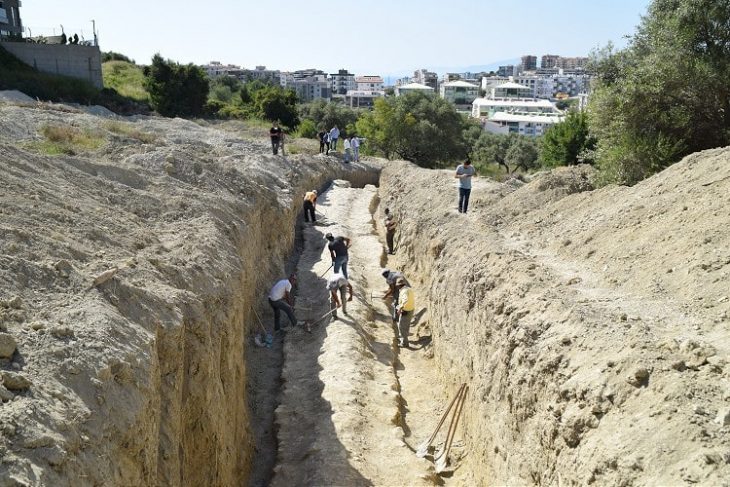
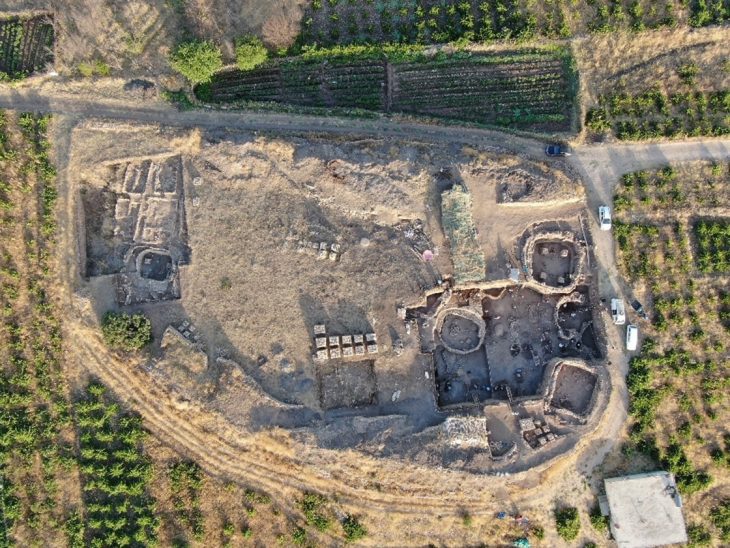
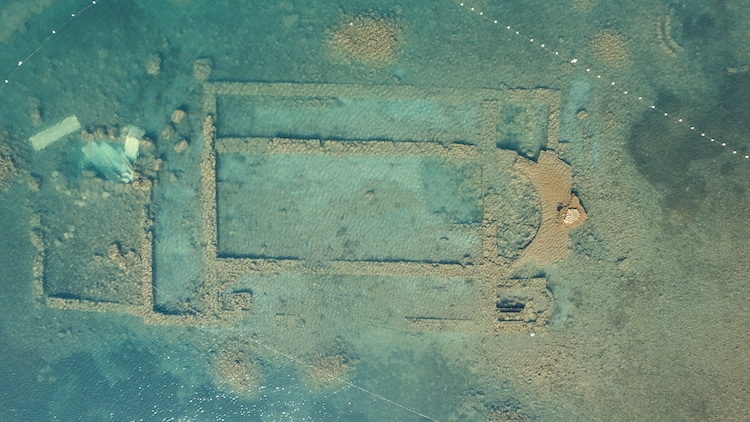
Underwater archaeological excavations and research, which were started 8 years ago in the basilica located 20 meters off the lake shore at a depth of 1.5-2 meters in the Iznik district of Bursa, in western Turkey, continue with new discoveries.
Historically, Iznik played a significant role as a center of culture during the Byzantine and early Christian eras. These ancient roots showed themselves in 2014 when a 1,600-year-old basilica was found submerged off the shores of Lake Iznik.
