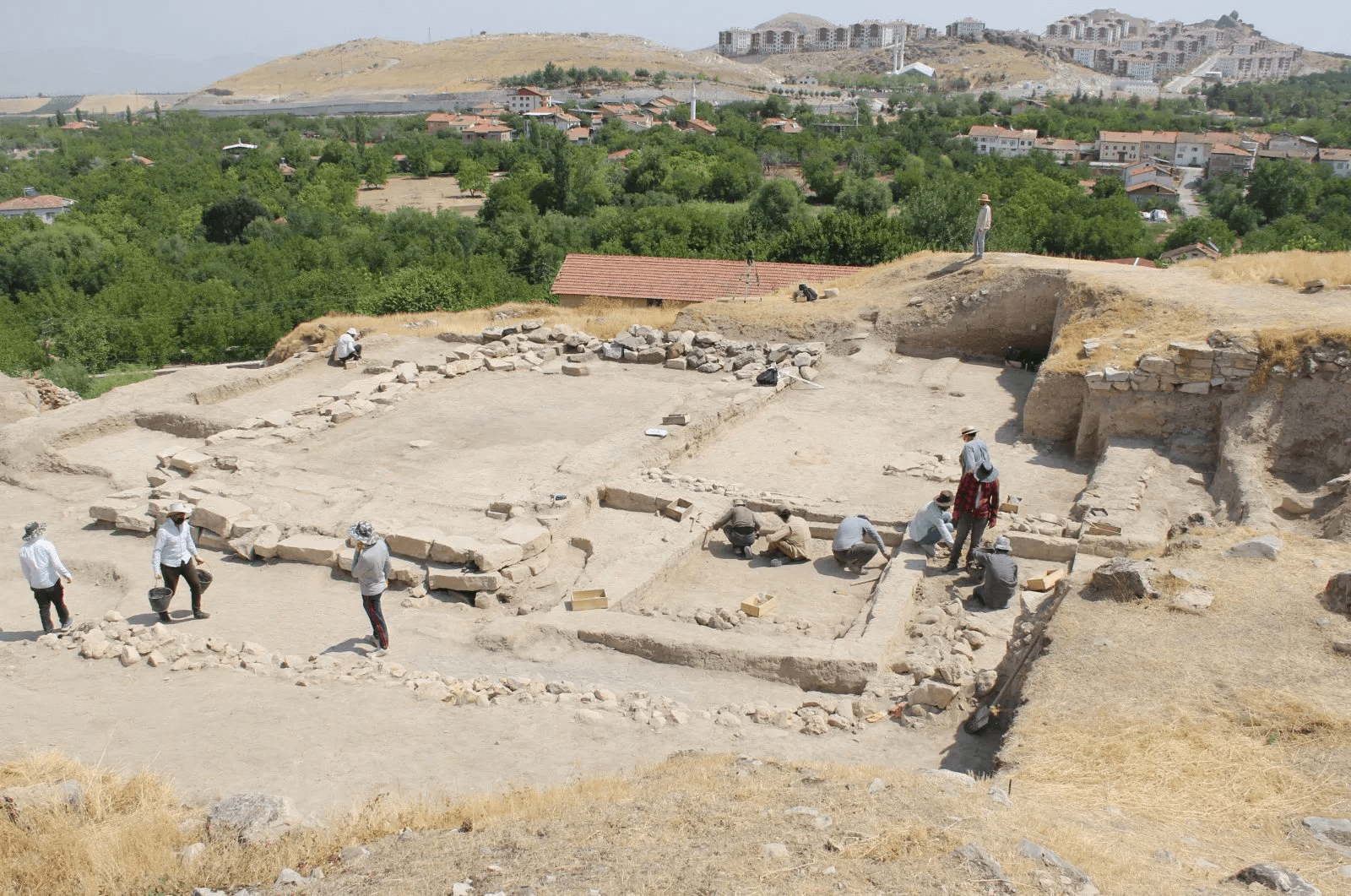
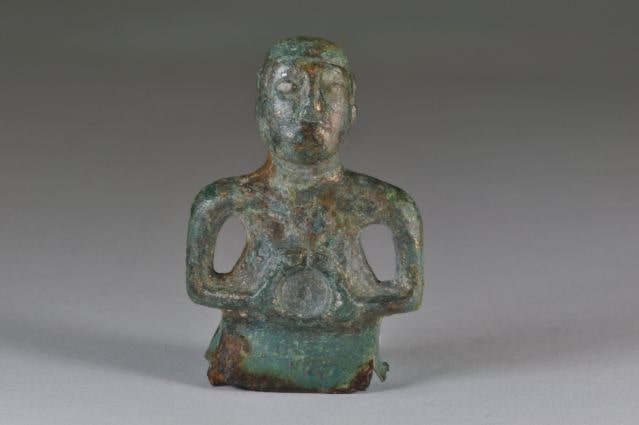
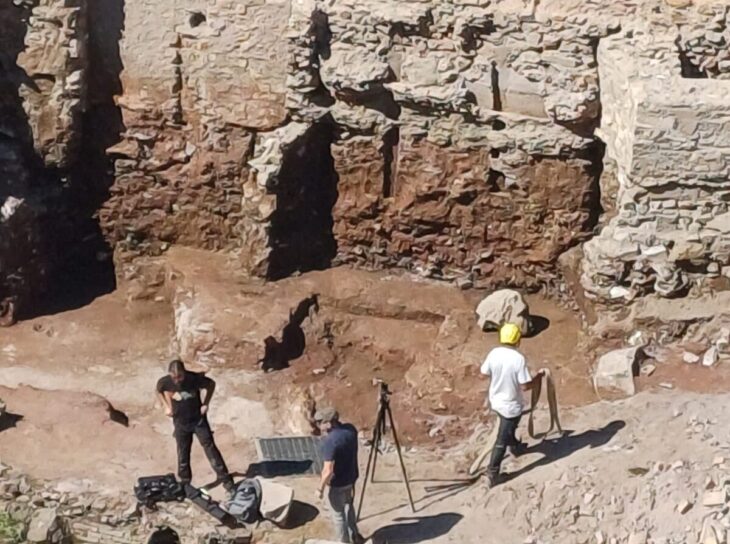
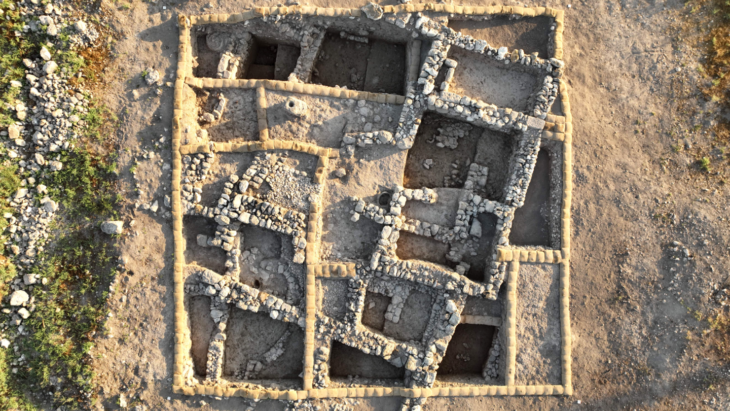
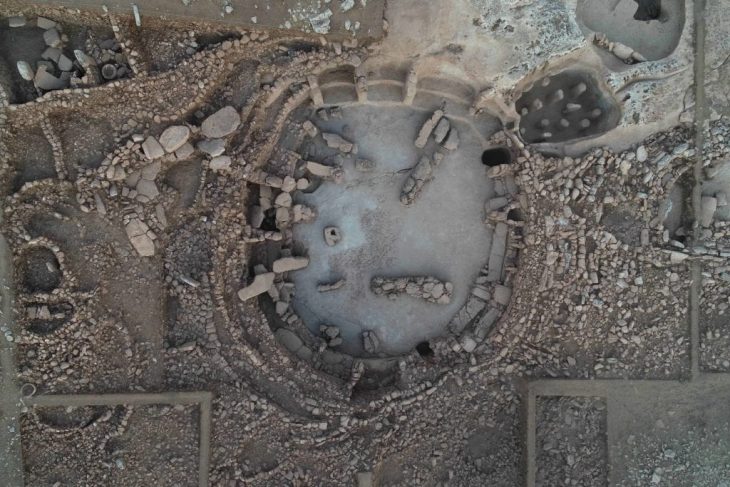
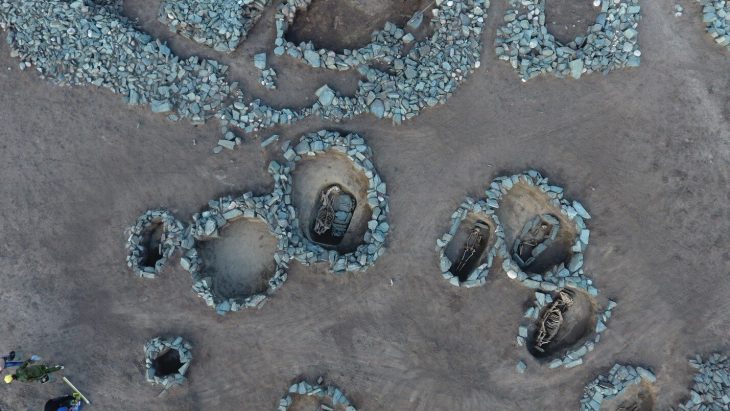
Archaeologists working at the Arslantepe Mound (Turkish: Arslantepe Höyük), a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Türkiye’s eastern Malatya province and thought to be the first city-state in Anatolia, have found two 7,000-year-old animal-figured seals.
