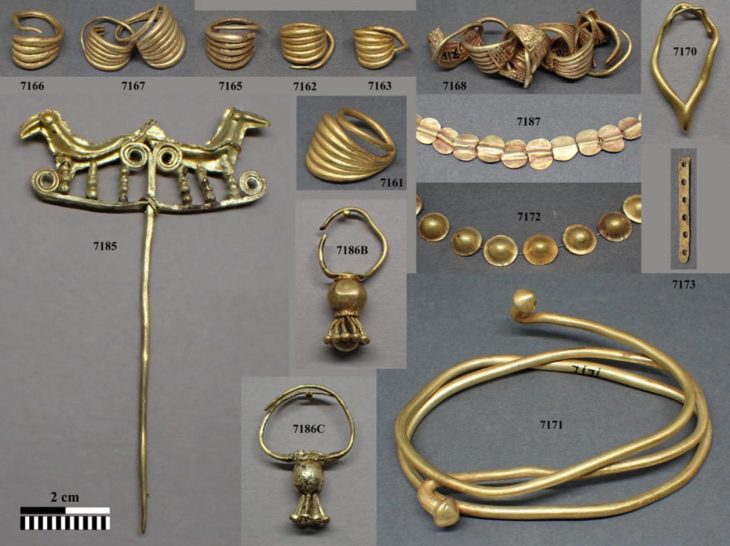
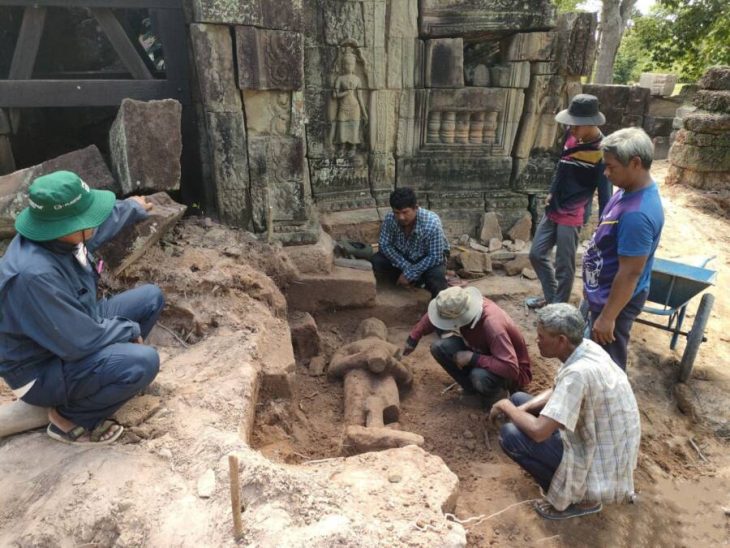
Spanish archaeologists made a ground-breaking discovery of rock-hewn Ptolemaic and Roman tombs, mummies, coffins, golden masks, and terracotta statues in the historic city of Al Bahnasa in the Minya governorate.
The archaeological excavations were led by Dr. Mayte Mascorro and Dr Esther Pons Melado from the University of Barcelona and the Ancient Near East Institute.
