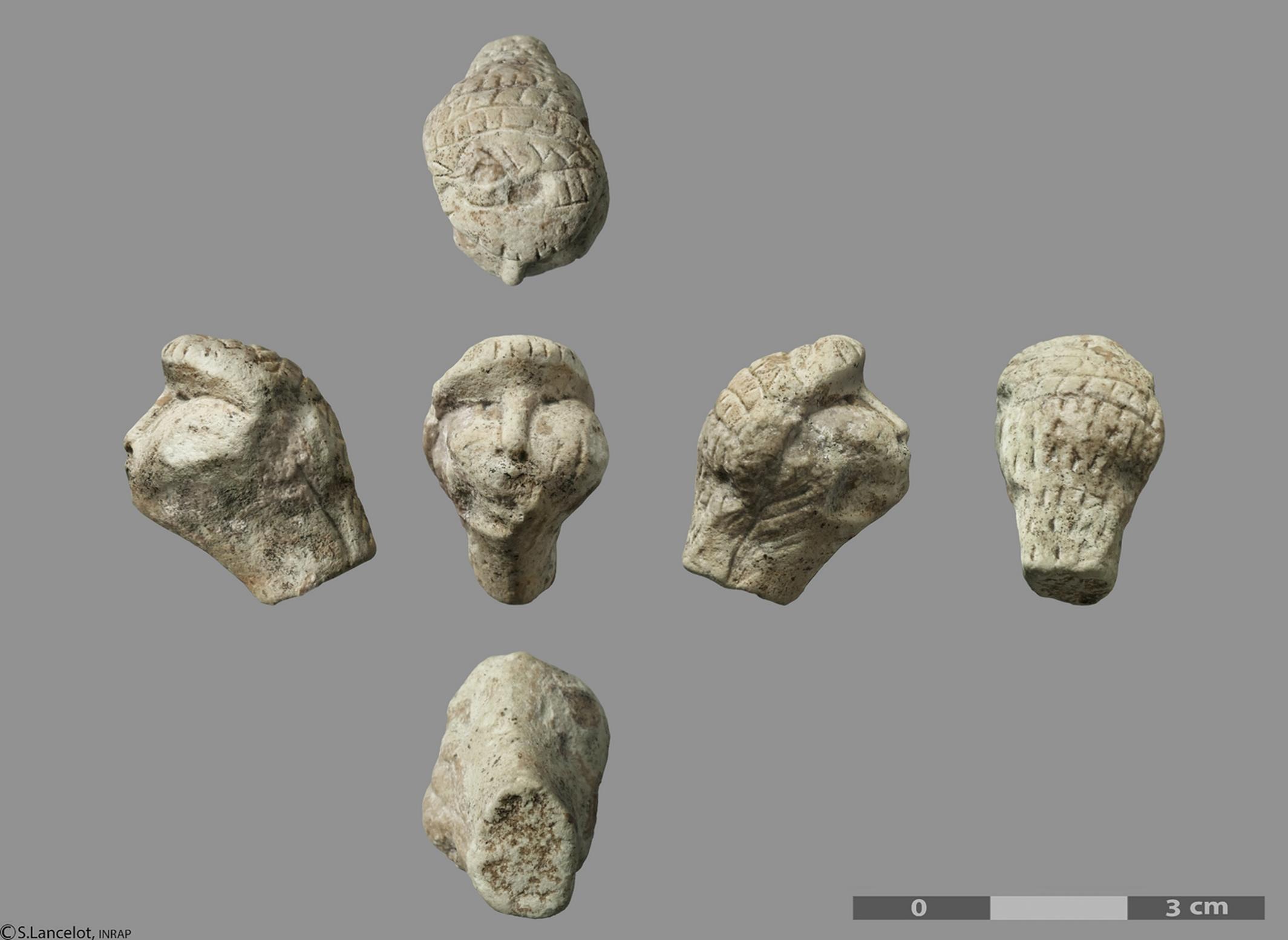
Recent archaeological excavations at the Amiens-Renancourt 1 site in northern France have unveiled an extraordinary Gravettian-era female figurine head, dating back approximately 27,000 years.
