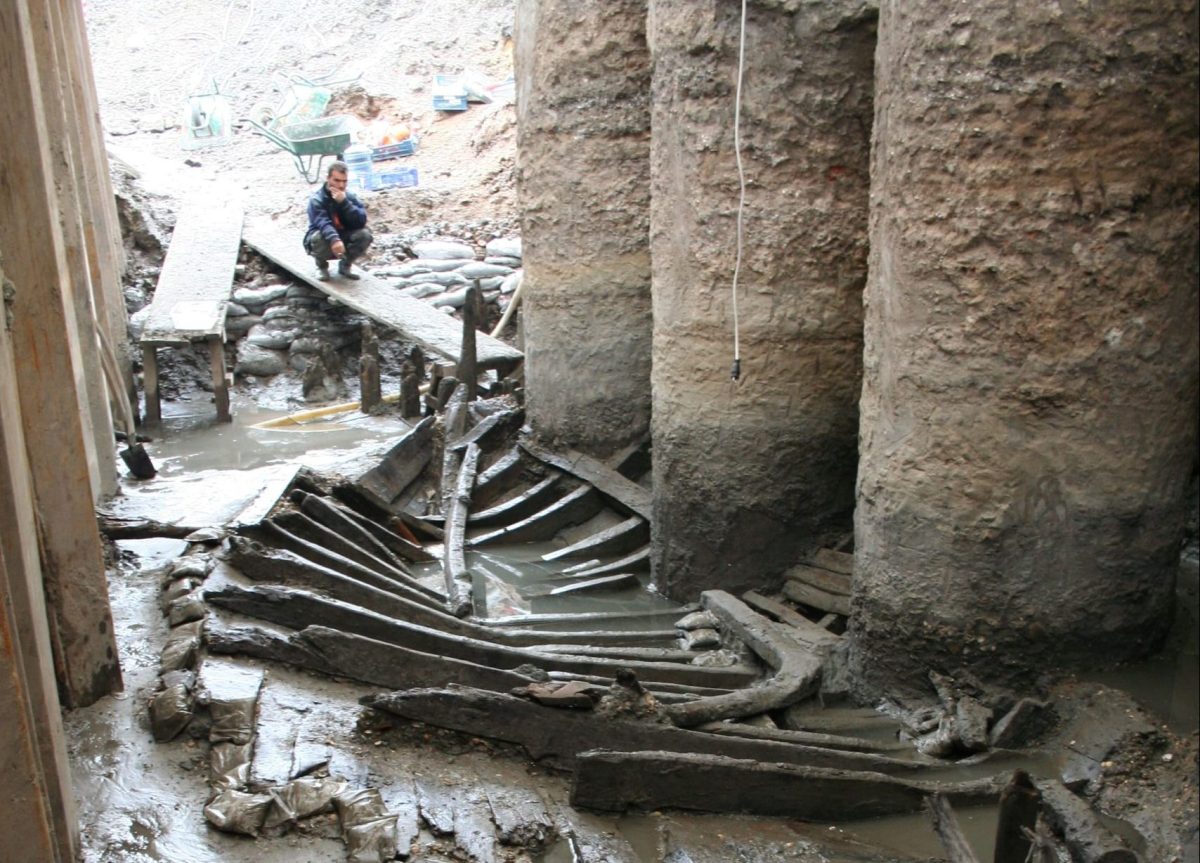
The conservation process of the Yenikapı shipwrecks, which were discovered during the Marmaray project and considered the largest collection of ancient ships in the world, was stopped due to the lack of a museum and warehouse.
During the construction of a new subterranean rail line linking Europe and Asia, hundreds of laborers and archaeologists of the Istanbul Archaeological Museums exposed remains of over 8,000 years of the city’s history, ranging from Neolithic dwelling foundations and burials to Ottoman cisterns and workshops.
The Yenikapı site, located in the Istanbul neighborhood of the same name, witnessed one of the world’s largest archaeological digs between 2004 and 2013. After the excavations finished in 2013, a conservation process started, which has been going on for 10 years.
Thanks to the waterlogged anaerobic sediments that filled the harbor at Yenikapı, many artifacts were recovered, including pottery, bone, glass, coins, and other metalwork, as well as organic objects such as wood, rope, and leather that were well preserved. In addition to hundreds of anchors and other items of ship’s equipment, archaeologists also uncovered 37 exceptionally well-preserved shipwrecks of 5th- to late 10th- or early 11th-century AD date.
