An analysis of DNA from 12th-century human remains has provided new insights into a significant historical crime and into Ashkenazi Jewish population history, reports a new study co-led by a UCL researcher.
Investigations of 17 individuals found in a medieval well suggest they were likely the victims of an antisemitic hate crime.
The study, published in Current Biology, involving work with historians, archaeologists, and the local Jewish community, also overturns the previously-held view that disease-related variants associated with Ashkenazi Jewish populations only became more common in the last 600 years.
In 2004, construction workers digging in advance of the Chapelfield shopping center development in Norwich, UK, uncovered a medieval well containing the remains of at least 17 people, most of whom were children. Scientists from the Natural History Museum, UCL, Mainz and Cambridge Universities, and the Francis Crick Institute, conducted analysis on the remains of six of these individuals, uncovering new genetic, medical, and historic information. The whole genome analyses reveal the individuals appear to be a group of Ashkenazi Jews who fell victim to antisemitic violence during the 12th century.
The remains of at least six adults and 11 children were recovered from the unusual burial location. Unlike other mass burial sites, where bodies are typically laid in an organized fashion, skeletons from the well were oddly positioned and mixed, likely caused by being deposited head-first shortly after death. These findings hint at mass fatalities such as famine, disease, or murder. Radiocarbon dating of the remains placed their deaths around the late 12th to early 13th century — a period which includes some well-documented outbreaks of antisemitic violence in England — leading researchers to consider foul play. A specific antisemitic riot in 1190 CE was recorded by the chronicler Ralph de Diceto in his Imagines Historiarum II:
“Many of those who were hastening to Jerusalem determined first to rise against the Jews before they invaded the Saracens. Accordingly on 6th February [in 1190 AD] all the Jews who were found in their own houses at Norwich were butchered; some had taken refuge in the castle.”
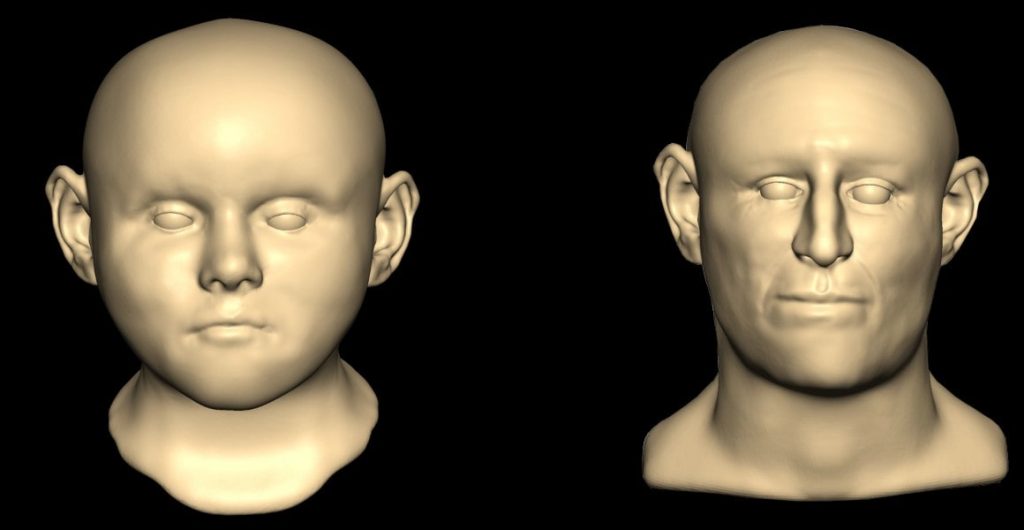

To piece together the individual’s past life and what led to their death, the team studied these remains at the time of their excavation, and with developments in DNA sequencing technology, were able to sequence whole genomes from six of these individuals.
Co-lead author Professor Mark Thomas (UCL Genetics, Evolution & Environment) said: “It was quite surprising that the initially unidentified remains filled the historical gap about when certain Jewish communities first formed, and the origins of some genetic disorders.
“Nobody had analysed Jewish ancient DNA before because of prohibitions on the disturbance of Jewish graves. However, we did not know they were likely Jewish until after doing the genetic analyses.”
Judaism is primarily a shared religious and cultural identity, but present-day Ashkenazi Jewish groups often carry genetic ancestries which reflect their distinctive diasporic population histories and endogamous marriage practices. The results showed that the individuals from the well shared similar diasporic genetic ancestries and were therefore almost certainly Ashkenazi Jews.
Among these burials, four were closely related, including three full-sibling sisters — a 5 to 10-year-old, a 10 to 15-year-old and a young adult. DNA analysis also allowed the researchers to infer physical traits for a 0 to 3-year-old boy. Their results suggested blue eyes and red hair, the latter a feature associated with historical stereotypes of European Jews.

The researchers also found that they carried markers associated with some genetic disorders for which modern day Ashkenazi Jewish populations are at higher risk. Genetic disorders that are particularly common in certain populations can arise during bottleneck events, where a rapid reduction of the population size can lead to big jumps in the number of people carrying otherwise rare genetic mutations.
It is generally thought that bottlenecks responsible for shaping the genetic diversity of modern-day Ashkenazi Jewish populations — including increasing the frequencies of certain genetic disease mutations — happened around 500 to 700 years ago. However, using computer simulations, the team showed that the number of such disease mutations observed in the 12th century individuals was very similar to what they would expect if these diseases were as common then as they are today. The results point to a significant bottleneck event that prior to the 12th century, earlier than generally thought.
Co-lead author Professor Ian Barnes (Natural History Museum) said: “When you study ancient DNA from people who’ve died several hundreds to thousands of years ago, you don’t often get to work with the living community at the same time.
“It’s been really satisfying to work with the community on a story that’s important to them.”
Co-lead author Dr. Selina Brace (Natural History Museum) said: “I’m delighted and relieved that twelve years after we first started analysing the remains of these individuals, technology has caught up and helped us to understand this historical cold case of who these people were and why we think they were murdered.”
Co-author Dr. Tom Booth (Francis Crick Institute) said: “Our study shows how effective archaeology, and particularly new scientific techniques such as ancient DNA, can be in providing new perspectives on historical events.
“Ralph de Diceto’s account of the 1190 AD attacks is evocative, but a deep well containing the bodies of Jewish men, women, and especially children forces us to confront the real horror of what happened.”
Cover Photo: Ashkenazi Jews by Maurycy Gottlieb, 1878