In A.D. 740, an earthquake destroyed the basilica, which later sank beneath the lake’s surface, leaving the ruins submerged.
Underwater excavations are continuing in Iznik Lake under the direction of Professor Mustafa Şahin, a professor at Bursa Uludağ University (BUU) Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Department of Archeology.
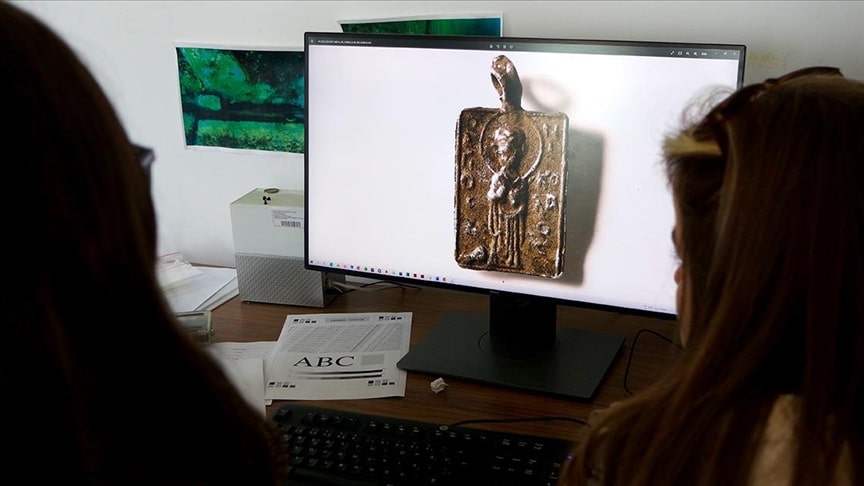
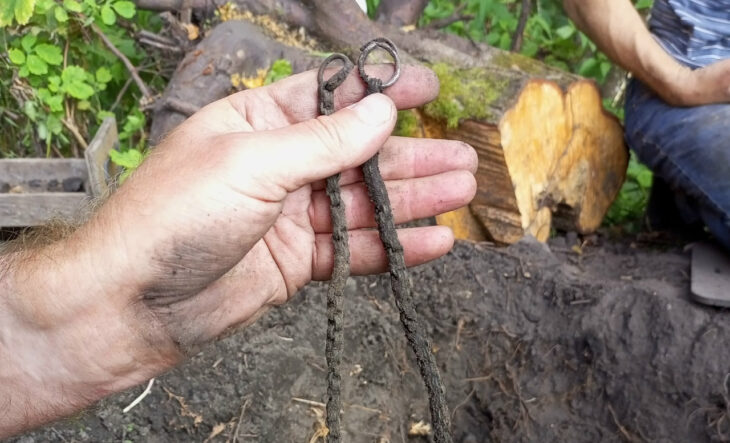
The research team unearthed a large number of finds and a pendant with the name and figure of St. Nicholas on it during the dives that continued since the beginning of August.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The finding of the pendant, which is thought to belong to a pilgrim, is considered as a sign that the basilica, which was named one of the 10 most important discoveries worldwide in 2014 by the American Archaeological Institute, was a pilgrim church at that time.
Professor Mustafa Şahin, Head of Underwater Excavations of the Basilica of Lake Iznik and Head of the Archeology Department of BUU Faculty of Arts and Sciences, told Anadolu Agency (AA) that they started the dives on August 3 this year and completed the dives at the end of last week.
Şahin, who gave information about the identity of St. Nicholas and his importance for Christianity:
“We know him more as ‘Santa Claus’. The saint’s relics are not currently in Demre, but his church is in Demre. The find is very important as it shows us that a pilgrimage group, or at least a pilgrim, came here. The pilgrim probably came to Demre after completing his pilgrimage to Jerusalem and bought this necklace. Then he visited the basilica where we were excavating. Unless she accidentally dropped the necklace, she left it at the church. This is important because it shows us that the church we excavated was originally a pilgrim church.”
