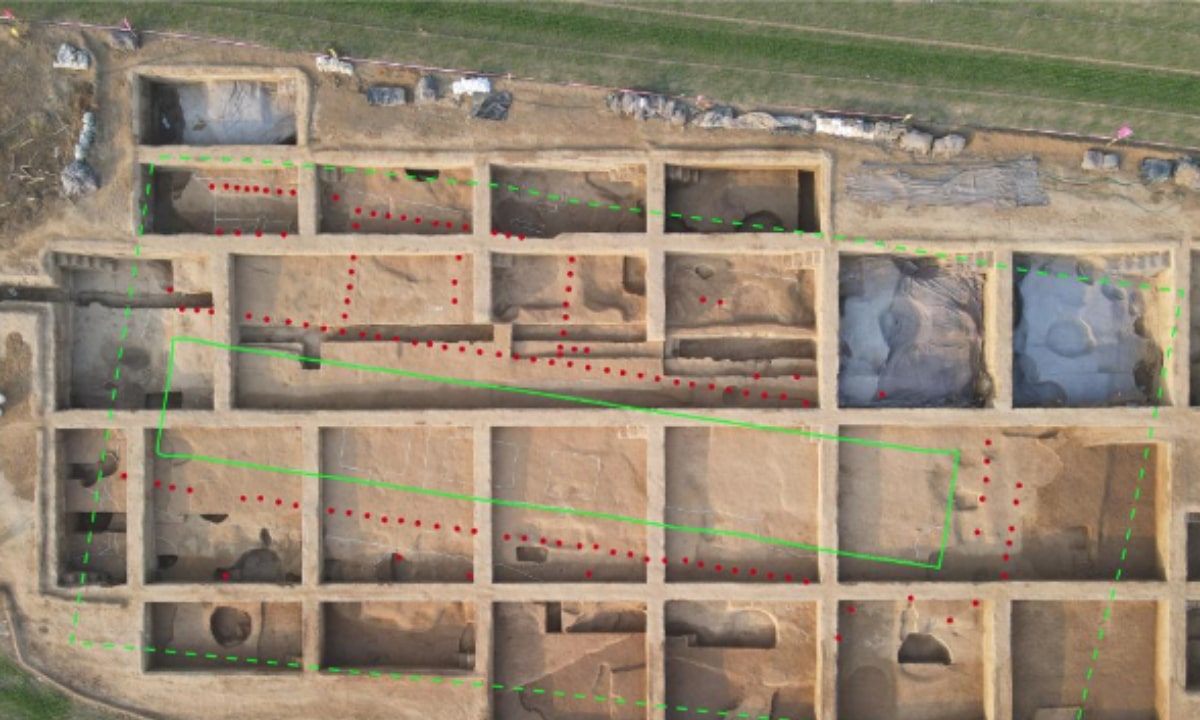
In Xinmi, in the Henan Province of Central China, a four-courtyard style palace complex from the Xia Dynasty (2070BC–1600BC), China’s earliest known dynasty, has been discovered.
The Guchengzhai site, located on a plateau east of the Zhen River in Xinmi, spans a total of over 176,000 square meters, according to state-run news agency Xinhua.
From 2021 to 2023, staff from the Henan Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology conducted systematic surveys and targeted excavations in both the inner and key outer areas of the site, yielding a series of significant achievements.
The two sites, the Zhuqiu Temple site in the city of Zhoukou and the ancient walled city at Xinmi are believed to have been built in the Xia Dynasty (2070 B.C.-1600 B.C.).
The Xia dynasty was the first of many ancient Chinese ruling houses, lasting from around 2070 BCE to 1600 BCE. However, the existence of this dynasty and culture has been disputed. Many scholars regard the Xia dynasty as a semi-mythical period of rule invented by the later Zhou dynasty to justify their overthrow of the Shang dynasty, which is said to have overthrown the Xia dynasty.
The first Xia king, Yu, is said to have repaired the damage caused by a major flood, and this is how he achieved the Mandate of Heaven (divine right to rule). While this was commonly dismissed as a creation myth, excavations by University of Peking archaeologists have found evidence of large-scale floods from around the Xia time period, thus possibly confirming part of the Xia dynastic story.