This rare find stands out among Upper Paleolithic art for its detailed facial features and intricate headdress—offering unprecedented insight into early human artistic expression during the late Palaeolithic era.
Discovery not only enriches our understanding of Upper Paleolithic art but also challenges long-held assumptions about Gravettian female statuettes, often referred to as “Venus figurines.“
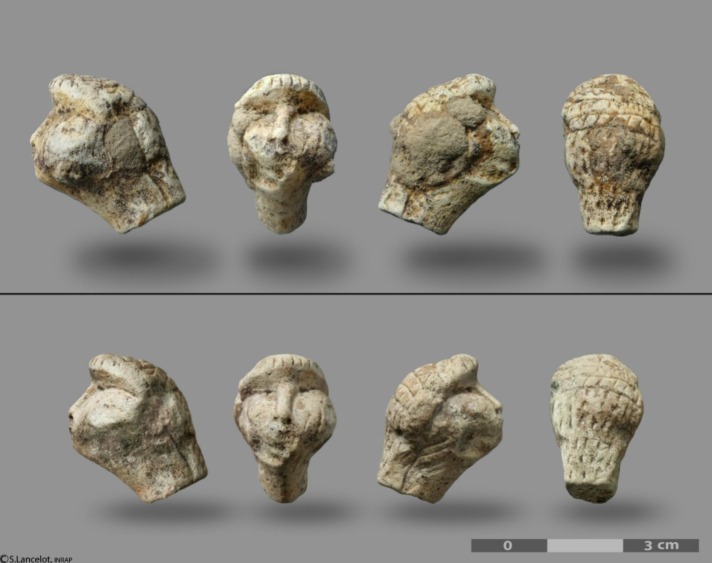

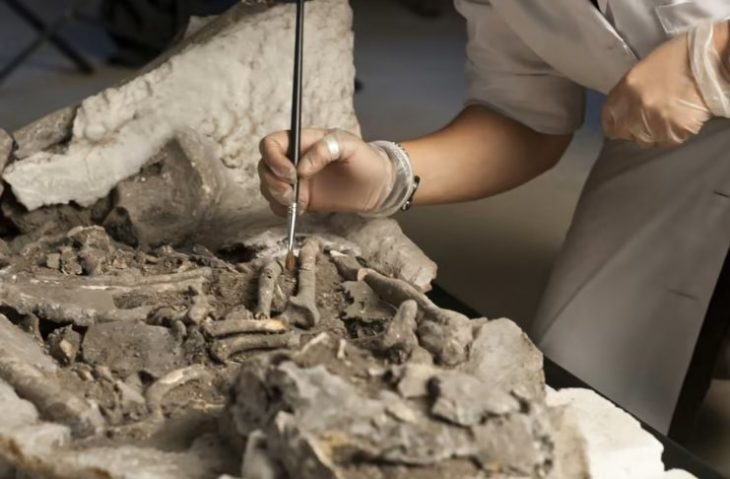
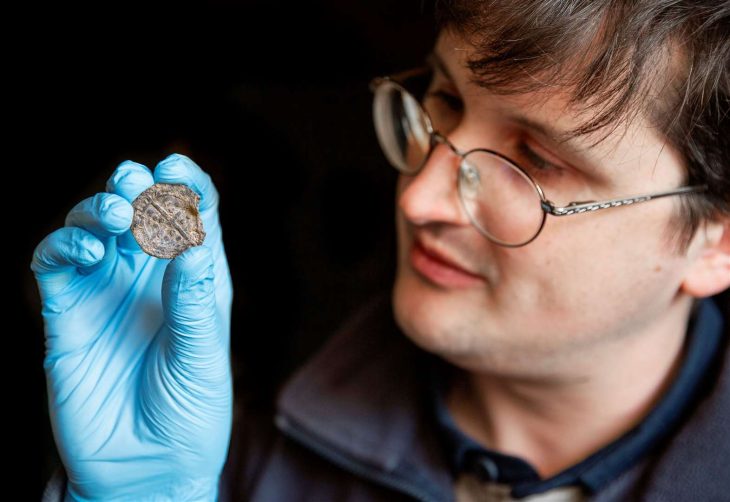
Figure Head shown before and after cleaning of concretions. Credit: Stéphane Lancelot, Inrap
