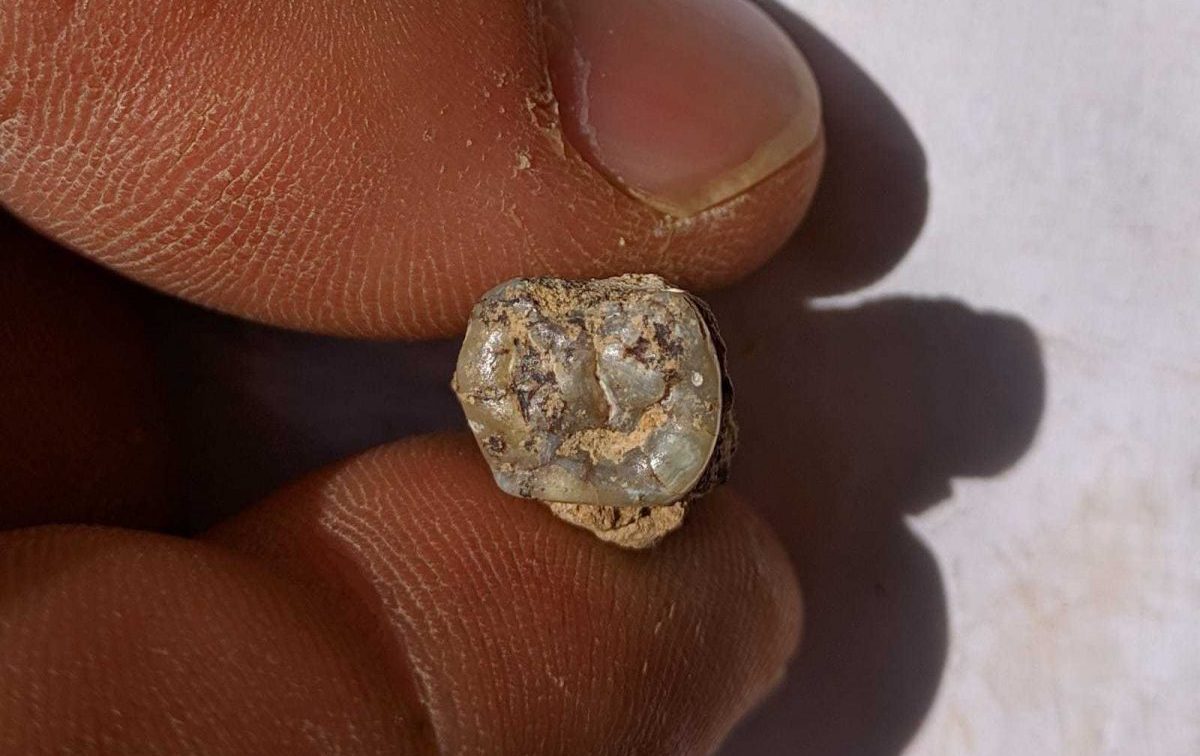
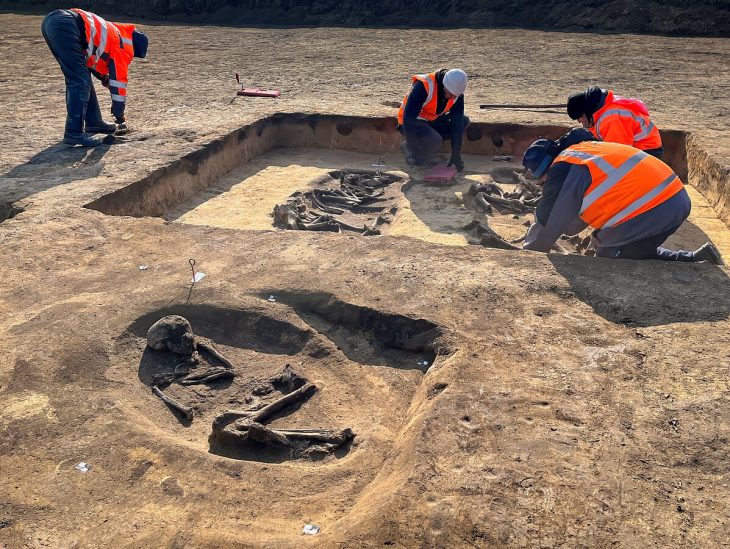
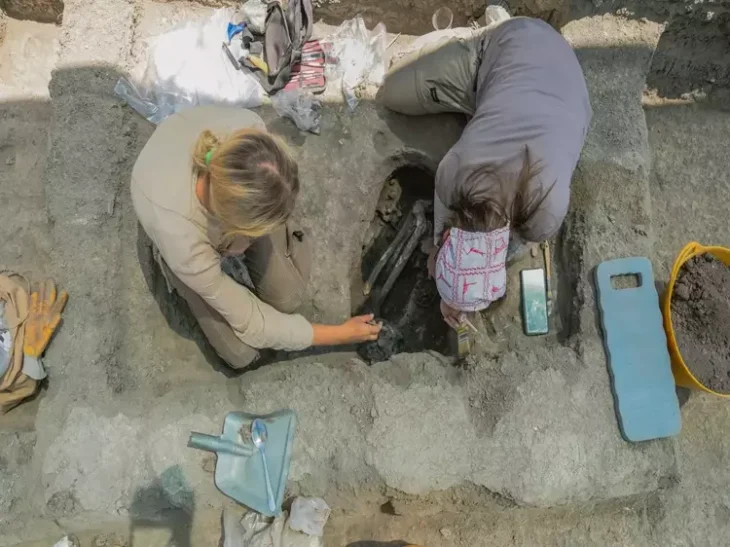
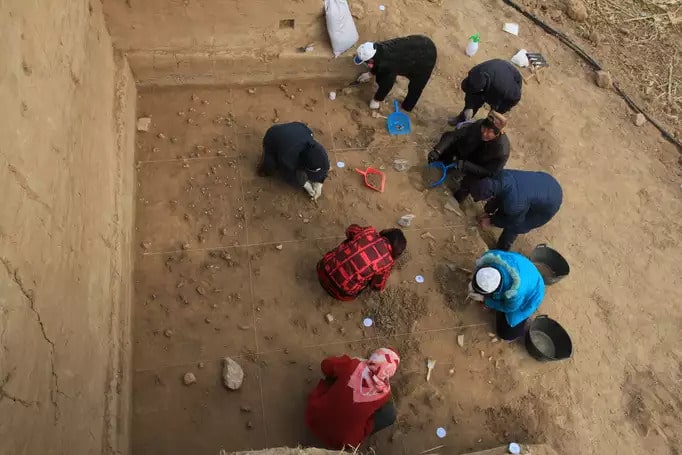
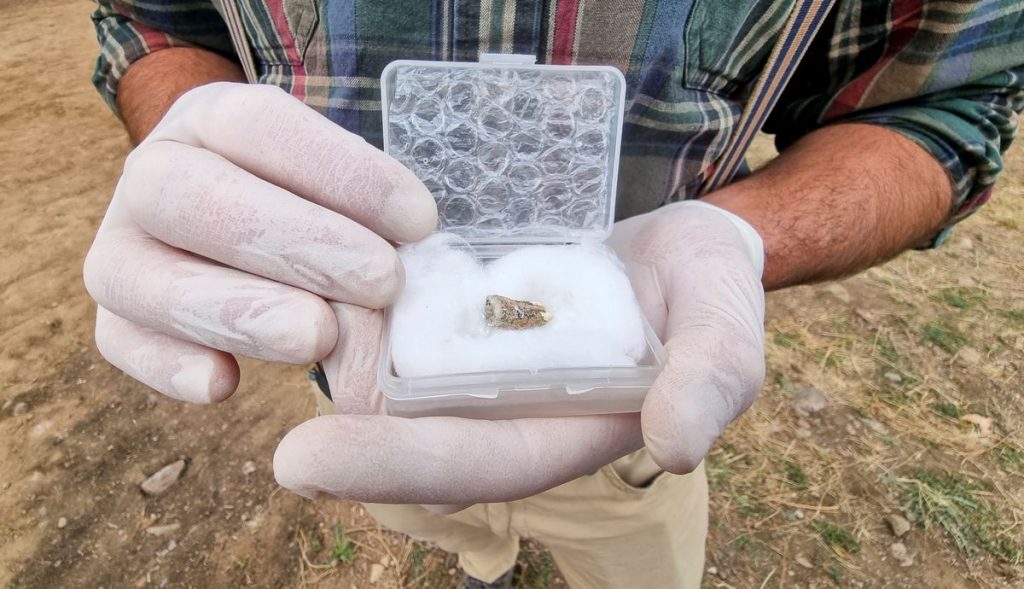
An ancient human tooth discovered by archaeologists in Georgia dates back 1.8 million years, firmly establishing the area as the site of one of the earliest prehistoric human settlements in Europe and possibly the world outside of Africa.
