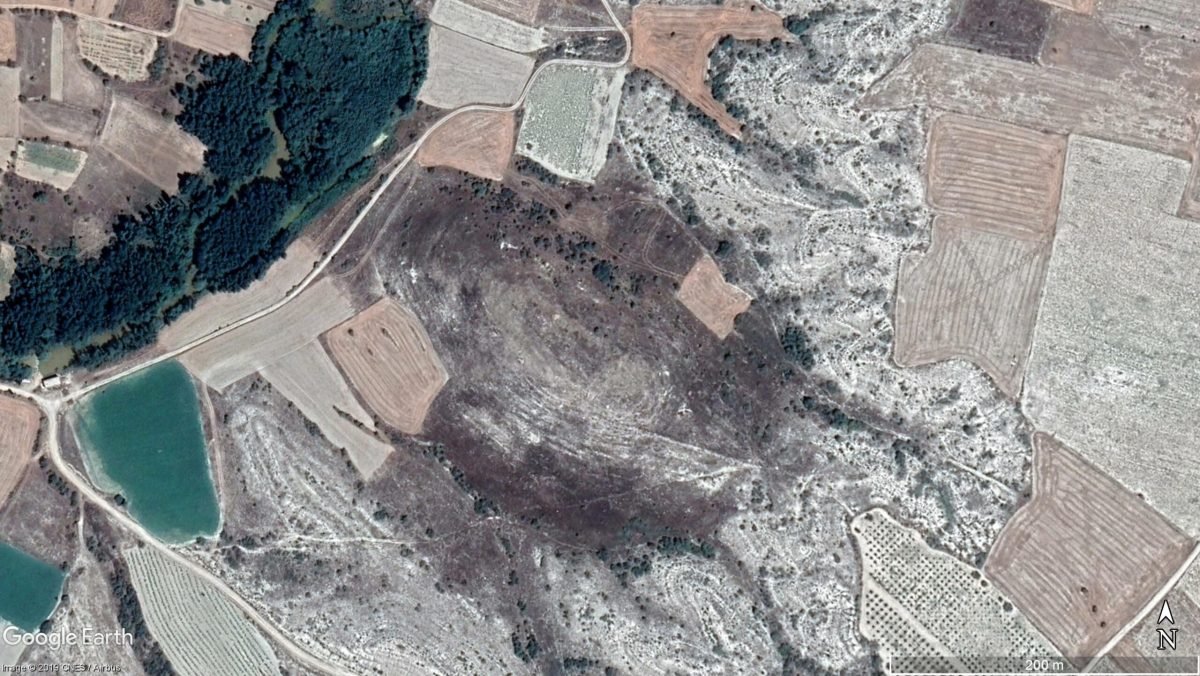
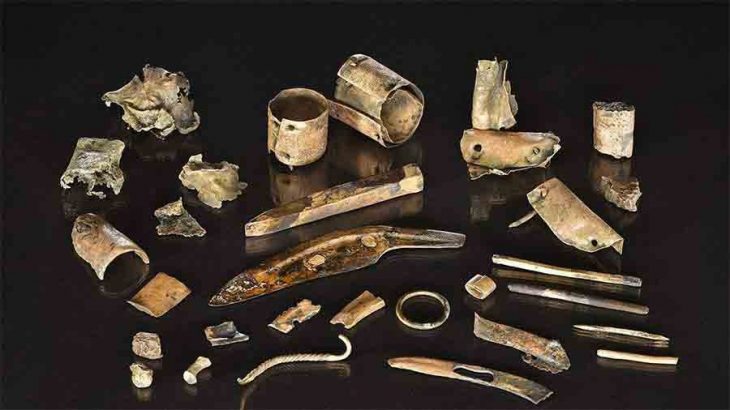
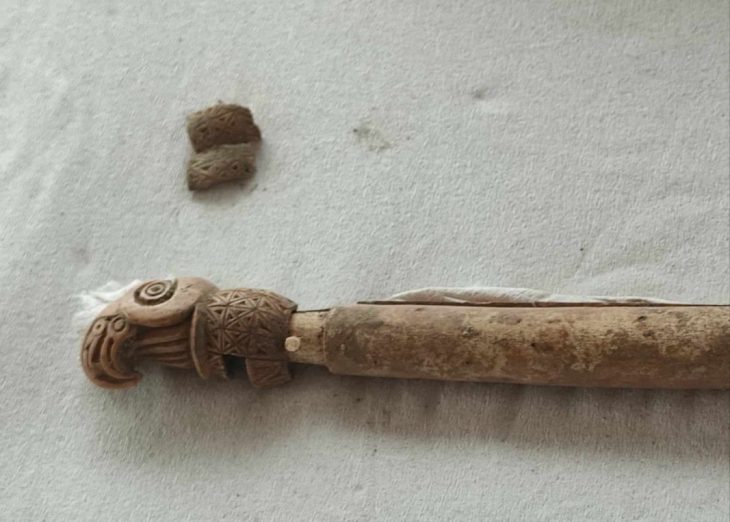
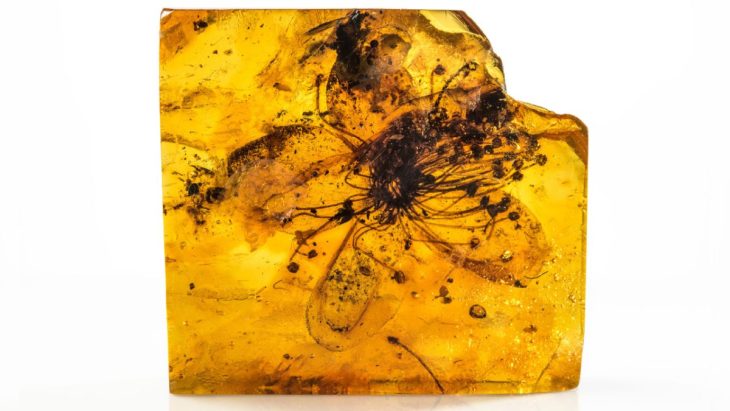
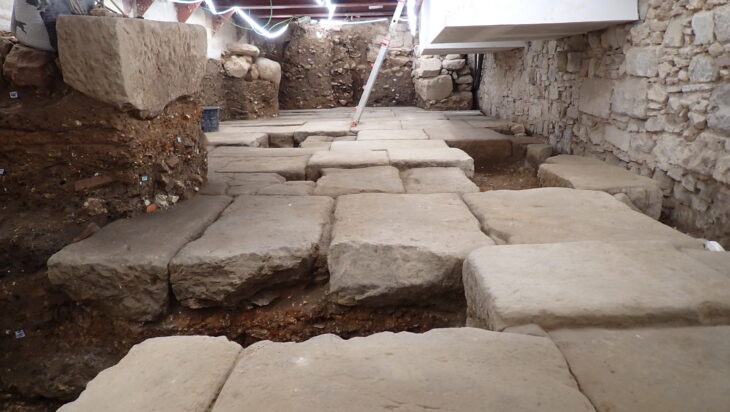
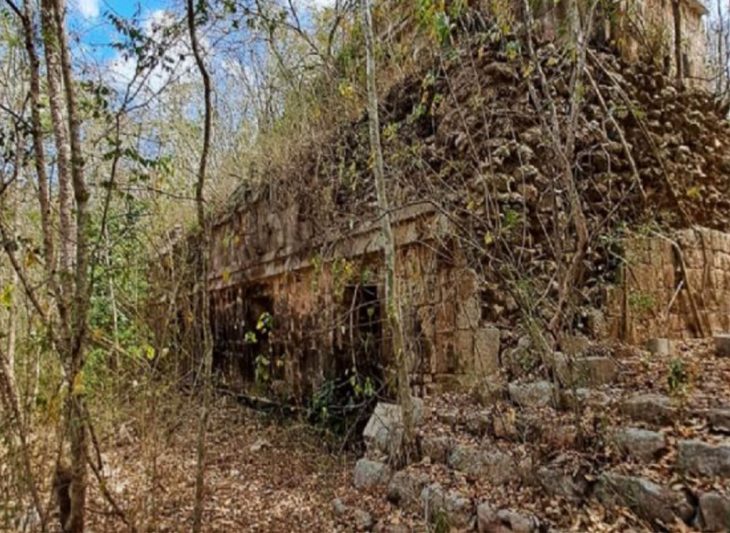
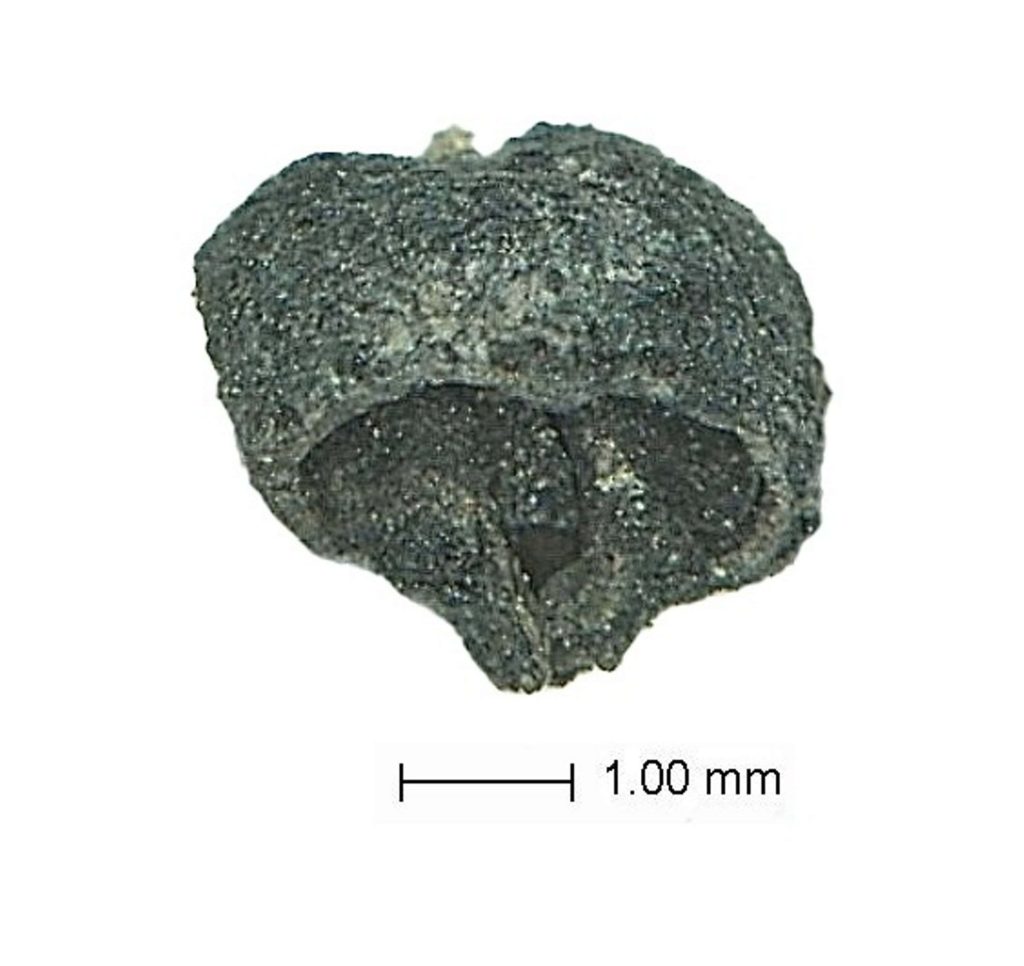
Archaeologists at the Aşağıseyit Höyük (Aşağıseyit Mound) site in western Anatolia’s Denizli have uncovered a 3,500-year-old grape seed.
Aşağıseyi Höyük Settlement is located within the boundary of Çal district of Denizli Province. It was strategically located on a natural passage and an important center surrounded by walls during the 2nd millennium BC.
Surveys conducted in the Upper Menderes Basin have revealed that the mountainous and plateau areas are at least as densely settled as in lowland sections and these areas have significant importance in archaeological point of view.