A Unique Find in Gravettian Archaeology
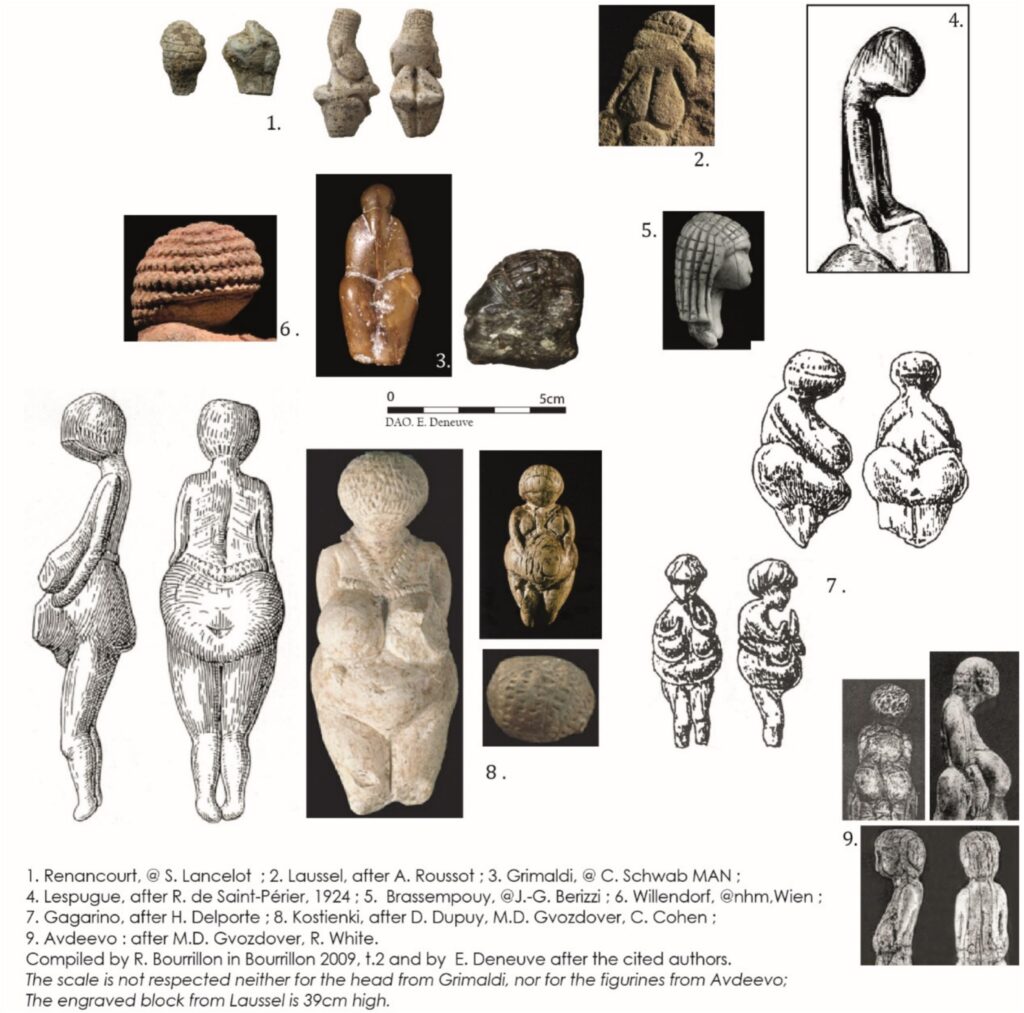
Since the late 19th century, female statuettes from the Gravettian period have fascinated researchers, primarily due to their symbolic importance and enigmatic nature. However, these figurines are typically small, fragmentary, and devoid of detailed facial features. Most lack heads altogether or present heavily abstracted forms. The discovery at Amiens-Renancourt is a rare exception: a finely carved chalk head featuring detailed facial anatomy and an elaborate headdress, offering a rare glimpse into Gravettian artistic expression.
