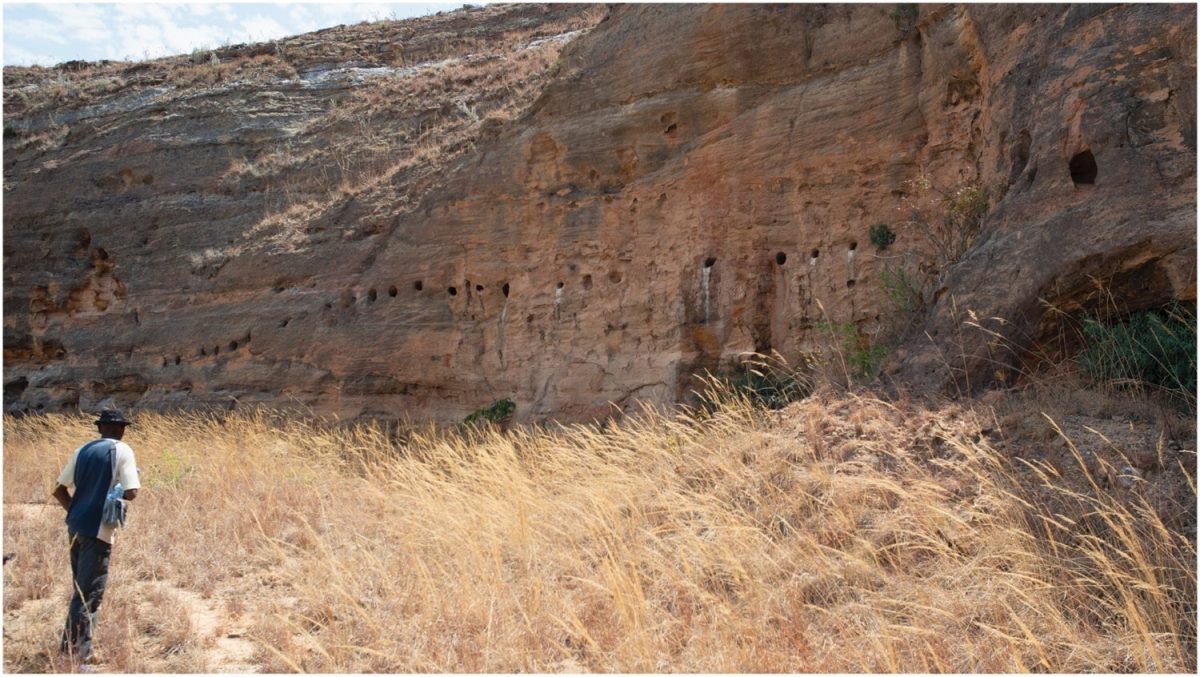
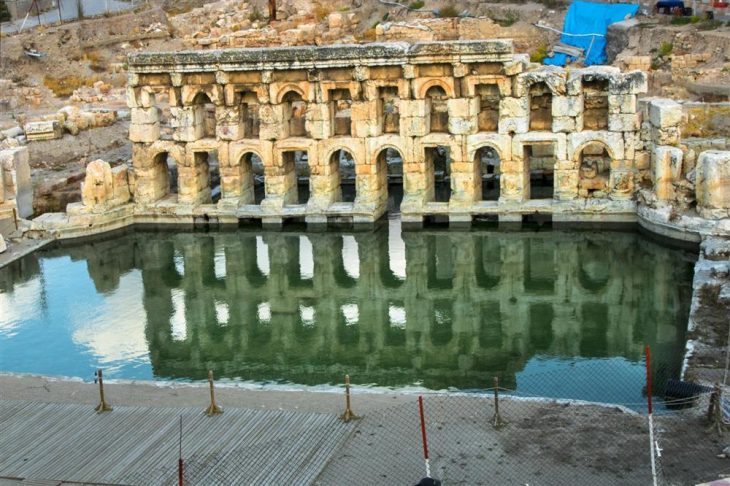
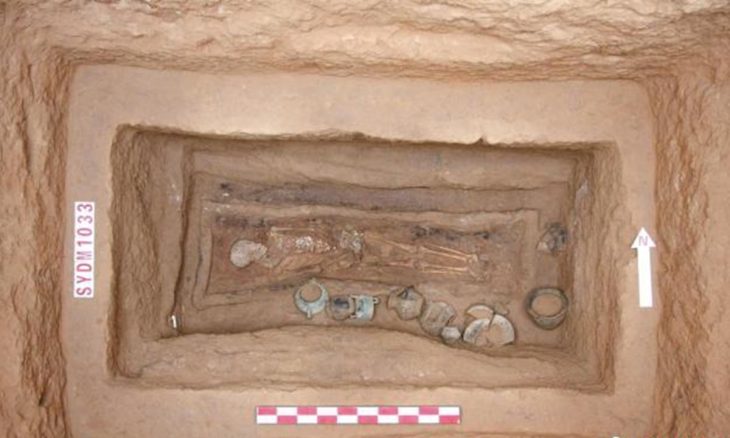
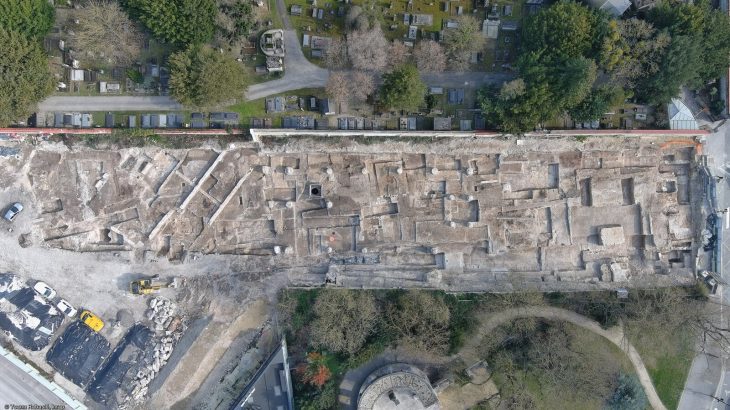
An international team of researchers found an enigmatic rock-cut architecture at Teniky, a site in the remote Isalo Massif in southern Madagascar, that