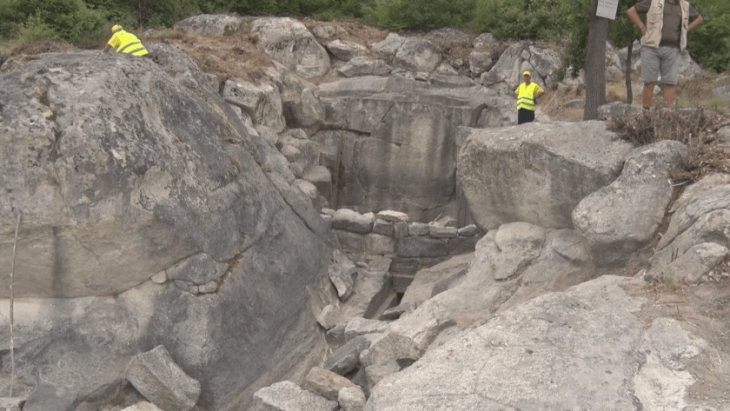
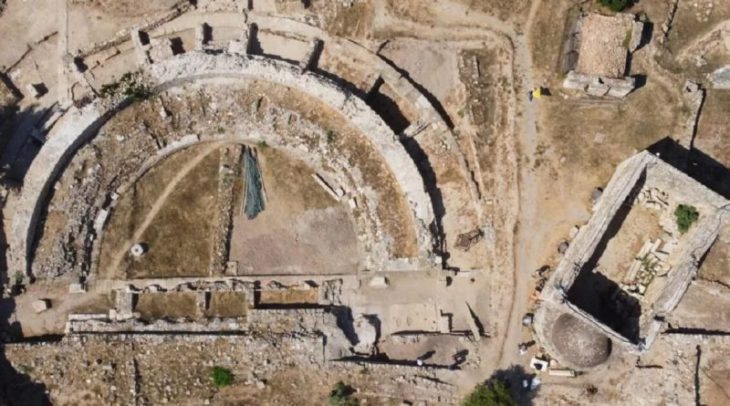
The Supreme Council of Antiquities’ Secretary-General, Dr. Mustafa Waziri, explained that the discovered Roman-era tombs were located in the eastern part of the Upper Cemetery of El-Bahnasa. These tombs feature a new burial style, directly excavated into the natural rock below the ground.
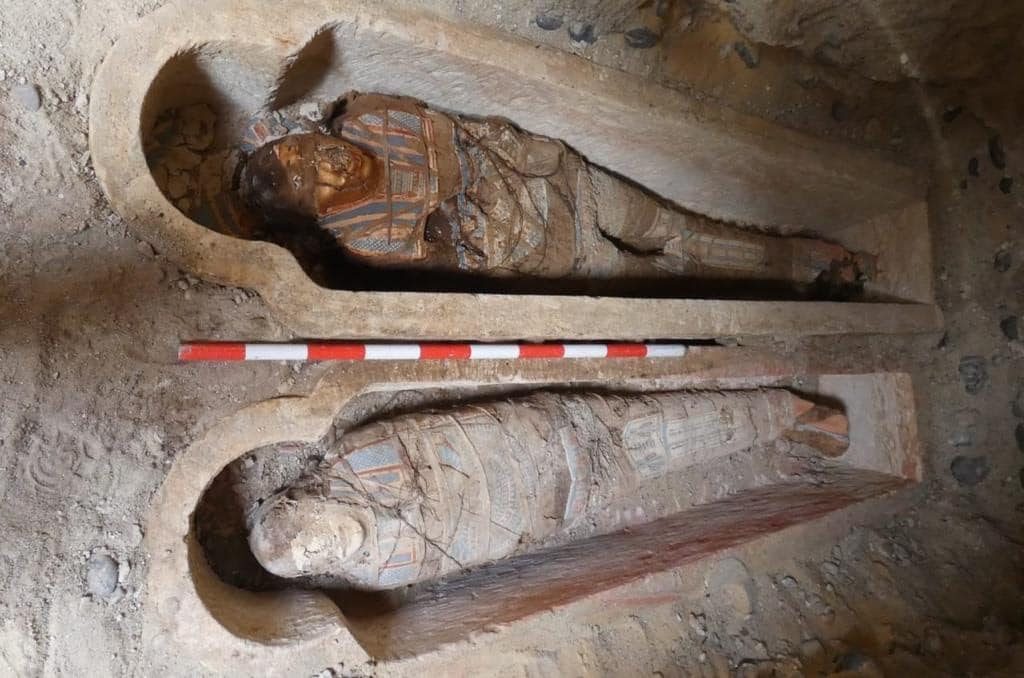

“The new discovery is shedding more light on the rich history of the region, as the team uncovered a series of rock-cut tombs dating back to both the Ptolemaic [305-30 BC] and Roman [30 BC-641 AD] periods, showcasing unique burial practices and artistic expressions of the time,” said Secretary General of the Supreme Council of Antiquities (SCA) Mostafa Waziri.
