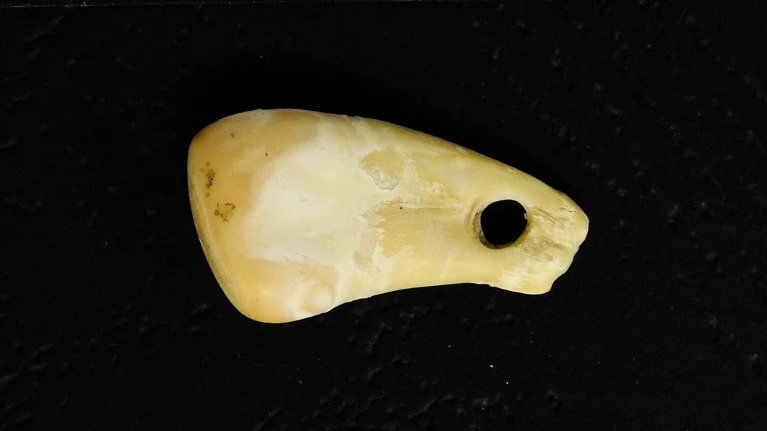
A pendant made of a deer tooth that was exposed to DNA about 20,000 years ago has yielded clues about the ancient woman who wore it.
The tooth, which was worn as a necklace bead, most likely absorbed DNA from the person’s sweat as it rubbed up against her chest and neck. Marie Soressi and her colleagues at Leiden University in the Netherlands were able to extract that DNA without damaging the tooth using a new process that took eight years to develop.
The technique might reveal unprecedented details about the social customs and gender roles of ancient populations, says Soressi.
The pendant was unearthed in Denisova Cave in Siberia, Russia, which was occupied by various species of hominin over 300,000 years. The study was published in Nature today.
“It’s almost like you open a time travel machine,” says study co-author Elena Essel, a molecular biologist who works on ancient DNA at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany. “With each sample we are able to learn a bit more and make more inferences about how these people lived.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Previously, it was impossible to link tools and jewelry to the people who used them unless the artifact was discovered near a specific burial.
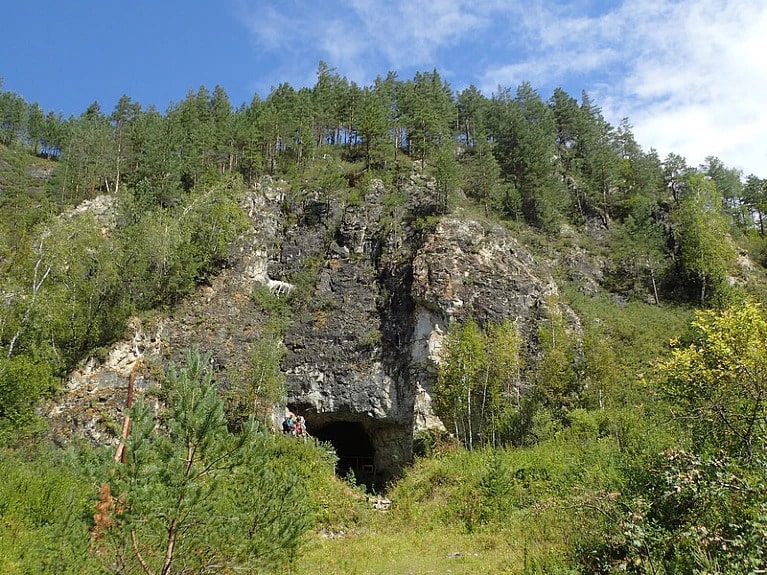

Essel and her colleagues coaxed DNA from inside the pores of the ancient pendant by soaking it in increasingly warm salt solution, which they found did not alter the pendant. Once released, the small amounts of genetic material were sequenced and compared with other sets of ancient DNA.
Mitochondrial DNA — which is handed down from mother to offspring — extracted from the pendant show that the object is roughly 19,000 to 25,000 years old and that the tooth belonged to a wapiti, also known as an elk (Cervus canadensis). Analysis of nuclear DNA from the ornament suggests that it had been made or worn by a female Homo sapiens whose genetic make-up resembles that of north Eurasian individuals who lived around the same time but were previously known only from remains found farther east in Siberia.
Study co-author Elena Zavala, a geneticist now at the University of California, Berkeley, says that the technique can connect ancient humans to “the tools that they created” — but, unlike other methods, does not destroy the artifact.
However, there are a number of drawbacks to the method. Modern DNA can easily contaminate an artifact, making analysis difficult. And even for the cleanest specimens, the DNA extraction method is time-consuming, requires sophisticated technology, and must be performed in a specialized laboratory. Essel and her colleagues are working to streamline their process. In the meantime, archaeologists can minimize contamination by wearing gloves and a face mask, and by immediately popping specimens into a refrigerator.
Still, Ludovic Orlando, a molecular archaeologist at the University of Paul Sabatier in Toulouse, France, who was not involved in the study, was impressed by the thoughtfulness and efficiency of the team’s procedure. The technique is not “a magic bullet”, says Orlando. But it still provides “a signature from nothing, from a piece of bone or tooth”, he adds. “You see the population signature of the people who interacted with the animal.”
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-023-0482-3
Cover Photo: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology