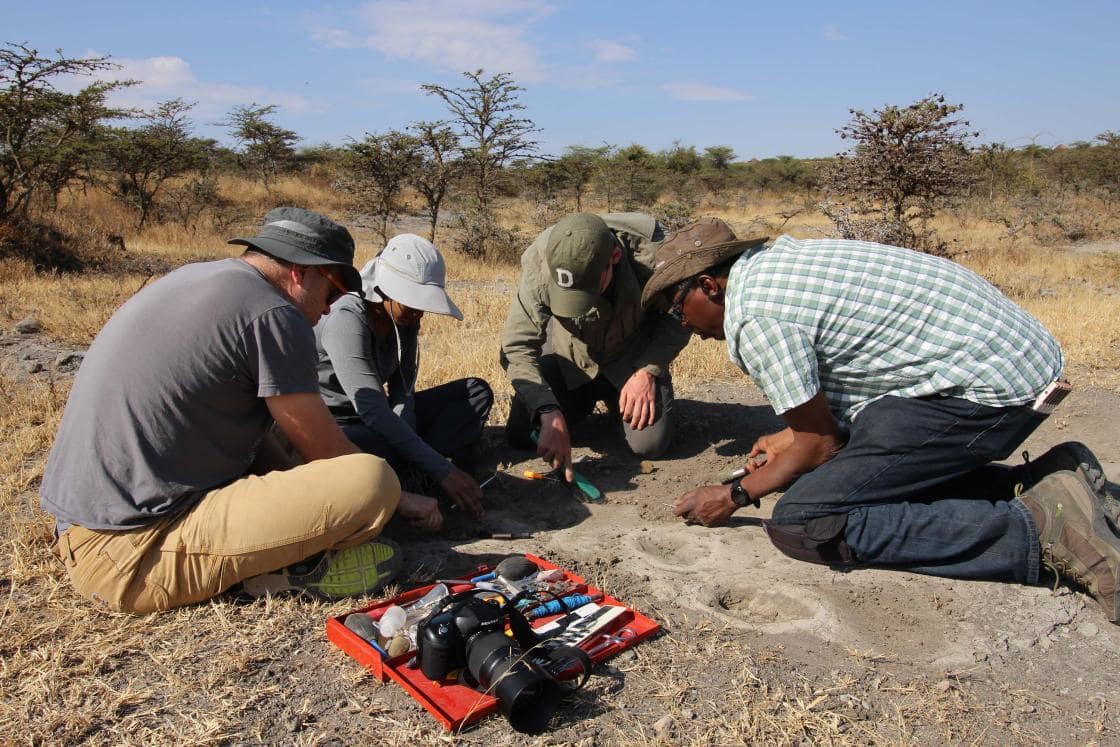
The prehistoric footprints discovered by archaeologists caused confusion because scientists looked at them again to determine whether they were left by humans or extinct animals.
The oldest clear evidence of upright walking in the human lineage is 3.7 million-year-old footprints discovered by paleontologist Mary Leakey and her colleagues in Laetoli, Tanzania, in 1978.
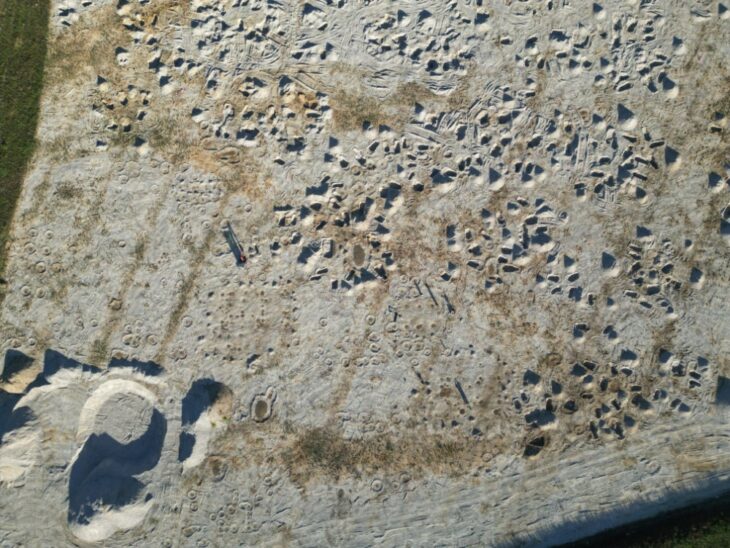
Another set of mysterious footprints was partially excavated at a nearby location, known as site A, in 1976 but dismissed as possibly having been made by a bear.