has no parallels on the island or the East African coast.
The research was initiated under Guido Schreurs, associate professor at the Institute of Geological Sciences at the University of Bern in Switzerland.
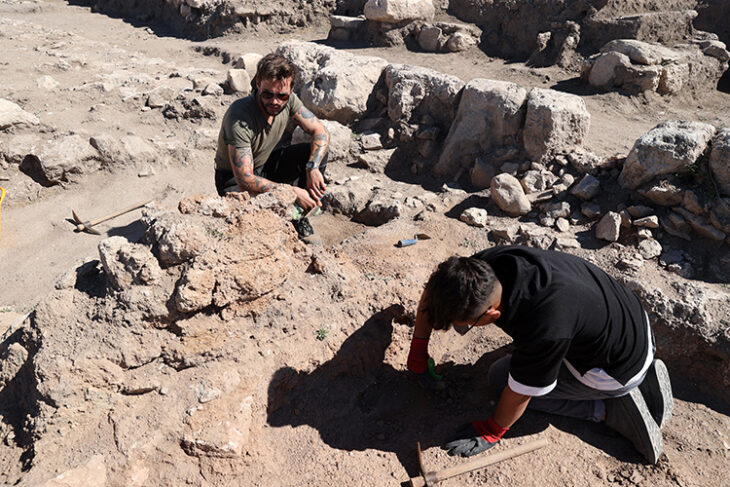
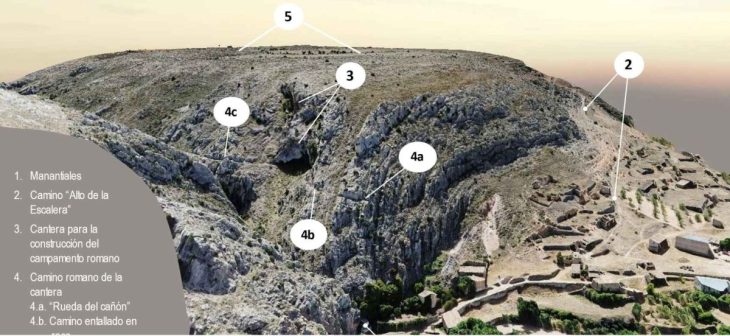
