A recent study in the Oxford University Press journal Molecular Biology and Evolution demonstrates that a condition known as Dupuytren’s illness is partly of Neanderthal origin.
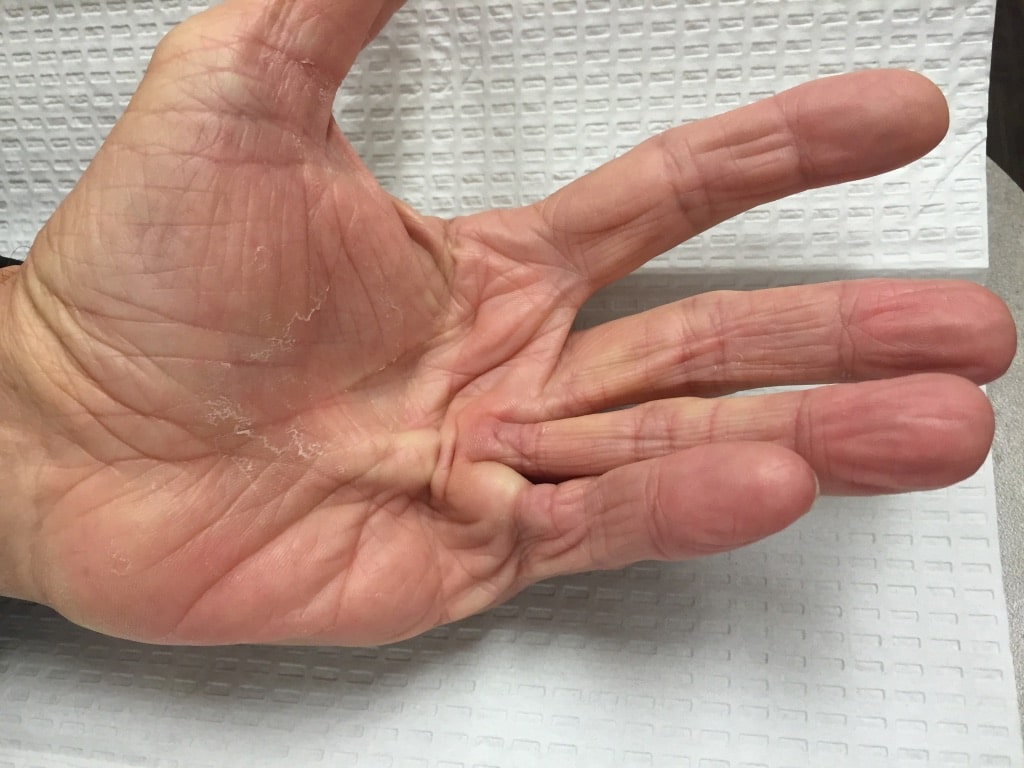
The so-called “Viking disease” causes the fingers of many aging northern European men to lock up in a bent position, and researchers now think they know why.
Genetic variants inherited from Neanderthal man appear to be the most powerful risk factors for developing Dupuytren’s contracture — called the Viking disease because it mainly affects men descended from northern Europeans. Researchers have long known that the disease was much more common in Northern Europeans than in those of African ancestry.
Dupuytren’s disease is a disorder affecting the hand. Those who suffer from the condition eventually see their hands become bent permanently in a flexed position. Although the condition can affect any finger, the ring and middle fingers are most often afflicted. Scientists have previously identified several risk factors for the condition, including age, alcohol consumption, diabetes, and genetic predisposition.
A 1999 Danish study reported 80% heritability for the condition, indicating a strong genetic influence. The condition is much more common in people of Northern European ancestry. One study estimated the prevalence of Dupuytren’s disease among Norwegians over 60 years to be as much as 30%. The condition is rare, however, for those of primarily African descent. This apparent geographic distribution has given Dupuytren’s disease the nickname “Viking disease.”
There are geographical differences in the extent of genetic ancestry linking present-day humans to now-extinct groups. People from Africa south of the Sahara have little ancestry from Neanderthals or Denisovans, who that lived in Europe and Asia until at least 42,000 years ago. In contrast, people with roots outside of Africa inherited as much as 2% of their genome from Neanderthals and some populations in Asia today have up to 5% Denisovan ancestry. Given these regional differences, archaic gene variants can contribute to characteristics or diseases found primarily in certain populations.

Given the prevalence of Dupuytren’s disease among Europeans, researchers here investigated its genetic origins. They used data from 7,871 cases and 645,880 controls from the UK Biobank, the FinnGen R7 collection, and the Michigan Genomics Initiative to identify genetic risk variants for Dupuytren’s disease.
They found 61 genome-wide significant variants associated with Dupuytren’s disease. Further analysis showed that three of these variants are of Neanderthal origin, including the second and third-most strongly associated ones. The finding that two of the most important genetic risk factors for Dupuytren’s disease are of Neanderthal origin leads the scientists to conclude that Neanderthal ancestry is a significant factor in explaining the prevalence of the disease in Europe today.
“This is a case where the meeting with Neanderthals has affected who suffers from illness, although we should not exaggerate the connection between Neanderthals and Vikings,” Hugo Zeberg said in an institute news release.
The new study appears in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution.