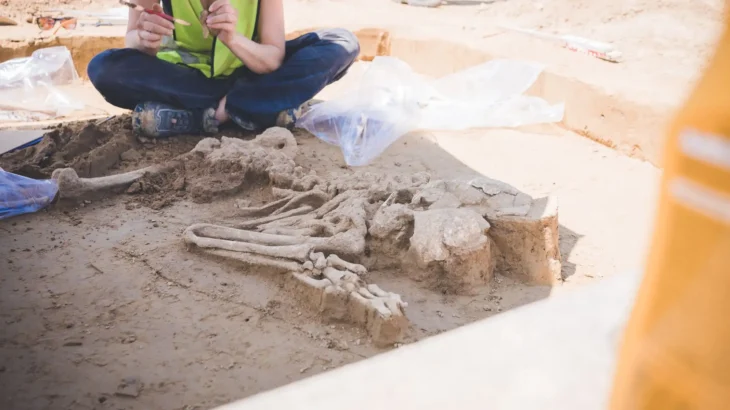
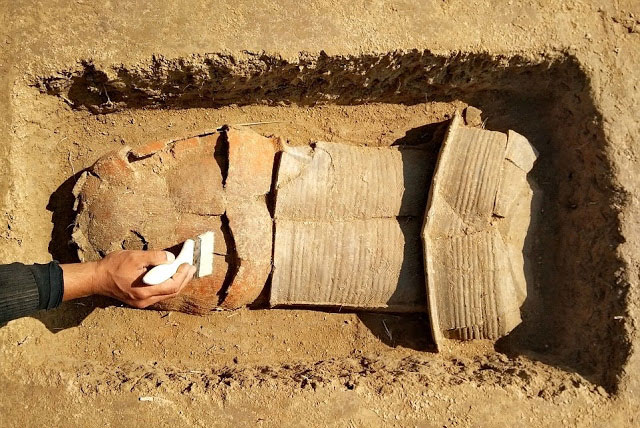
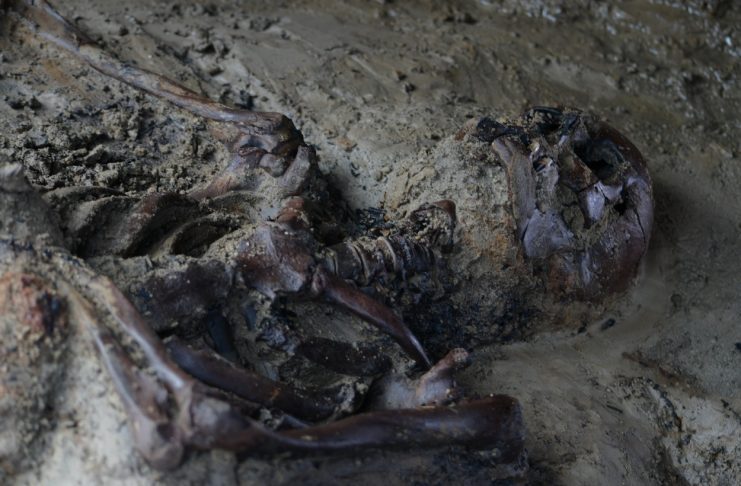
Archaeologists released haunting images Wednesday of the skeletal remains of a man buried by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in the ancient Roman city of Herculaneum, close to Pompeii, in 79 AD.
Archaeologists said the man, believed to have been aged between 40 and 45, was killed just steps away from the sea as he tried to flee the eruption. Alongside the skeleton was a cloth shoulder bag, where analysis has identified various materials: a wooden box containing objects in metal, pieces of cloth, and probable traces of gold finish.
His remains were discovered on what would have been the town’s beach with the head pointing back in the direction of the sea.
The skeleton was surrounded by carbonized wood, including a roof beam that might have crushed his skull.