Arslantepe, a 30 m high mound located around 7 km east of Malatya, is home to remains found in layers dating from 5000 BC to the 11th century.
In particular, the discoveries made in the layers that date back to 3000 BC revealed the first indications of how humanity evolved into a sophisticated social structure and established a state before the invention of written documents. Arslantepe was an administrative and commercial hub, as evidenced by the palace structure and numerous seals discovered there that date to 3300–3000 BC. Furthermore, Arslantepe, whose oldest settlement dates back to the Chalcolithic Era, is home to the world’s first known swords. The city was known then as Malitiya, according to Hittite sources. Arslantepe is thought to be the first city-state in Anatolia.
Inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2021.
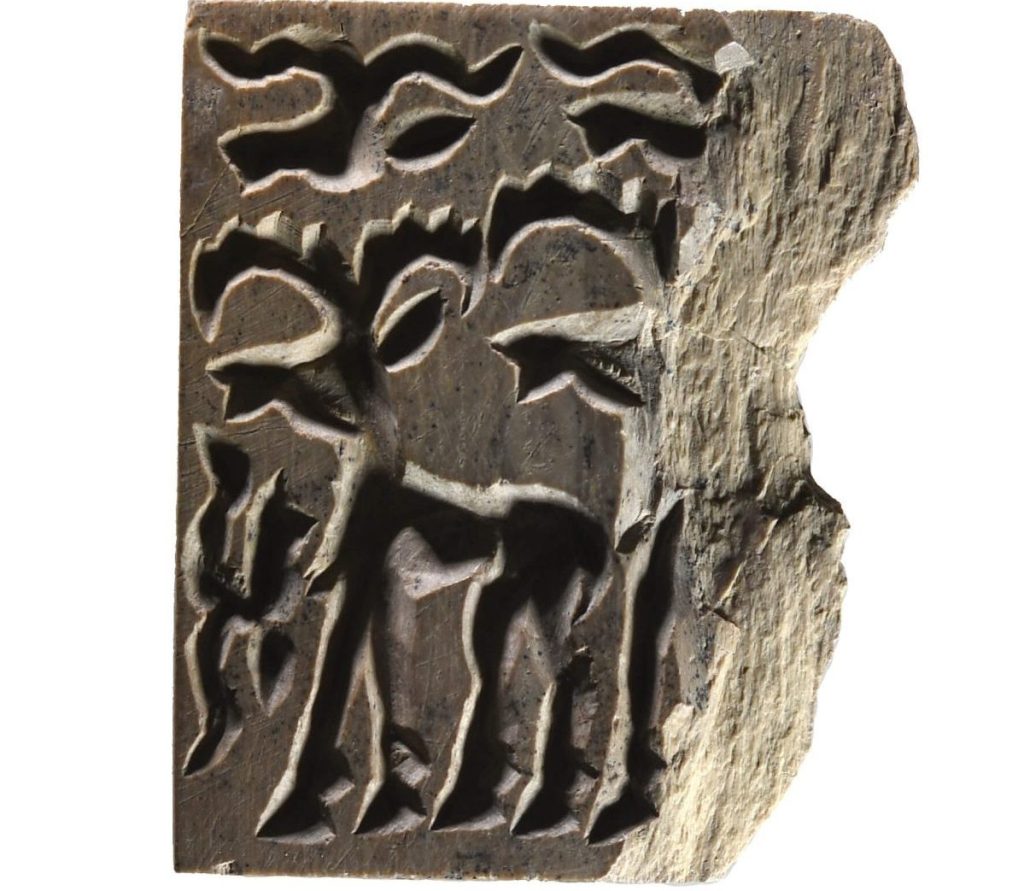

Italian Professor Francesca Balossi Restelli, the head of the excavation team, says the seals might date back an even earlier.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Restelli told Anadolu Agency that they compared the styles of the seals in other regions to determine the date from their motifs.