However, a museum has not been established since that period so that these works can be exhibited.
Stating that the Theodosius Harbor is the largest medieval ship collection in the world, Istanbul University’s Professor Ufuk Kocabaş said that thousands of archaeological artifacts await a museum.

“Istanbul has great potential in terms of underwater archeology. The city has the world’s largest repertoire of medieval sunken ships. This collection is not yet on display at a museum. But now the time has come. A museum where the artifacts from Yenikapı shipwrecks will be exhibited will attract millions of tourists to Istanbul and will bring this heritage to the fore,” he said.
Reminding that in 2010, when Istanbul became the world capital, a project had been designated to establish a museum in the region where Yenikapı Marmaray and metro stations are located, Kocabaş said: “ Kadir Topbaş, the mayor at that time, organized an international competition for the museum station project. Various projects were delivered in this competition, and as a result, a project was chosen to establish a museum in the area where Marmaray and metro stations are located in Yenikapı. After the completion of the process, tenders were expected to be held in 2015 for implementation. Unfortunately, a museum has not been established since then. I don’t see any preparation at the moment, too. Tens of thousands of Istanbul residents travel every day in a historical texture.”
Speaking to Demirören News Agency, Kocabaş said that the conservation process of the artifacts requires a long procedure due to a large number of shipwrecks.
“There are many water-absorbed wood in the shipwrecks. These have absorbed water into their tissues and are degraded. In this process, chemical substances need to be slowly absorbed into these artifacts. We also use advanced technological devices to dry the works. These procedures continue because the number of wrecks is too many, and it is a long procedure. But the realization of the museum project will pave the way for us. Since a museum or a very good warehouse has not been established, we cannot move on to new shipwrecks. In this sense, there is a break in our workflow. A museum must be established in order to preserve the artifacts,” he said.
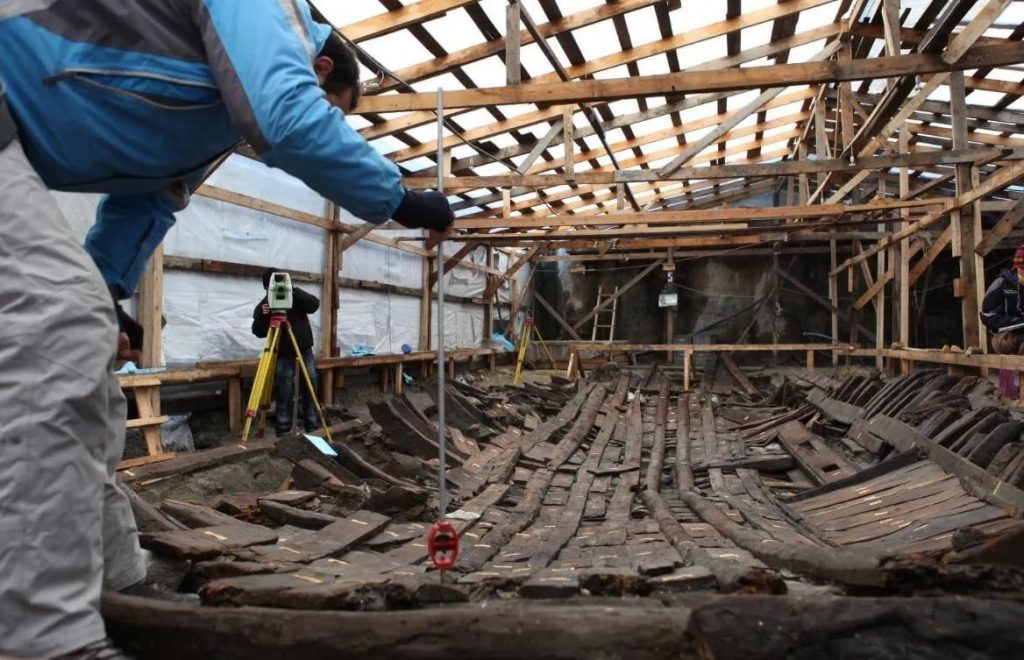
Cover Photo: Seventh-century shipwreck YK 11 prior to dismantling. Photo: INA, Yenikapi 2019