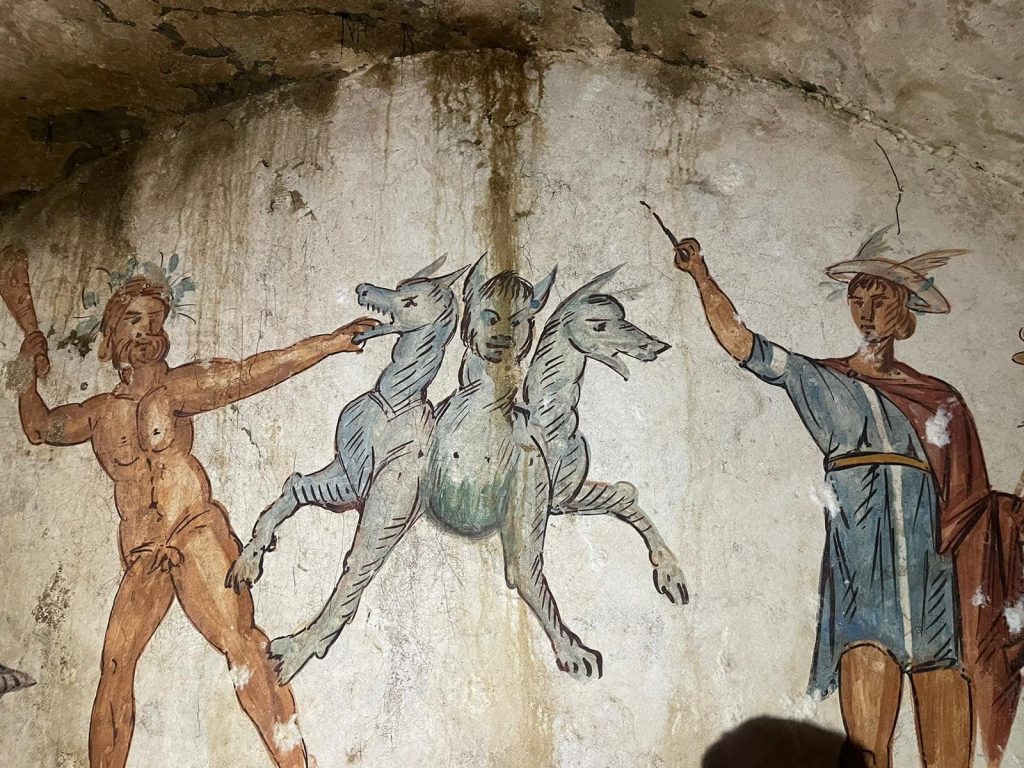
The latest surprise revealed by investigations at the Tomb of Cerberus in Giugliano: The remains of a corpse covered with a shroud, with ointment and perfume containers nearby.
This discovery was announced today by the Superintendency of Archaeology, Fine Arts, and Landscape for the metropolitan area of Naples.
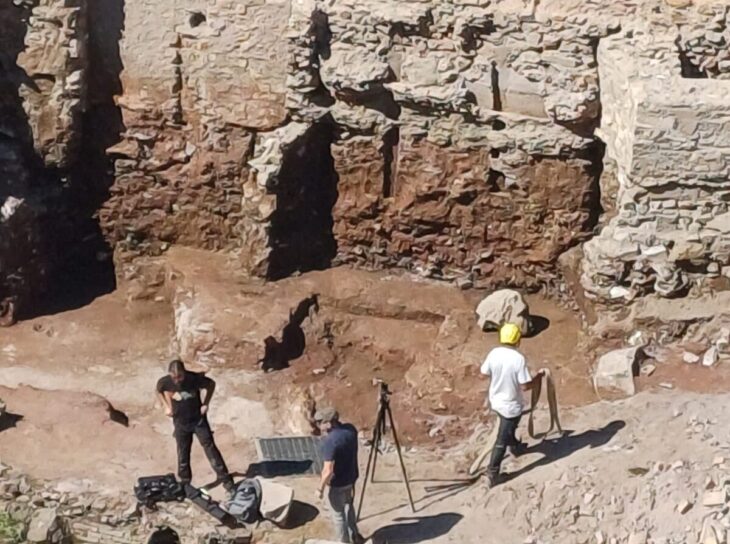
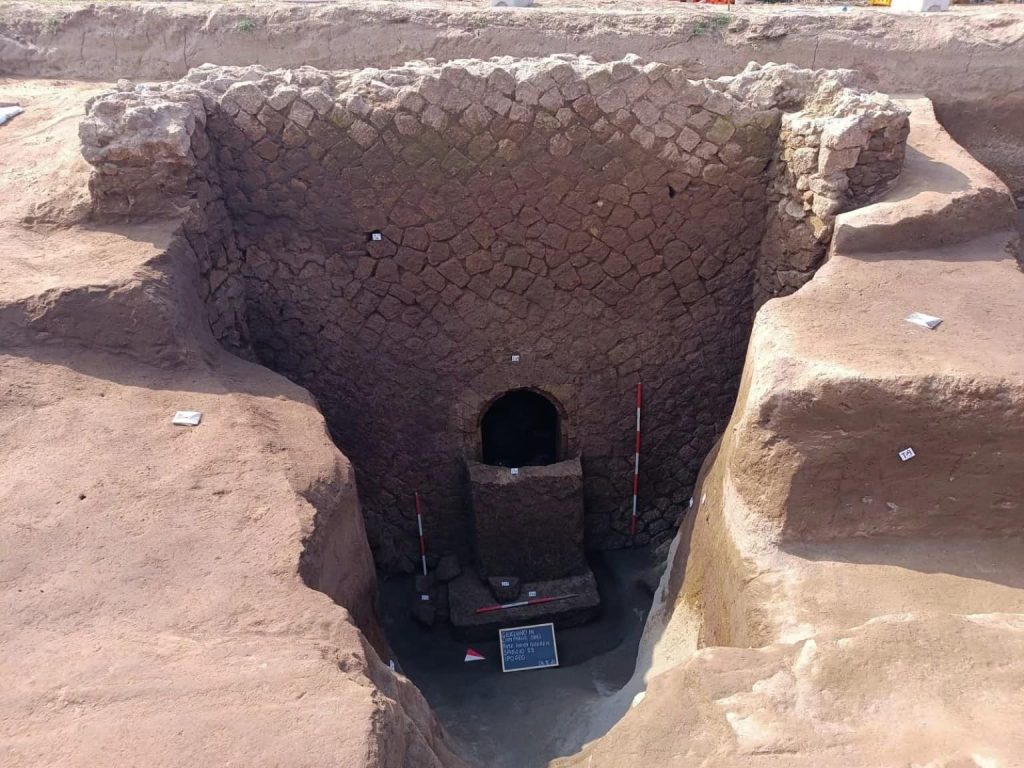
In preparation for excavations in the nearby necropolis and the Ministry of Culture-funded restoration of the frescoes, investigations into the Tomb of Cerberus in Giugliano are ongoing. The sarcophagus had been sealed for over 2,000 years, but now a gap has been opened, providing access to its interior, thanks to a targeted intervention and the use of a micro camera.