“When we look at the style, I think that the date of these seals will be older, 5,000 BC,” Restelli said.
Noting that animal figures were carved on the seals, she said they are the oldest seals found so far at Arslantepe.
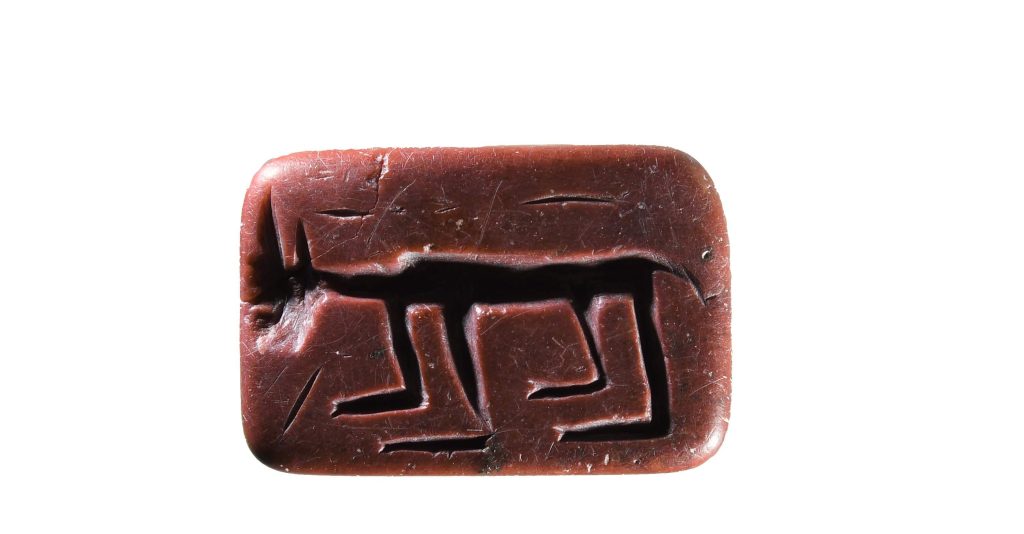

“There are definitely older ones because there are layers 10 meters (32 feet) below the hill. I am sure we will find older seals as we descend,” she added.
More than 2,000 stamp seals have been found in the mound so far. The site was occupied at least since the sixth millennium BCE, according to archaeological evidence, and continued until the late Roman era.