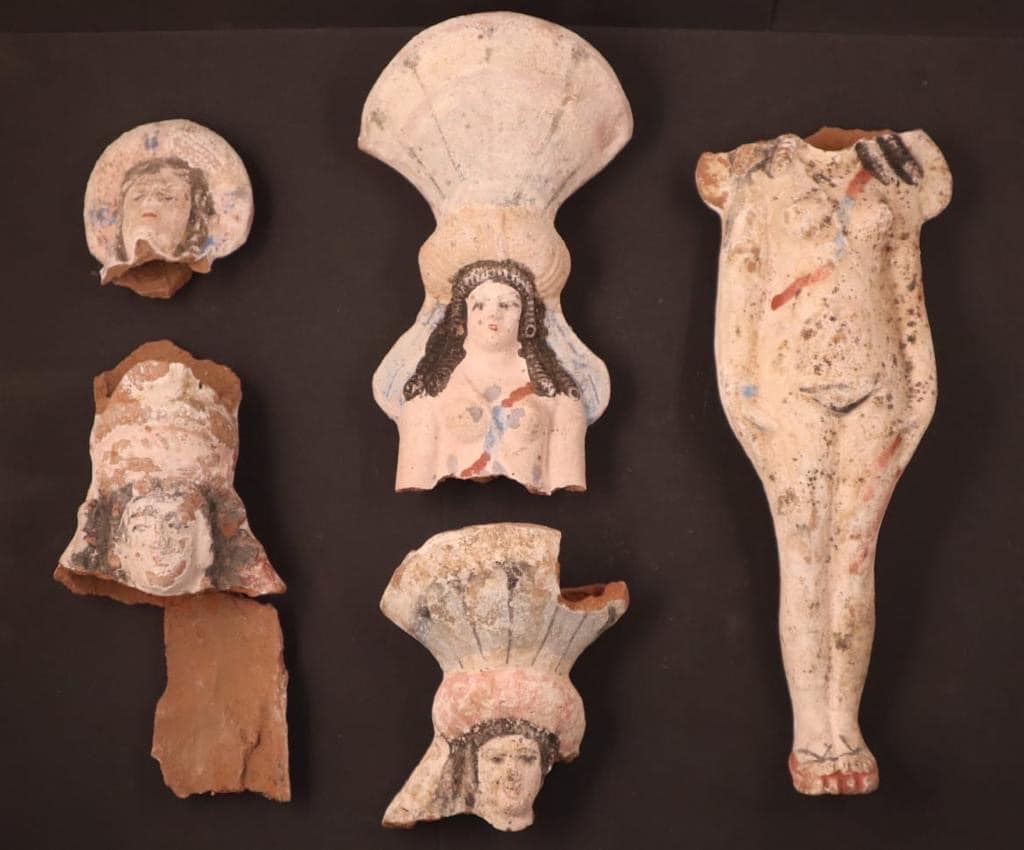
He pointed out that one of the most remarkable findings is the discovery of terracotta statues depicting deity Isis-Aphrodite adorned with foliage crowns, representing a significant addition to the archaeological record.
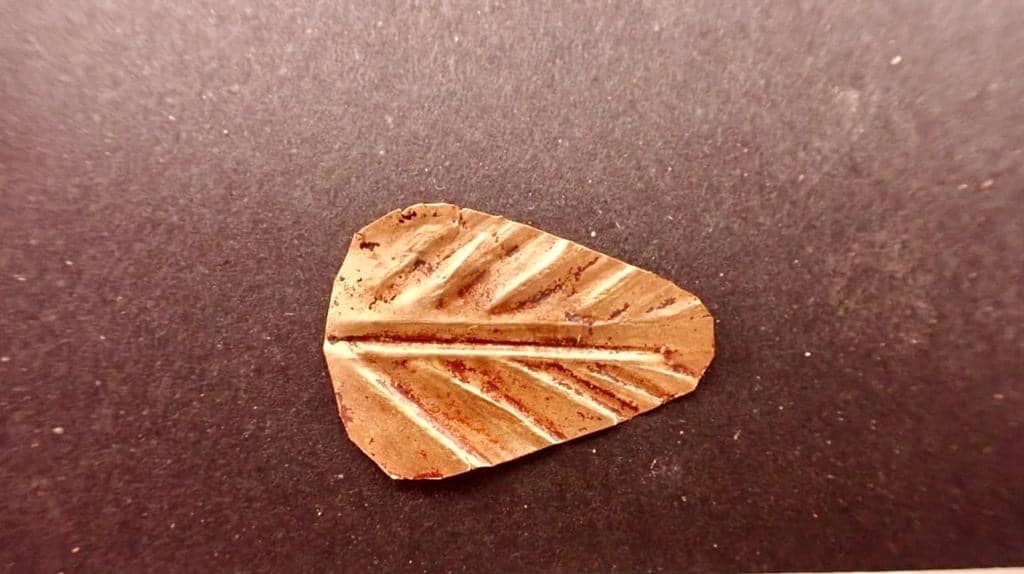

Terracotta figurines representing goddesses such as Isis and Aphrodite with floral crowns were also found for the first time in El-Bahnasa. This suggests that the area still holds many secrets about the funeral rituals of different historical periods.