Measuring only 2.1 cm in height, the figurine’s facial features—such as the nose, eyes, and cheeks—are rendered with unusual precision. Notably, the upward gaze, indicated by sunken eye sockets, contrasts with the downward-facing heads of most known Gravettian figurines. The back of the head is adorned with intricate incisions, including grid-like patterns, vertical lines, and notches, which researchers interpret as representing braided hair, a net, or a ritual headdress. Such detailed representation of hairstyle is unique among Gravettian art and may reflect social or ritual significance.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Contextualizing the Discovery: Amiens-Renancourt 1
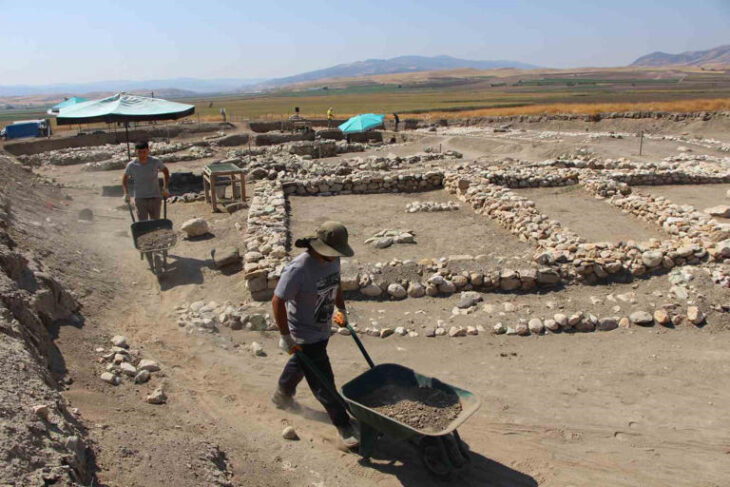
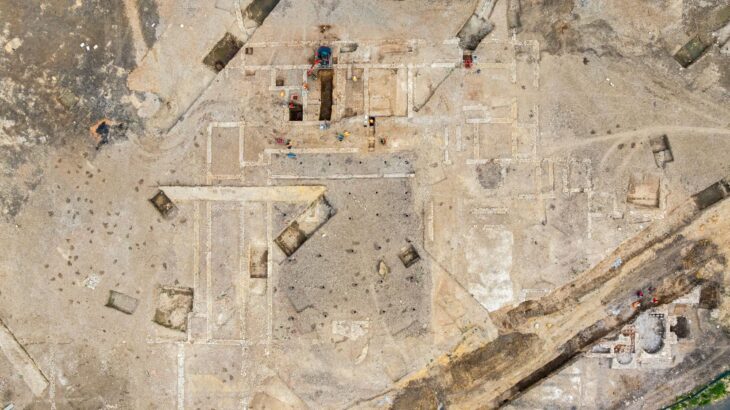
Located near the Selle and Somme valleys, the Amiens-Renancourt 1 site has been a focus of intensive archaeological study since 2013. The site provides one of the best-preserved stratigraphic and paleoenvironmental contexts for Gravettian occupation in Europe, dating to approximately 27,200–27,800 years ago during a milder interstadial climate phase.