A recent re-excavation of the site A footprints at Laetoli and comparative analysis reveal that the footprints were made by an early human— a bipedal hominin, according to a new study reported in Nature.
“Given the increasing evidence for locomotor and species diversity in the hominin fossil record over the past 30 years, these unusual prints deserved another look,” says lead author Ellison McNutt, Guarini ’19, who started the work as a graduate student in the Ecology, Evolution, Environment, and Society program, and is now an assistant professor of instruction at the Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine at Ohio University. At Dartmouth, she focused on the biomechanics of walking in early humans and utilized comparative anatomy, including that of bears.
McNutt was fascinated by the bipedal (upright walking) footprints at site A. Laetoli is famous for its impressive trackway of hominin footprints at sites G and S, which are generally accepted as Australopithecus afarensis—the species of the famous partial skeleton “Lucy.” But because the footprints at site A were so different, some researchers thought they were made by a young bear walking upright on its hind legs.
![Comparing the A3 (photo on left) and G footprints revealed that the A3 and G footprints differ in width. On right is a cast of G1. (Photos by Jeremy DeSilva [left] and Eli Burakian ’00)](https://arkeonews.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/footprints-min-1024x683.jpeg)
To determine the maker of the site A footprints, in June 2019, an international research team led by co-author Charles Musiba, an associate professor of anthropology at the University of Colorado Denver and a Montgomery Fellow, went to Laetoli, where they re-excavated and fully cleaned the five consecutive footprints. They identified evidence that the fossil footprints were made by a hominin—including a large impression for the heel and the big toe. The footprints were measured, photographed, and 3D-scanned by Anjali Prabhat ’20; Catherine Miller, Guarini ’23; and Luke Fannin, Guarini ’24, who are co-authors of the paper.
The researchers compared the site A tracks to the footprints of black bears, chimpanzees, and humans.
They teamed up with co-authors Ben and Phoebe Kilham, who run the Kilham Bear Center, a rescue and rehabilitation center for black bears in Lyme, N.H. They identified four semi-wild juvenile black bears at the center with feet similar in size to that of the site A footprints. Each bear was lured with maple syrup or applesauce to stand up and walk on its two hind legs across a trackway filled with mud to capture its footprints.
Over 50 hours of video on wild black bears were also obtained. The bears walked on two feet less than 1% of the total observation time, making it unlikely that a bear made the footprints at Laetoli, especially given that no footprints were found of that individual walking on four legs.
“As bears walk, they take very wide steps, wobbling back and forth,” says senior author Jeremy DeSilva, an associate professor of anthropology. “They are unable to walk with a gait similar to that of the site A footprints, as their hip musculature and knee shape does not permit that kind of motion and balance.”
Bear heels taper and their toes and feet are fan-like, while early human feet are squared off and have a prominent big toe, according to the researchers. Curiously, though, the site A footprints record a hominin crossing one leg over the other as it walked—a gait called “cross-stepping.”
“Although humans don’t typically cross-step, this motion can occur when one is trying to reestablish their balance,” says McNutt. “The site A footprints may have been the result of a hominin walking across an area that was an unlevel surface.”
Based on footprints collected from semi-wild chimpanzees at Ngamba Island Chimpanzee Sanctuary in Uganda and two captive juveniles at Stony Brook University, the team found that chimpanzees have relatively narrow heels compared to their forefoot, a trait shared with bears. But the Laetoli footprints, including those at site A, have wide heels relative to their forefoot.
The site A footprints also contained the impressions of a big toe and second digit. The size difference between the two digits was similar to humans and chimpanzees, but not black bears. These details further demonstrate that the footprints were likely made by a hominin moving on two legs. But comparing the Laetoli footprints at site A and the inferred foot proportions, morphology, and likely gait revealed that the site A footprints are distinct from those of Australopithecus afarensis at sites G and S.
“Through this research, we now have conclusive evidence from the site A footprints that there were different hominin species walking bipedally on this landscape but in different ways on different feet,” says DeSilva, who focuses on the origins and evolution of human walking. “We’ve had this evidence since 1976. It just took the rediscovery of these wonderful footprints and a more detailed analysis to get us here.”