Recent excavations by archaeologists from the Hebrew University in the Ophel area south of the Temple Mount uncovered the remains of a monumental public building from the Second Temple period that was destroyed in 70 CE.
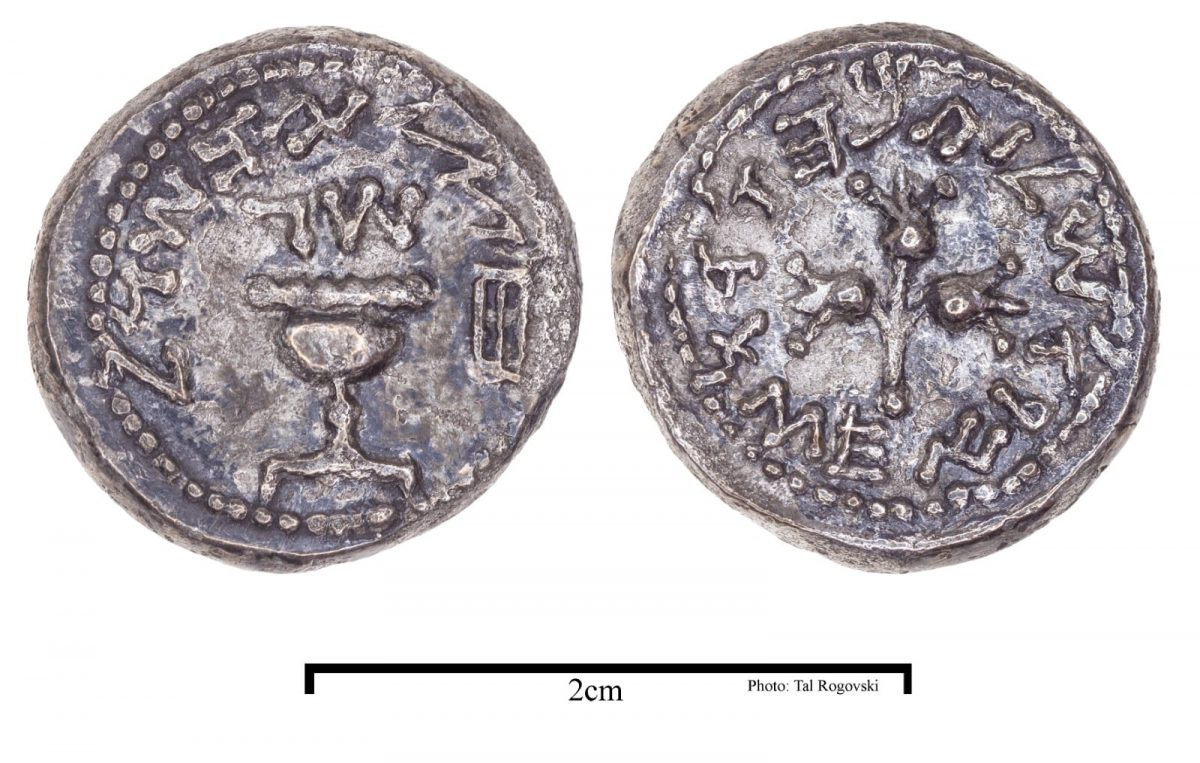
Numerous Jewish coins, the majority of which were bronze, from the Great Revolt (66-70 CE) were discovered in the destruction layer. This collection also contained a particularly uncommon and rare discovery: a silver coin with a half-shekel denomination that dates to around 69/70 CE.
The Great Revolt was the first of several uprisings against the Roman Empire by the Jewish population of Judea.
The revolt was in response to the Romans’ increasing religious tensions and high taxation, which resulted in the looting of the Second Temple and the arrest of senior Jewish political and religious figures. A large-scale rebellion overran the Roman garrison in Judea, forcing the pro-Roman King Herod Agrippa II to abandon Jerusalem.
A coin discovered in the ruins of a Second Temple-era building was most likely used to pay an annual tax for worship at the site; most coins of this type are bronze.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The dig was carried out by a team from the Hebrew University, led by Prof. Uzi Leibner of the Institute of Archaeology, in partnership with the Herbert W. Armstrong College in Edmond, Oklahoma, and with the support of the East Jerusalem Development Company, the Israel Antiquities Authority, and the Israel Nature and Parks Authority. The rare coin was cleaned at the conservation laboratory of the Institute of Archaeology and identified by Dr. Yoav Farhi, the team’s numismatic expert and curator of the Kadman Numismatic Pavilion at the Eretz Israel Museum in Tel Aviv.
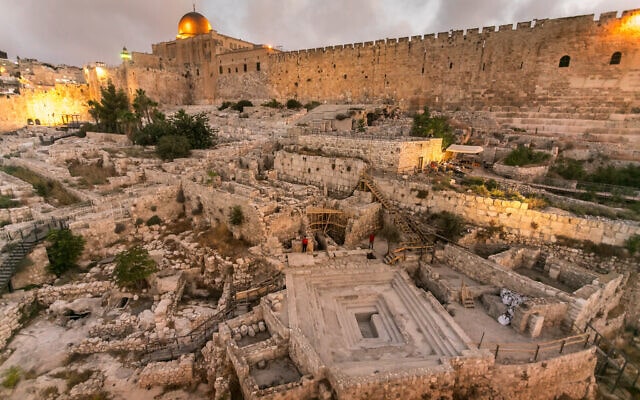

“This is the third coin of this type found in excavations in Jerusalem, and one of the few ever found in archeological excavations,” said the researchers.
During the Great Revolt against Rome, the Jews in Jerusalem minted bronze and silver coins. Most of the silver coins featured a goblet on one side, with ancient Hebrew script above it noting the year of the Revolt. Depending on its denomination, the coins also included an inscription around the border noting either, “Israel Shekel,” “Half-Shekel,” or “Quarter-Shekel.” The other side of these coins showcased a branch with three pomegranates, surrounded by an inscription in ancient Hebrew script, “Holy Jerusalem.”
Throughout the Roman era the authority to produce silver coins was reserved solely for the emperor. During the Revolt, the minting of coins, especially those made of silver, was a political statement and an expression of national liberation from Roman rule by the Jewish rebels. Indeed, throughout the Roman period leading up to the Great Revolt, no silver coins were minted by Jews, not even during the rule of King Herod the Great.
According to the researchers, half-shekel coins (which had an average weight of 7 grams) were also used to pay the “half-shekel” tax to the Temple, contributed annually by every Jewish adult male to help cover the costs of worship.
Dr. Farhi explained, “Until the revolt, it was customary to pay the half-shekel tax using good-quality silver coins minted in Tyre in Lebanon, known as ‘Tyrean shekels’ or ‘Tyrean half-shekels.’ These coins held the image of Herakles-Melqart, the principal deity of Tyre, and on the reverse they featured an eagle surrounded by a Greek inscription, ‘Tyre the holy and city of refuge.’ Thus, the silver coins produced by the rebels were intended to also serve as a replacement for the Tyrean coins, by using more appropriate inscriptions and replacing images (forbidden by the Second Commandment) with symbols. The silver coins from the Great Revolt were the first and the last in ancient times to bear the title ‘shekel.’ The next time this name was used was in 1980, on Israeli Shekel coins produced by the Bank of Israel.”
The precious silver coins are thought to have been minted inside the Temple complex, according to a Monday statement from the Armstrong Institute.