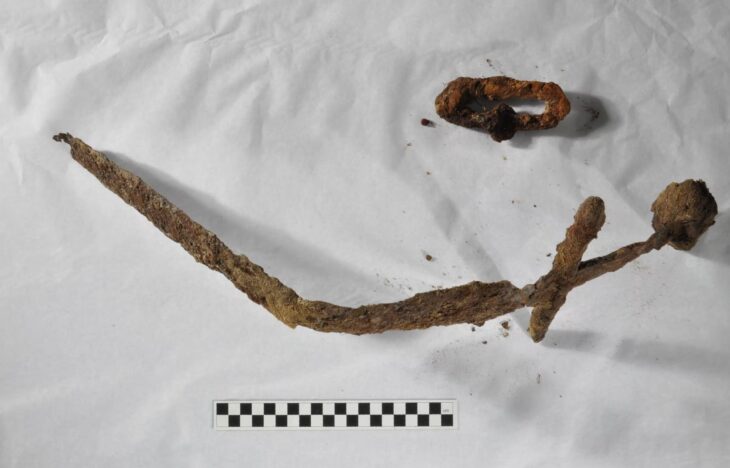
The excavation also revealed Roman-era mummies, some of which were adorned with gilded and colored funeral masks. Inside the mouths of two mummies, golden tongues were discovered, a known funeral practice from the Roman era in El-Bahnasa to preserve the deceased’s ability to speak.
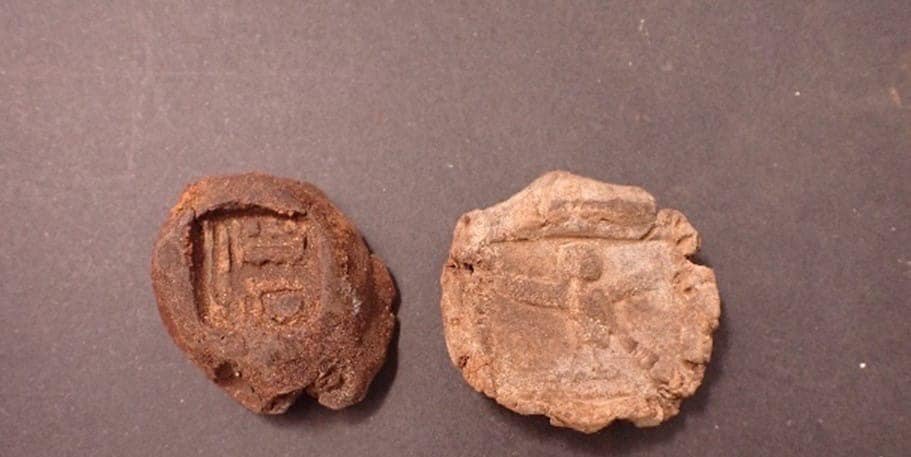

“The team discovered parts of a ruined structure adorned with captivating drawings depicting intricate details of plants, grapevines, and various animals, providing valuable insights into the daily life and cultural significance of Al Bahnasa during ancient times,” explained Adel Okasah, head of the Central Administration Department for Middle Egypt Antiquities.
The mission will continue working at the site in future campaigns to reveal more secrets of Al Bahnasa.
Cover Photo: Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities of Egypt