Previous excavations in the 1980s of the town’s shoreline discovered skeletons on the beach and in the first six so-called boat sheds. Archaeologists at the time suggested that these victims were waiting for rescue when they were killed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
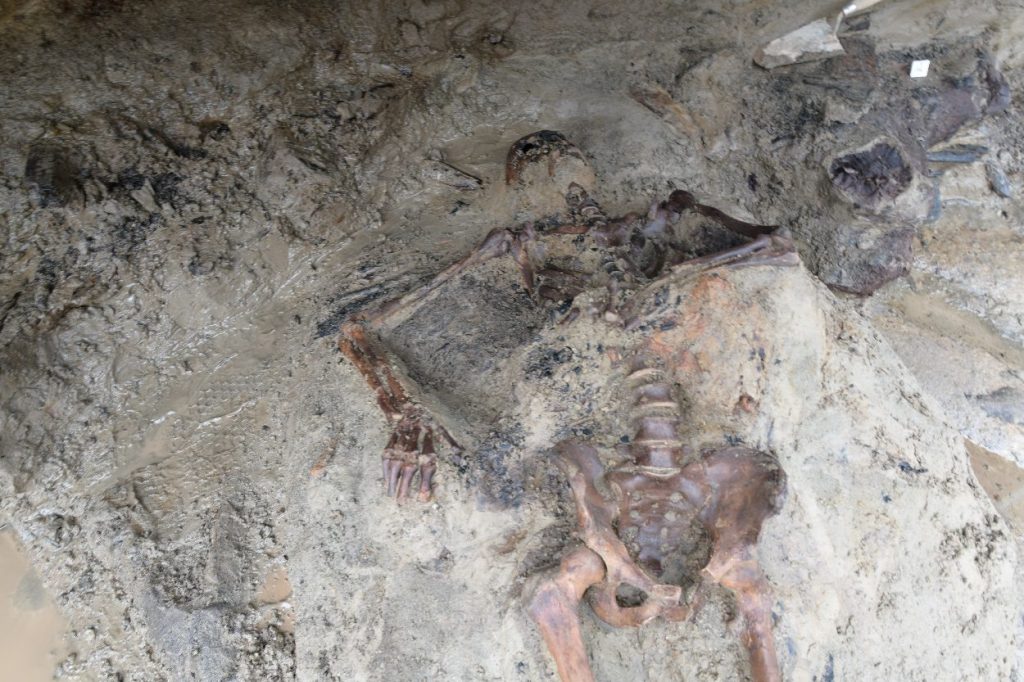

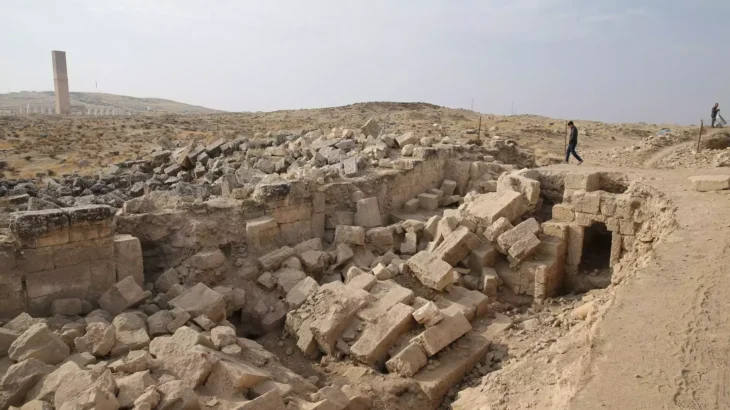
For the first time since the 1980’s excavations, archaeologists have started to explore the periphery of the town, focusing again on the beachfront where they discovered the remains of a man aged between 40-45 years of age.
The Manager of the Herculaneum Conservation Project Jane Thompson said: “The Packard Humanities Institute in recent years has concentrated its energies precisely on the boundaries of the site because, as in the case of the ancient beach, the explorations had been partial and had left unresolved and critical conditions.”
“This is a modern excavation,” says Francesco Sirano, the director of the archaeological park, describing it as “a multidisciplinary open-air laboratory” in which each phase of work is systematically documented and surveyed to give a snapshot of the tragedy that unfolded on the beach.
Although the town was smaller than the city of Pompeii, Herculaneum was a wealthy resort for the Roman elite, reflected in their grand and luxurious villas
Archaeological Park of Herculaneum
Header Image Credit: Archaeological Park of Herculaneum