A 1.8-million-year-old jaw tooth and fourth premolar tooth belonging to an early human species were found in Kvemo Orozmani, a village in the Dmanisi Municipality of Kvemo Kartli region of Georgia.
The tooth was found near the village of Kvemo Orozmani, where human skulls dating back 1.8 million years were discovered in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
These finds were the world’s oldest such discovery outside of Africa, and they altered scientists’ understanding of early human evolution and migration patterns.
Experts say the latest discovery at a site 20 kilometers away provides further evidence that the mountains of the South Caucasus may have been one of the first places early humans settled after migrating from Africa.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
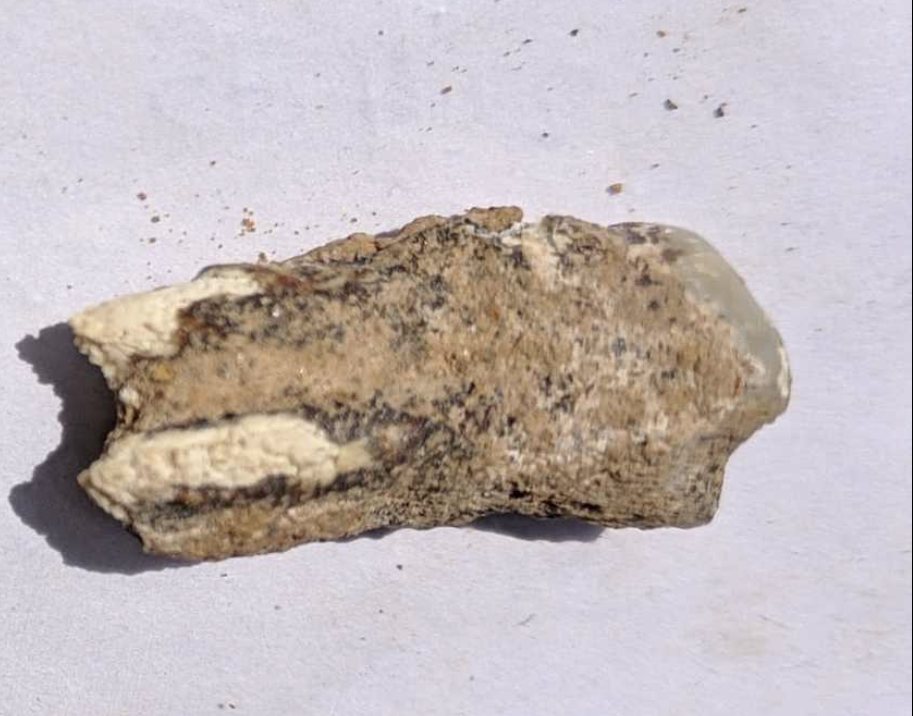

The tooth was discovered on Thursday, according to the National Research Centre of Archaeology and Prehistory of Georgia. In the statement, “Orozmani, together with Dmanisi, represents the center of the oldest distribution of old humans – or early Homo – in the world outside Africa,” it was said.
Giorgi Bidzinashvili, the scientific leader of the dig team, said, “This discovery is the most important thing that could happen at an archaeological site – we found a direct human remains in the form of the fourth premolar of the lower jaw. At first glance, he looks like an adult individual. and gender etc. it is difficult to determine, but together with paleoanthropologists, we can say with certainty that this is indeed an archaic human mandibular tooth. Most likely Homo erectus. However, anthropological research will make this certain for us”.
Giorgi Bidzinashvili, moreover considers the tooth belonged to a “cousin” of Zezva and Mzia, the names given to two near-complete 1.8-million-year-old fossilized skulls found at Dmanisi.

A partial jaw discovered in modern-day Ethiopia is the world’s oldest Homo fossil, dating back around 2.8 million years.
Homo erectus, a hunter-gatherer species thought to be the ancestor of modern humans, is thought to have left Africa about two million years ago. Although 2.1 million-year-old tools have been found in modern-day China, the oldest early human remains ever discovered outside of Africa were found at the Georgian sites.