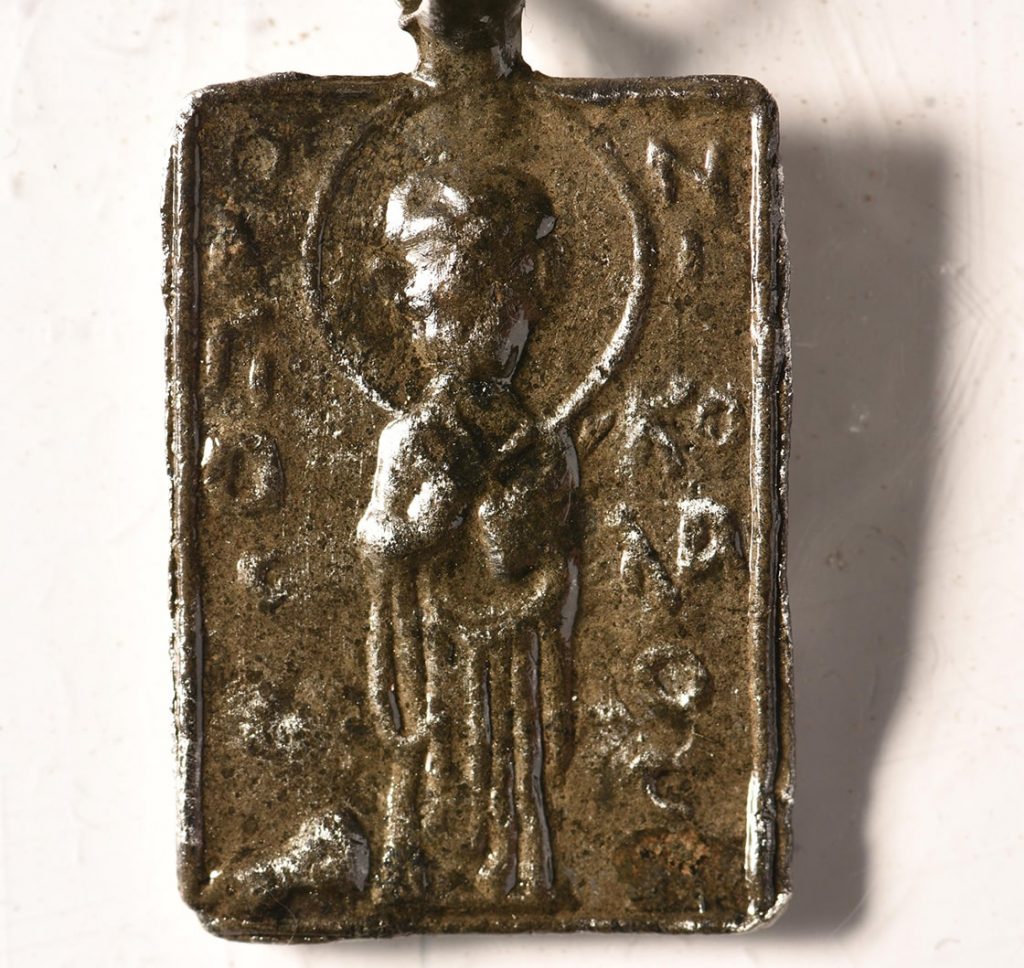

Şahin said that the pendant with “Hagios” on one side and “Nikolaos” on the other side writing and the figure of St. Nicholas in the middle was delivered to the Iznik Museum.
“Our most important goal next year is to reach important information, findings, and documents on whether the 1st Council really convened here. We will continue to work on this issue.”
The ancient city of Nikaia (İznik) is well known in Christian circles as the site of an early and significant statement of faith: The Nicene Doctrine.
During their excavations, the team learned a lot about the early Christian church. They not only dated the basilica to the late fourth or early fifth century CE, but they also discovered that it was most likely built over an earlier structure.
Researchers in previous years also discovered several graves as well as the skeletons of several young children and an adult. Because of the church’s close relationship with St. Neophytos, burials at the site would have been common at the time. This saint was martyred in Nicea when he refused to make a sacrifice to the pagan gods under the orders of the governor. It is believed that the basilica, which was built outside the city walls, sits on the site of St. Neophytos’ grave, and it was not uncommon for worshippers to want to be buried near a saint.