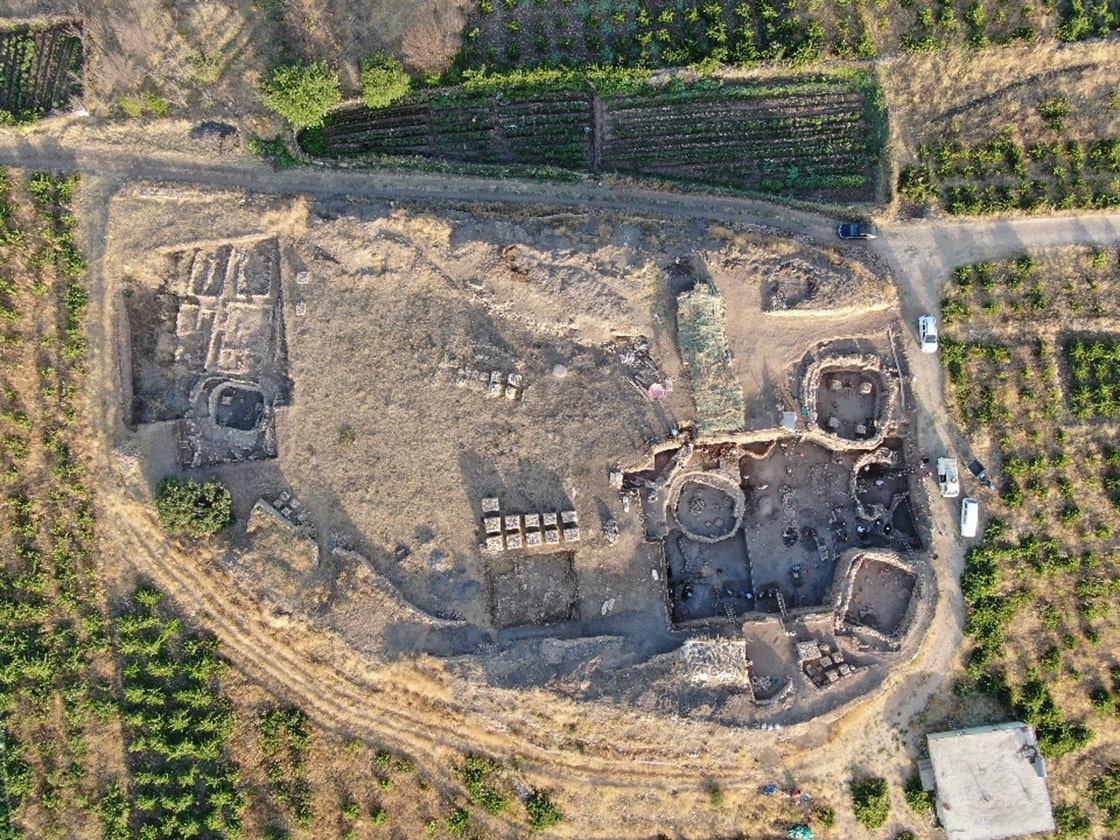
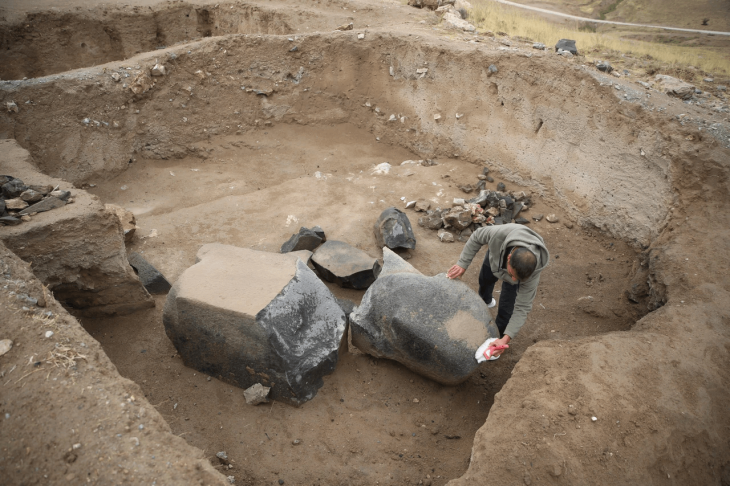
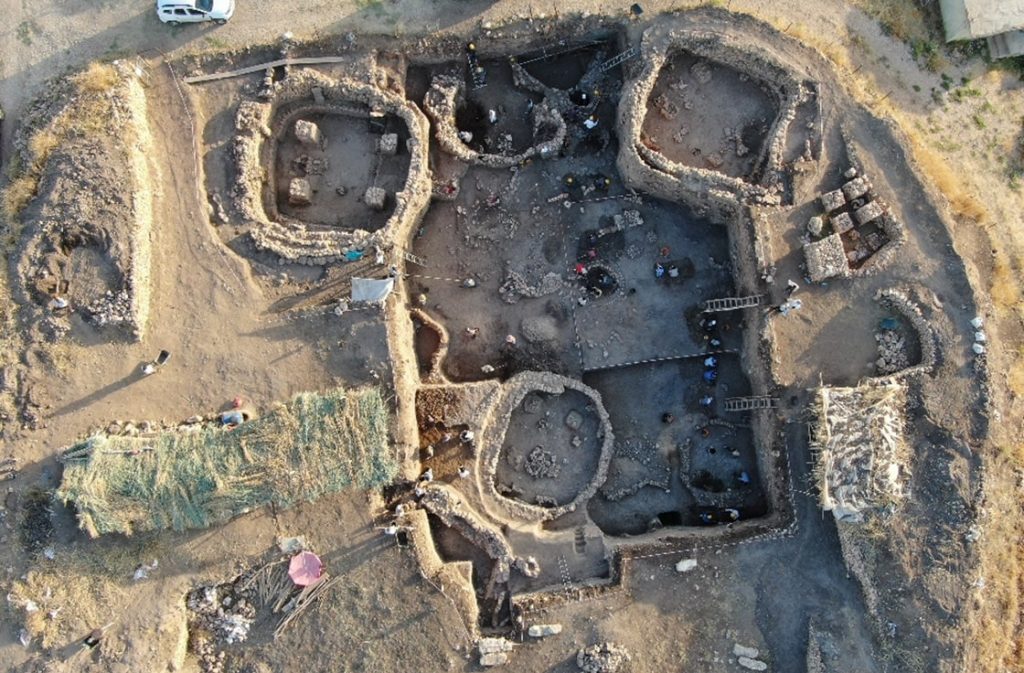
Pit-bottomed structures dating to the Pre-Pottery Neolithic period were found at Gre Fılla Höyük (Gre Fılla Mound) in the province of Diyarbakir in eastern Turkey. It was determined that the steles found in one of these buildings were contemporary with Göbeklitepe.
Excavations have been carried out in the mound since 2018, under the chairmanship of the Diyarbakır Museum Directorate, under the scientific consultancy of Kocaeli University Faculty of Arts and Sciences Archeology Department Head Prof Dr. Ayşe Tuba Ökse.
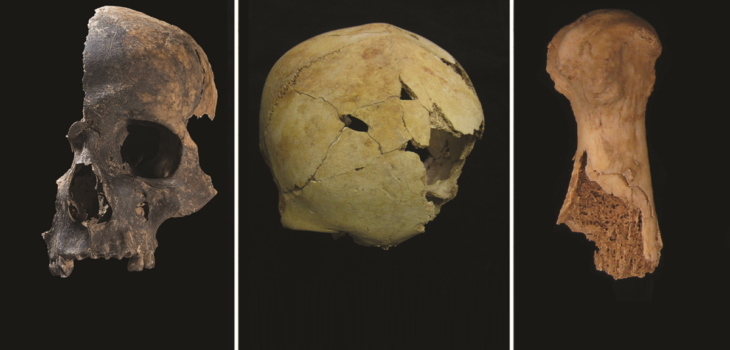
During the ongoing excavations in the mound, the remains and religious and social living areas of societies that lived in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic Period (PPNA) were determined. In this settlement, which dates back 11,000 to 12,000 years, excavations continued for four years, revealing the finding of the oldest settled communities.
During the excavations carried out in the mound, it was determined that the oldest settlement started in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic Period, and Ambar Höyük and Kendale Hecala, a few hundred meters away, were populated in the Early Neolithic Age.
In this mound, where the oldest known settlement in Diyarbakır was seen, it was observed that first round-planned shelters were used, and then the settlement became narrow-planned.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Prof Dr. Ayşe Tuba Ökse said that three different pit structures with a diameter of almost 10 meters were unearthed.

“There were steles in one of the pit structures that are contemporary with Göbeklitepe. There were 4 steles in them to carry the roof. According to the artifacts, we can say that a certain amount of ritual behavior is exhibited here. We can define it as common usage areas where a belief and social life coexist. We don’t want to call them temples directly. Because we don’t have that much data yet, it is more appropriate to say that these are special structures. Just like in Göbeklitepe.”
Stating that they have excavated two main periods, one of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic and one of the Late Antique Age graveyards, Ökse says that they can define these areas as areas where the people around them can socialize collectively and where they can perform their rituals in the context of belief.
Özlem Ekinbaş Can, a doctoral student at the Department of Archeology at Kocaeli University, who was part of the excavation team, said that Gre Fılla could be a symbol for the region for the Tigris line, just as Göbeklitepe is a symbol for the Euphrates line.
Özlem Ekinbaş Can said, “It is our duty to somehow carry future the 11,000-year-old structures that have survived from the past to the present.”
Can also added that the altars with figures found inside one of the pit structures were delivered to the museum.
During the excavations that have been going on for 4 years, 2 thousand 687 artifacts dating back to 7 thousand BC until today were unearthed.