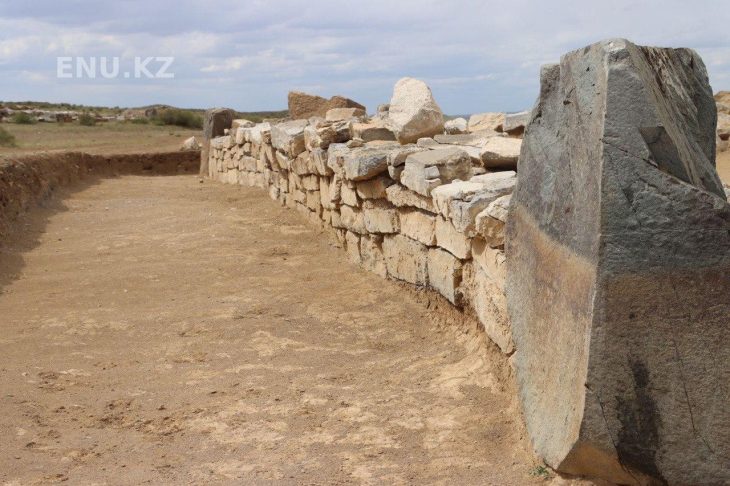
The ancient city is believed to be a large-scale, well-preserved city built in the late period of the Longshan Culture, a civilization found in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River.
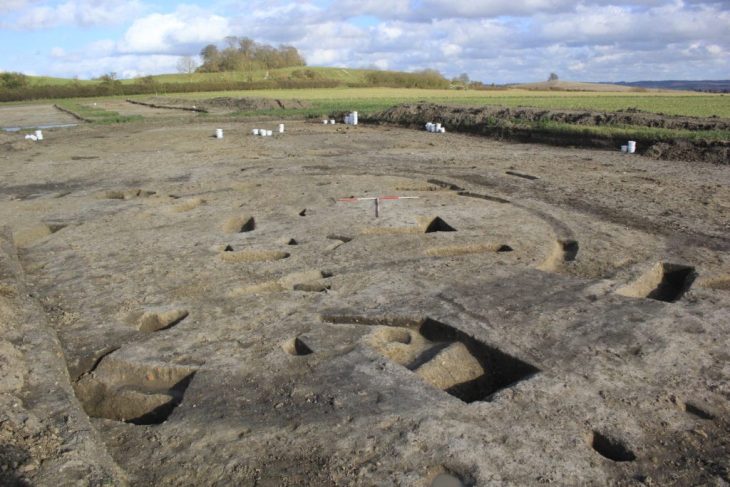
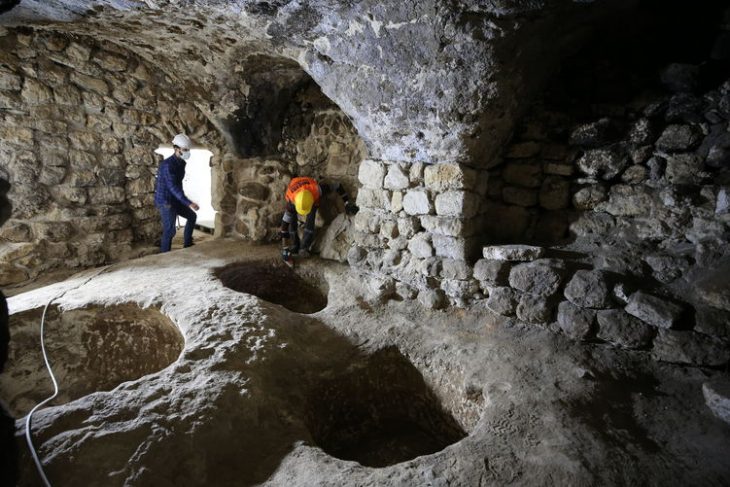
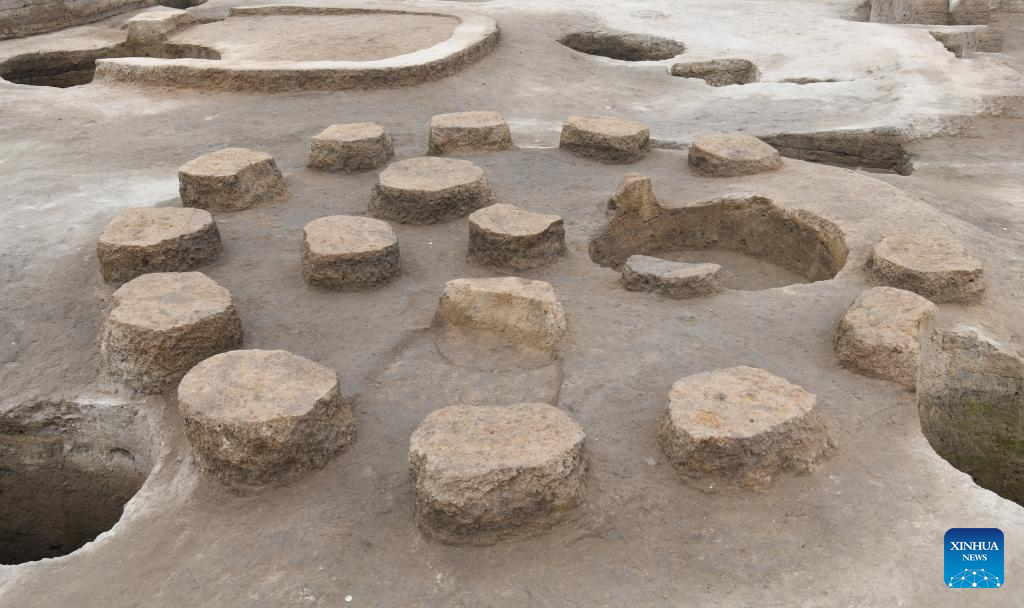
Now, archaeologists working at the site have discovered a rammed-earth foundation structure they believe to be part of the city’s ancient palace compound. The new discovery measures 60 meters long and 30 meters wide, and covers about 1,800 square meters. It is high at the center and low on all four sides, with a flat surface and rows of column holes evenly distributed.
“From the distribution pattern of the column holes, it can be observed that the overall structure of this rammed earth platform is oriented north-south, with rooms arranged in rows, a central courtyard, and corridors on the east and west sides. It has a grand scale and complex structure,” said Li Bo, head of the excavation team.
On the eastern side of the No. 1 rammed-earth platform, archaeologists have also discovered another rammed-earth relic. Currently, part of it has been unveiled, measuring approximately 25 meters in length from north to south and about 10 meters in width from east to west. It is believed to belong to the same architectural complex as the No. 1 rammed-earth platform.