Led by associate professor Erim Konakçı from the Department of Archaeology at Izmir Democracy University, the team has been working on the excavation project.
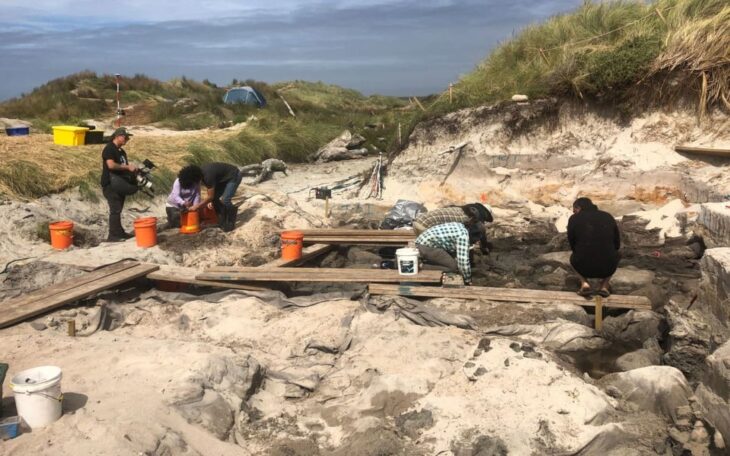
Among the finds reached by the excavation team this year, the remains of grape seeds dating back 3,500 years stand out.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The significance of the discoveries made during the excavation was highlighted, and Konakçı noted: “We have reached layers dating back to as early as 1600 B.C. Surface surveys have already indicated that the history of this mound extends back to the late Chalcolithic period. Furthermore, we are aware of the existence of settlements during both the early and late Bronze Ages. We anticipate further exploration in the coming years to delve into these layers.”
Konakçı also revealed that during the excavation, they had identified two phases dating to the Late Bronze Age, between the 12th and 16th centuries B.C., and discovered structures, hearths and ovens from these periods. These findings have been evaluated by archaeozoologists and archaeobotanists.
Regarding the plant species and seed types used during both the Hellenistic and Late Bronze Ages in the region, Konakçı stated: “We have acquired data suggesting the consumption of barley and wheat. A single grape seed was found, providing new insights into grape consumption in the region around 1500 B.C. As you may know, there is a long history of grape cultivation and winemaking along the western coast of Anatolia and central Anatolia. We are aware of the crucial role grapes play in interregional trade. The discovery of a grape seed aligns with this broader historical context.”