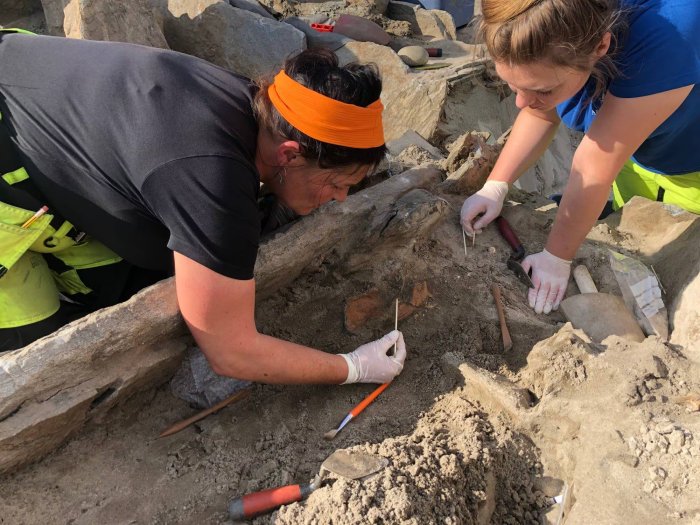
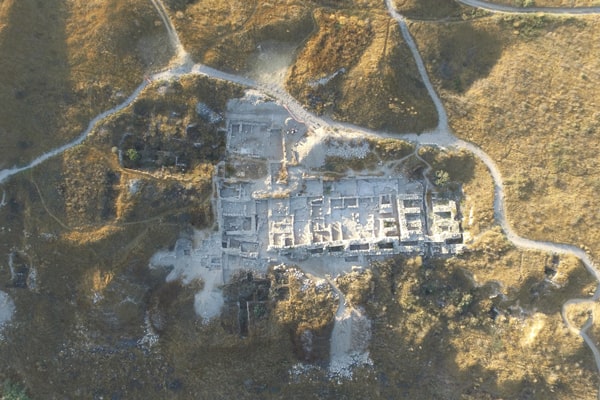
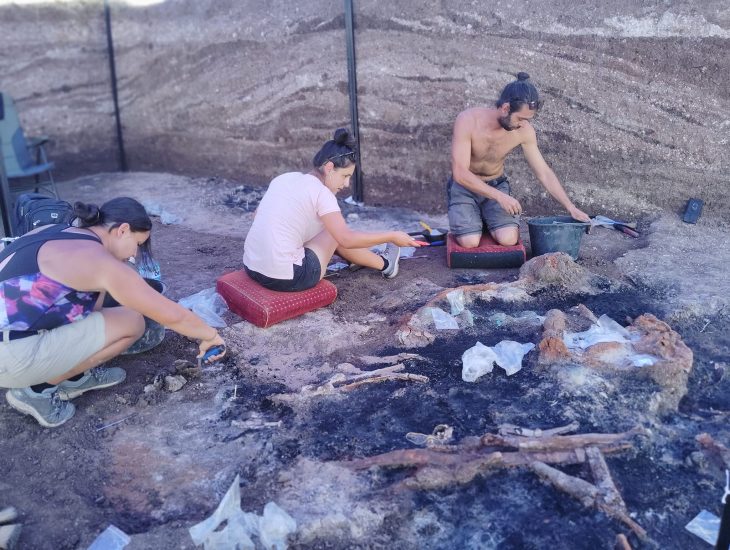
According to one opinion: About 2 million years ago, our first ancestors moved north from their hometown and left Africa.
The ergaster (or Homo erectus) may be the first human to leave Africa. Fossil remains indicate that this species has extended its range to southern Eurasia before 1.75 million years ago. Their descendants, the Asian Homo erectus, later spread eastward and were established in Southeast Asia at least 1.6 million years ago.