“Considering previous archaeological excavations, the central-eastern area of the Guchengzhai is identified as the core palace zone,” noted Li, adding that “the newly discovered No. 1 rammed earth platform and the rammed earth remains in the eastern part, together with previously found palace foundations and corridor bases, collectively forming a four-courtyard style architectural complex in terms of the overall layout.”

He noted that the new findings could improve people’s understanding about the layout of ancient cities, and provide important evidence for studies of the origin and development of Xia palace buildings.
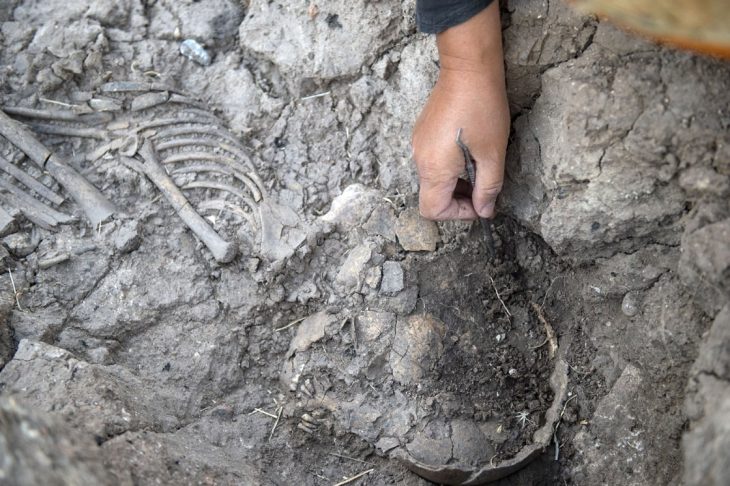
The second discovery took place at the Zhuqiu Temple site. Archaeologists working at the site since 2022 have unearthed more than 100 relics, including the remains of ash pits, ditches, and architecture.
The discovery, according to the excavation team’s leader, Fang Lixia, will offer fresh resources for researching the history of barn construction in ancient northern China, as well as the degree of development of dry farming agriculture and grain storage technology.
Cover Photo: Henan Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology/Xinhua News Agency