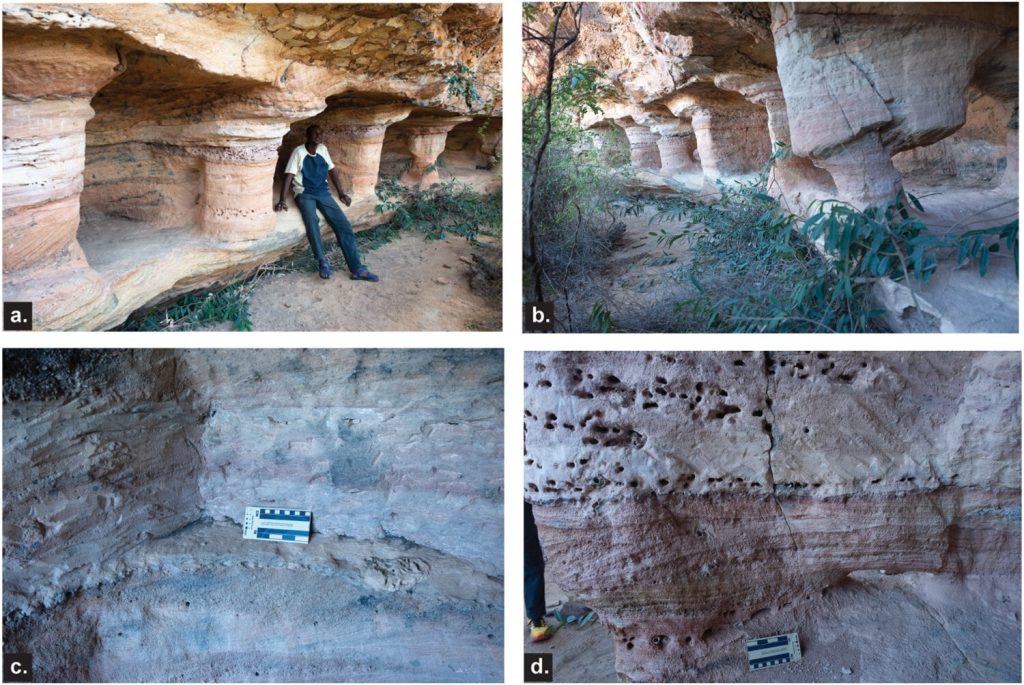
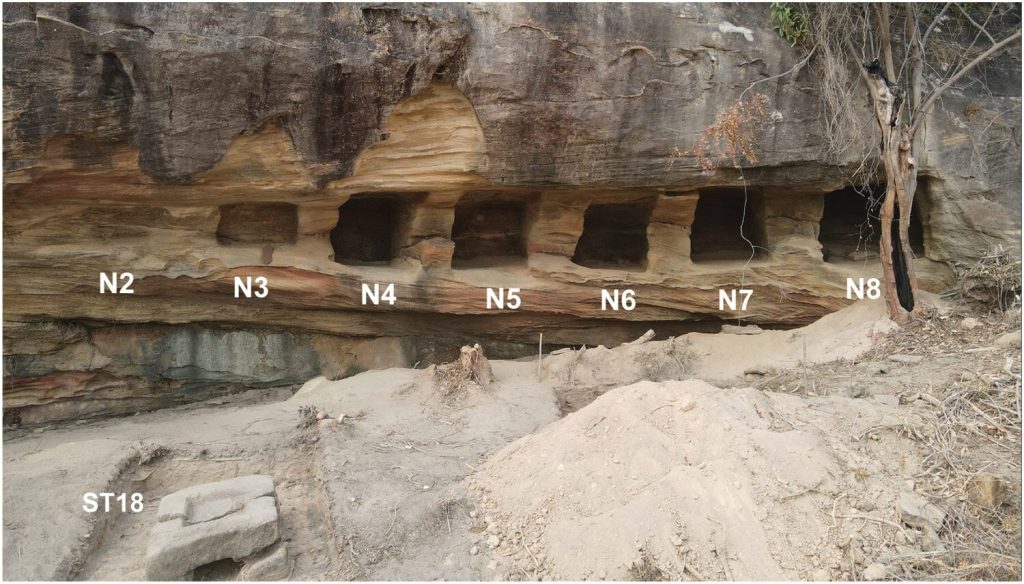
Researchers have documented many newly discovered archaeological structures, including terraces, stone walls, stone basins, and rock-cut structures in various sizes, shapes, and forms constructed in the late first/early second millennia AD.