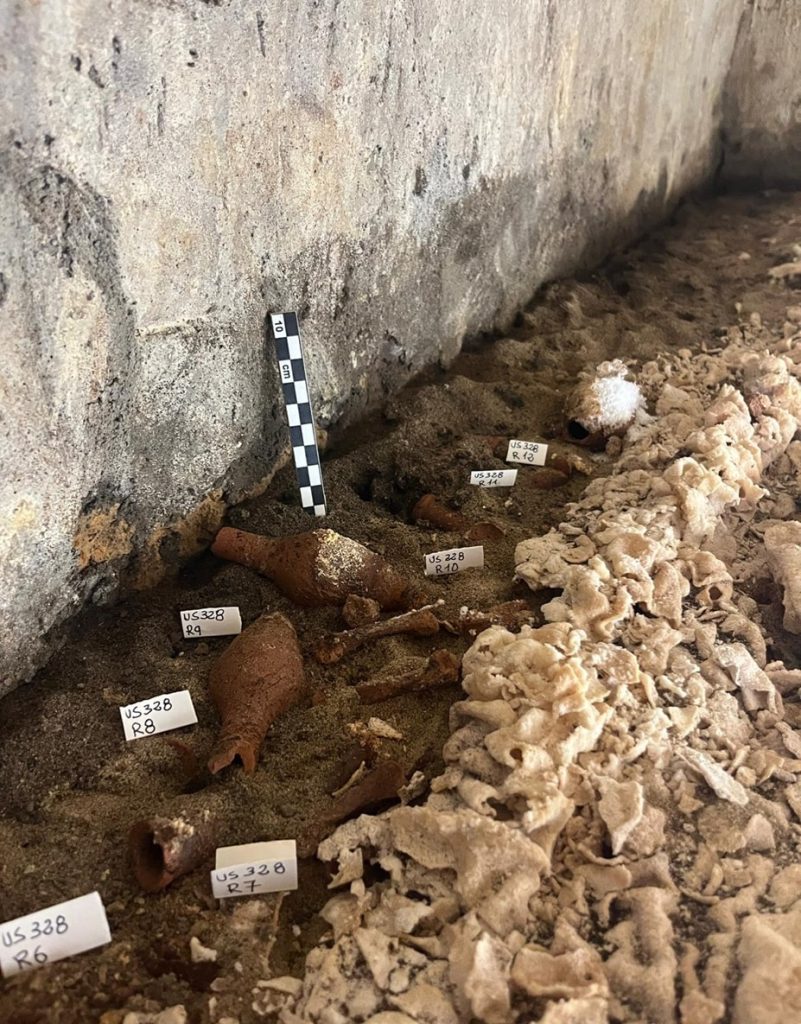
The excavation activities, coordinated by the archaeologist Dr. Simona Formola, have led to the exceptional discovery of a burial in excellent condition, with a supine body covered by a shroud, probably mineralized due to the unique climatic conditions of the burial chamber, surrounded by grave goods, among which several unguentaria and strigils stand out. The particular care given to the buried individual and the chronology of the objects found suggests that it could be the progenitor of the family for whom the mausoleum was built.

“The Tomb of Cerberus continues to provide valuable information about the Phlegraean area near Liternum, expanding knowledge of the past and offering opportunities for multidisciplinary research,” declared Superintendent Mariano Nuzzo.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
A multidisciplinary team of researchers has taken samples from previous inhumations on the funeral beds within the mausoleum and examined them. A genus of perennial herb known as goosefoot, chenopodium, and wormwood were found through pollen analysis and microscope observation. To help stop decomposition, these were probably rubbed onto the bodies in the form of creams. DNA analysis is being done on samples taken from the human remains.
“In recent months, laboratory analyses conducted on samples taken from the burials and depositional beds have yielded a significant amount of data on the treatment of the bodies and the funerary rituals performed, significantly enriching our understanding,” stated a team guided by the Superintendency.

More intriguing data from the hypogeum and surrounding necropolis, along with ongoing laboratory sampling and analysis activities, will surely be uncovered in the upcoming months. These data will be helpful in reconstructing the historical and social landscape of an ancient community that still has a lot to tell.
Superintendency of Archaeology, Fine Arts, and Landscape for the metropolitan area of Naples
Cover Photo: Superintendency of Archaeology, Fine Arts, and Landscape for the metropolitan area of Naples