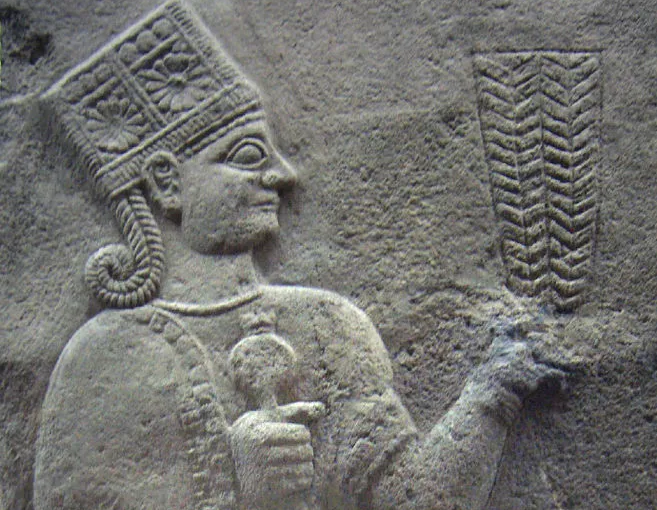
However, another theory suggests that anthroposomes may have migrated out of Africa before the first Homo erectus in Asia before the evolution of Homo erectus about 2 million years ago. These human-derived proteins may be Augustine, or more likely an unknown race, and their appearance is similar to that of apes. In this theory, the population found in Dmanisi represents the missing link in the evolution of Homo erectus/ergaster. Perhaps the evolution of the apes also occurred outside of Africa, and there is a considerable flow of genes between Africans and Eurasians. In recent years, due to DNA research, this theory has gained more support.
According to a new research result, researchers found that there is evidence that the ancestral connection between gorillas and humans occurred in the Eastern Mediterranean, not Africa, and according to research, the first pre-human humans (ie, humans) entered the Balkan region of northern Greece. Published in the scientific journals of “Science PLOS One” and “Science Daily”.
Until the time scientists made the discovery in 2017, scientists assumed that lineages diverged five to seven million years ago and that the first pre-humans had developed in Africa.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
However, an international research team from Germany, Bulgaria, Greece, Canada, France, and Australia, headed by Professor Madelaine Bohme from the Senckenberg Centre for Human Evolution and Palaeoenvironment at the University of Tubingen and Professor Nikolai Spassov from the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, believe that human history began a few centuries earlier — and in the general area of the Balkans.
New theories
Publishing their results in two articles in the scientific journal PLoS ONE in May 2017, the researchers explained that the two only known specimens of the fossilized hominid Graecopithecus Freyberg include the lower jaw found in Greece and the upper premolar from Bulgaria.
Previously, it was thought that the ape had been extinct for three million years before that, which made it the youngest fossil ape-like ever recorded in Europe.
Using state-of-the-art computed tomography, scientists visualized the internal structures of the fossils and showed that premolars’ roots were widely fused, and scientists studying the two Graecopithecus Freyberg fossils concluded that they actually belonged to them. to the pre-humans.
“While great apes typically have two or three separate and diverging roots, the roots of Graecopithecus converge and are partially fused — a feature that is characteristic of modern humans, early humans, and several pre-humans including Ardipithecus and Australopithecus,” said Bohme.
“This condition is so far only known to occur regularly in hominins – pre-humans and humans,” Spassov says. “It is extremely rare in recent chimps.”
The lower jaw, which scientists have dubbed “The Graeco,” has additional dental root characteristics, suggesting that the species Graecopithecus Freyberg could belong to prehumans or hominids. In addition, the researchers also found that it featured relatively small canines, which does not yet exist. another hominid trait.
The sedimentary layers of the Graecopithecus fossil sites in Greece and Bulgaria show that the ages of the two fossils are almost synchronized, the 7.24 years and 7.175 million years before the present.
“It is at the beginning of the Messinian, an age that ends with the complete desiccation of the Mediterranean Sea,” Bohme explained.
Professor David Begun, the University of Toronto paleoanthropologist and co-author of the study added, “This dating allows us to move the human-chimpanzee split into the Mediterranean area.”
For the full article: Plos One