Archaeological excavations and field prospecting at Teniky reveal a much larger and more important archaeological landscape than previously known.
Surprisingly, the closest stylistic parallels to this architecture can be found thousands of kilometers away, in present-day Iran, specifically in the Fars region. The rock-cut niches at Teniky show similarities to those known from various sites throughout Iran, dated to the first millennium or older and related to Zoroastrian funerary practices.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
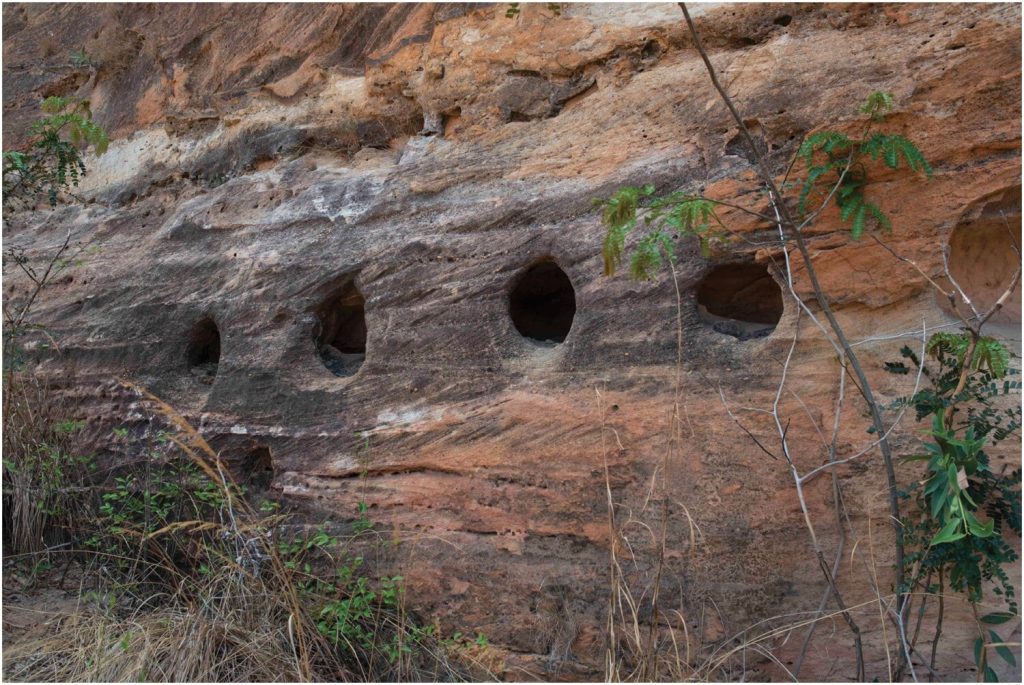

The recently discovered rock-cut niches and carved sandstone walls were constructed in the late first millennium/early second millennium, roughly the tenth to twelfth century AD, according to radiocarbon dating of charcoal found during excavations. This dating coincides with the presence of sherds of Chinese and Southeast Asian pottery, generally dating to the 11th to 14th centuries.
Despite being more than 200 kilometers from the closest coast, this finding is especially intriguing because it demonstrates that Teniky’s residents were a part of Indian Ocean trade networks during the medieval era.
The researchers interpreted the rock-carved architecture at Teniky as part of a former necropolis made by settlers with Zoroastrian origins. However, they note that further archaeological research is needed to test this hypothesis and address general questions.

Researchers have not excluded the possibility that the archaeological structures at Teniky were the work of a group of people whose specific rites and beliefs developed and evolved after their arrival on the island and whose rock-cut structures show, by chance, formal similarities to Zoroastrian ones in Iran.
However, they believe that the people who came to the coast of Madagascar and eventually settled on Teniky brought their rituals and beliefs from outside the island and continued to practice them in a similar way while there.
Dr. Schreurs and his colleagues emphasize independent of the origin, religion, and funerary rites of Teniky’s former inhabitants, further archaeological studies are required to fully situate it within Madagascar and the western Indian Ocean.

https://doi.org/10.1080/0067270X.2024.2380619
Cover Image: G. Schreurs et al.