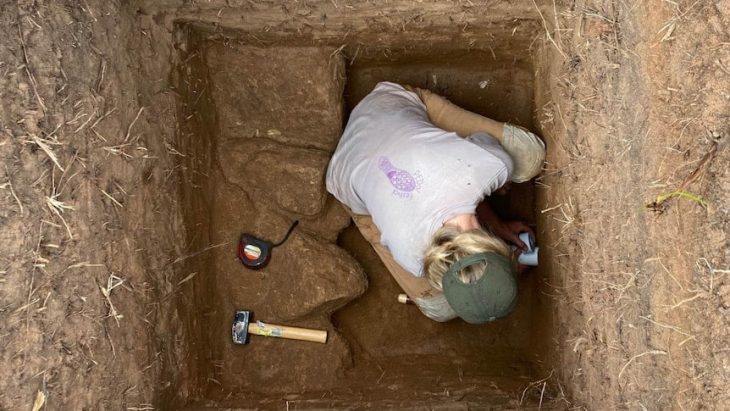
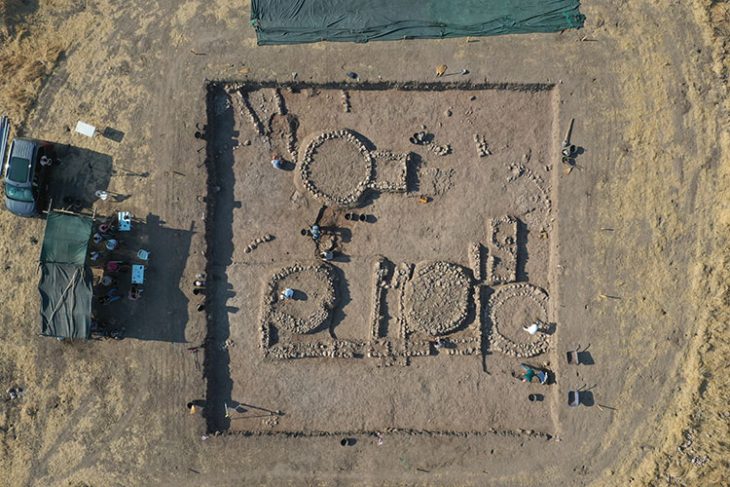The statue of a nymph (water fairy) discovered last month during excavations in the Ancient City of Amastris was identified as a statue of Aphrodite.
The statue was examined in detail by academics and experts from Bartın University and the Culture and Tourism Ministry. Experts closely examined approximately 20 examples of Aphrodite statues found in Türkiye and determined that the statue had the characteristics of both a nymph and Aphrodite. Further examinations revealed that the statue was Aphrodite.
While investigations into the statue, which resembles both Aphrodite and a nymph, continue, the statue was placed on display at the Amasra Museum in a ceremony.
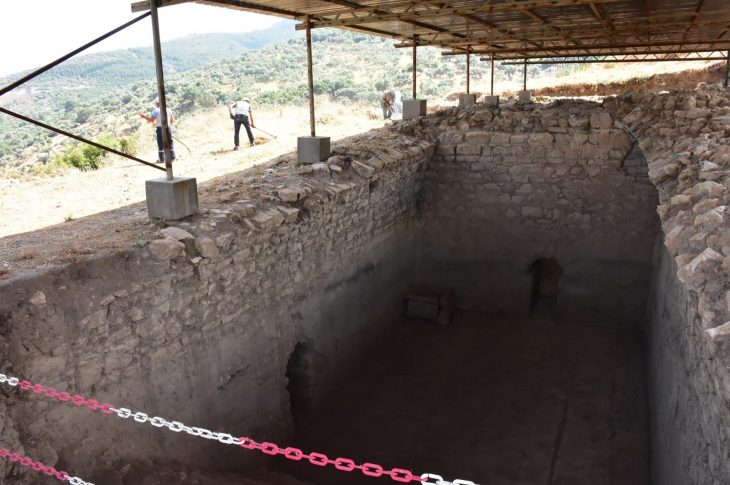
Amasra’s coast was host to the Phoenician colony, Sesamus, in the 12th century B.C. The colony’s heyday was during the rule of Iranian Princess Amastris. It was among the most important of the Byzantine fortress harbors on the south shore of the Black Sea.
