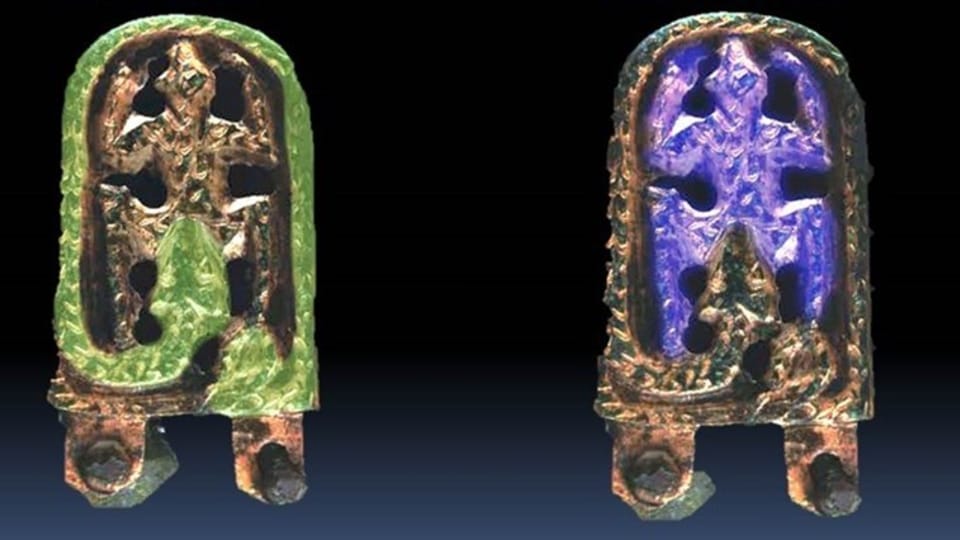
Czech archaeologists have unearthed a bronze belt buckle from the early Middle Ages, depicting a snake devouring a frog-like creature.
Researchers believe that the finding may shed more light on the spiritual life of people in the pre-Christian period, about which little is known.
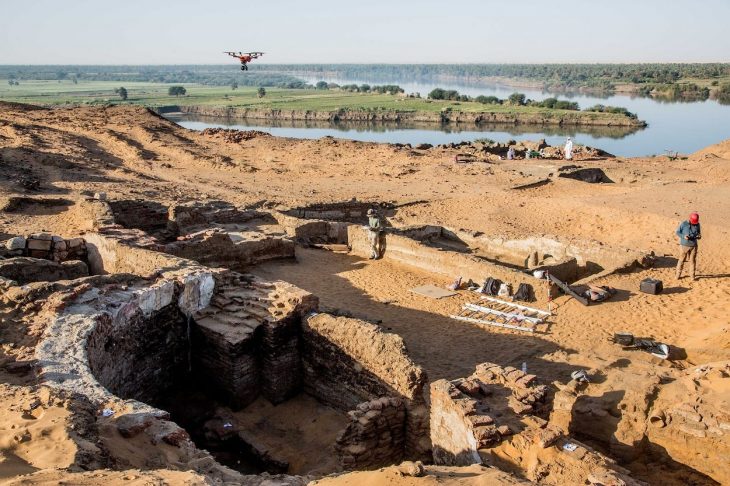
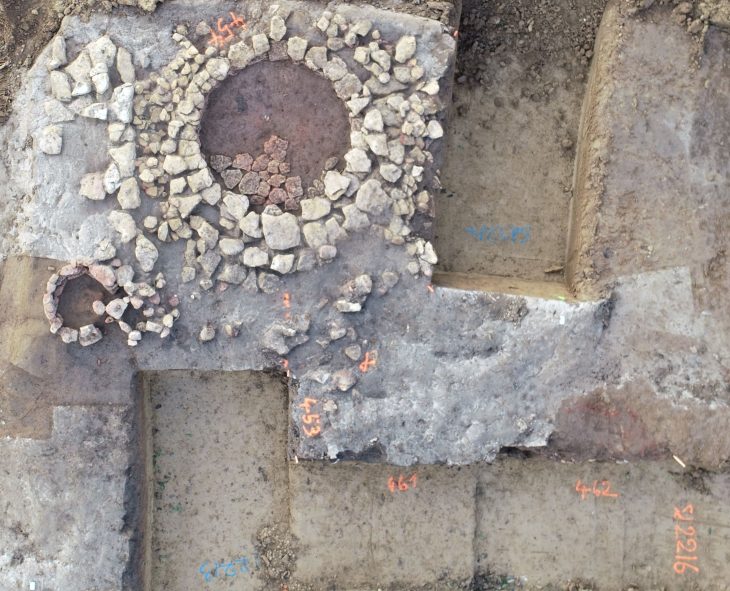
The discovery was made by archaeologists from Masaryk University in Brno, near the town of Břeclav in Southern Moravia, and dates to the eighth century.
Such ornaments were worn by elites in East Central Europe in the early Middle Ages, Jiří Macháček, head of the university’s department of Archeology and Museology, told Radio Prague.
“It was a part of a costume worn by the Avars, the nomadic people settled in the Carpathian basin, in today’s Hungary. However, it was also worn by neighbouring nations or groups of people. It was a very interesting discovery for us because we came across this Avar belt while excavating a settlement of early Slavs” he said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The belt depicts a snake devouring a frog-like creature. This motif which is common for Germanic, Avar as well as Slavic mythology and which is most likely associated with the myth of the world’s creation or the fertility cult. Also, this scene in nature can signify the end of a cycle and the beginning of something new.

Hundreds of kilometers apart, nearly similar belt buckles have already been found in other parts of Central Europe. However, experts believe that this motif played a very crucial role in the religious and spiritual life of the people who lived in this part of the world in the early Middle Ages.
“The problem is that we know very little about the pre-Christian religion among the Germanic people and the Slavic people. We have nearly no written sources about it. We believe that this scene of the fighting snake could be connected with the pre-Christian religion of the people of central Europe. Therefore, such archaeological discoveries could be very important to the discussion about the religion of these people before Christianity.” said Mr. Macháček.
Macháček stated that after the discovery, they established an international team of experts and tried to analyze the five samples they had.
“Using very special methods, they try to identify the origin of such ornaments, for example by lead isotope analysis or scanning electron microscopy. This way, we may be able to say if they were perhaps produced in the same workshop and then distributed all over central Europe,” he said.
Cover Photo: Masaryk University Brno