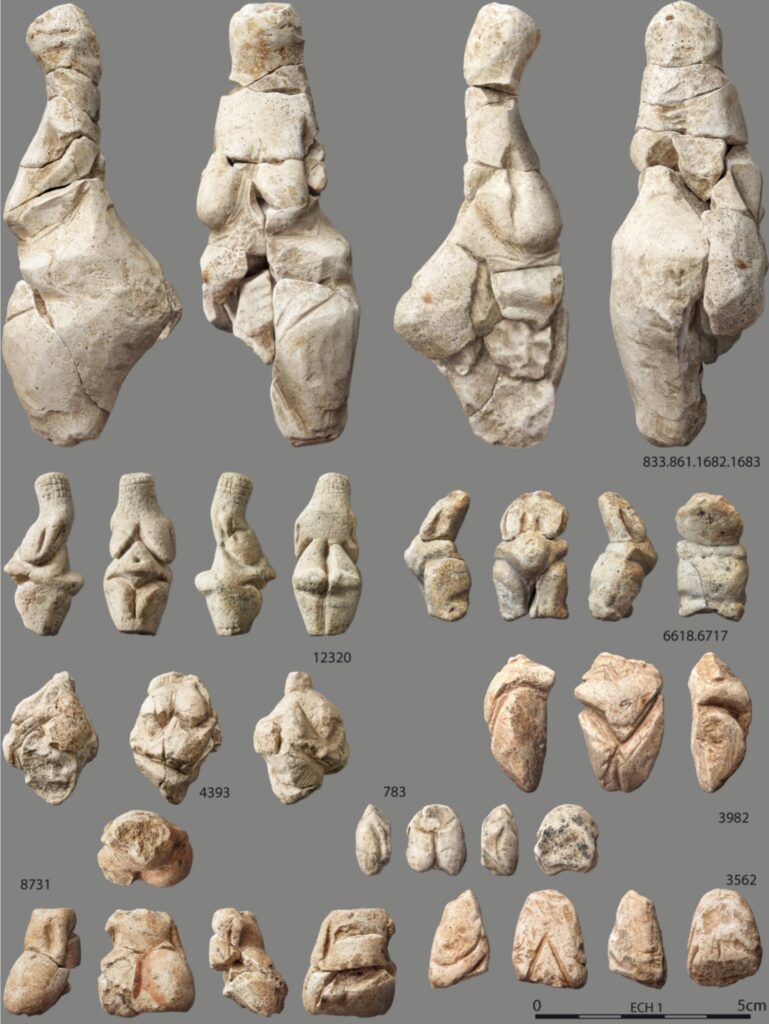
Excavations have uncovered over twenty statuettes, primarily carved from ivory and soft stone, with a notable use of chalk—an uncommon material for the period. The statuettes typically depict nude female forms with exaggerated hips and minimal limb detail, consistent with Gravettian artistic conventions. Importantly, the statuettes and fragments were produced on-site, reflecting an active workshop or habitation area with complex social and artistic activity.
Significance for Paleolithic Art and Culture
This newly discovered figurine challenges the conventional perception of Gravettian “Venus” figurines as anonymous, stylized symbols of fertility or female deities. Instead, the individualized facial features and distinct headdress suggest a possible portrayal of a specific individual or social role. The grid patterns and ornamentation echo motifs found across Europe and Russia, indicating cultural connections and shared artistic traditions among Gravettian groups.
Moreover, the craftsmanship reveals sophisticated techniques in carving fragile chalk, preserving fine details such as scraping and polishing marks. This underlines the technical skill and aesthetic sensibility of Upper Paleolithic artisans.

Future Research and Display
Following meticulous restoration, including microscopic cleaning and 3D modeling, the figurine is slated for exhibition at the Musée de Picardie in Amiens, alongside other findings from the site. Ongoing interdisciplinary studies aim to deepen our understanding of the social, artistic, and environmental contexts of this exceptional discovery.
Clément Paris, Émeline Deneuve, Claire Brière, David Hérisson, Pierre Antoine, Paule Coudret, Sylvie Coutard, Jean-Pierre Fagnart, Nejma Goutas, Jessica Lacarriere, Olivier Moine, Caroline Peschaux, Maxence Toubin. “A new face for the Gravettian. Exceptionnal discovery of a female statuette at Amiens-Renancourt 1 (France)”. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, Volume 66, October 2025, 105285, doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2025.105285
