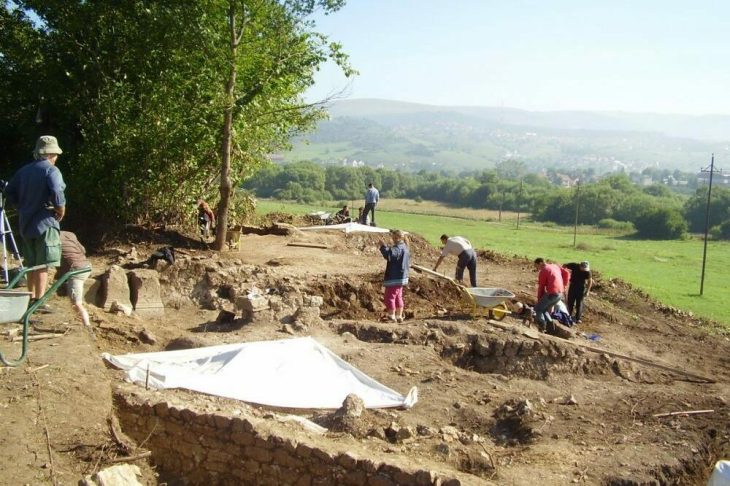
The statue was discovered at a depth of approximately 3.70 meters while drilling to determine the ground in an ancient city’s Gymnasium structure. The 1.53-meter-tall nymph statue is thought to date from the second century A.D.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
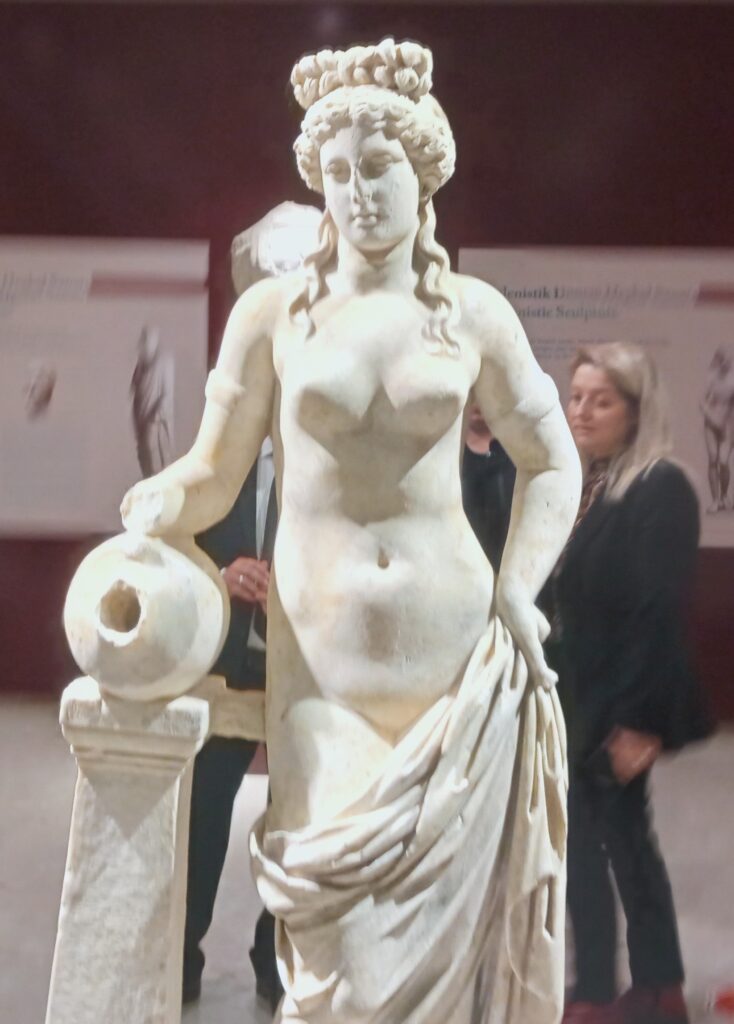

Speaking about the statue, Amasra Museum Deputy Director Güray Can Aytekin said, “Our aim was to reach the floor of the Gymnasium structure, and we found the statue, approximately 4 meters underground. Then removed it as a whole. We introduced it as a water fairy because the area where we found it was an area that we considered as a pool. But examinations revealed that it was more like an Aphrodite.”
Speaking about the features of the statue, Aytekin said, “We see examples of this statue in the 4th century B.C. as there were S-curve works made during this classical period. The posture of this statue is also in the S position. We see this example especially in Praxiteles’ School. We know that this form was further shaped during the later Hellenistic period, and its copies were made in the Roman period, too. We estimate that our statue is from the Roman period. It is possible to date it to the Roman period between 180 and 200 A.D., that is, in the last quarter of the second century.”
Aytekin also pointed out the importance of the statue for the museum and the region, saying, “The statue is also important for our museum in this respect. To date, there have not been many scientific excavations in the history of the museum. The museum is home to the artifacts recovered from the surface and foundation excavations in and around Amasya. This work is very important for the city and museum in terms of its layer, its location and its appearance as a whole. At the same time, it is a work that will contribute to the literature. The region is already on the UNESCO Tentative List with its castle structure. And thanks to this statue, we will announce to the world the fact that it was an important port city in the Roman period.”
The site of the excavation was donated to the Ministry of National Education in 2014 and construction started for the building of a school on the land in 2017 when some remains believed to belong to the Roman period were discovered, upon which the construction works were stopped and the area was taken under protection.
Cover Photo: Bartın Halk Gazetesi