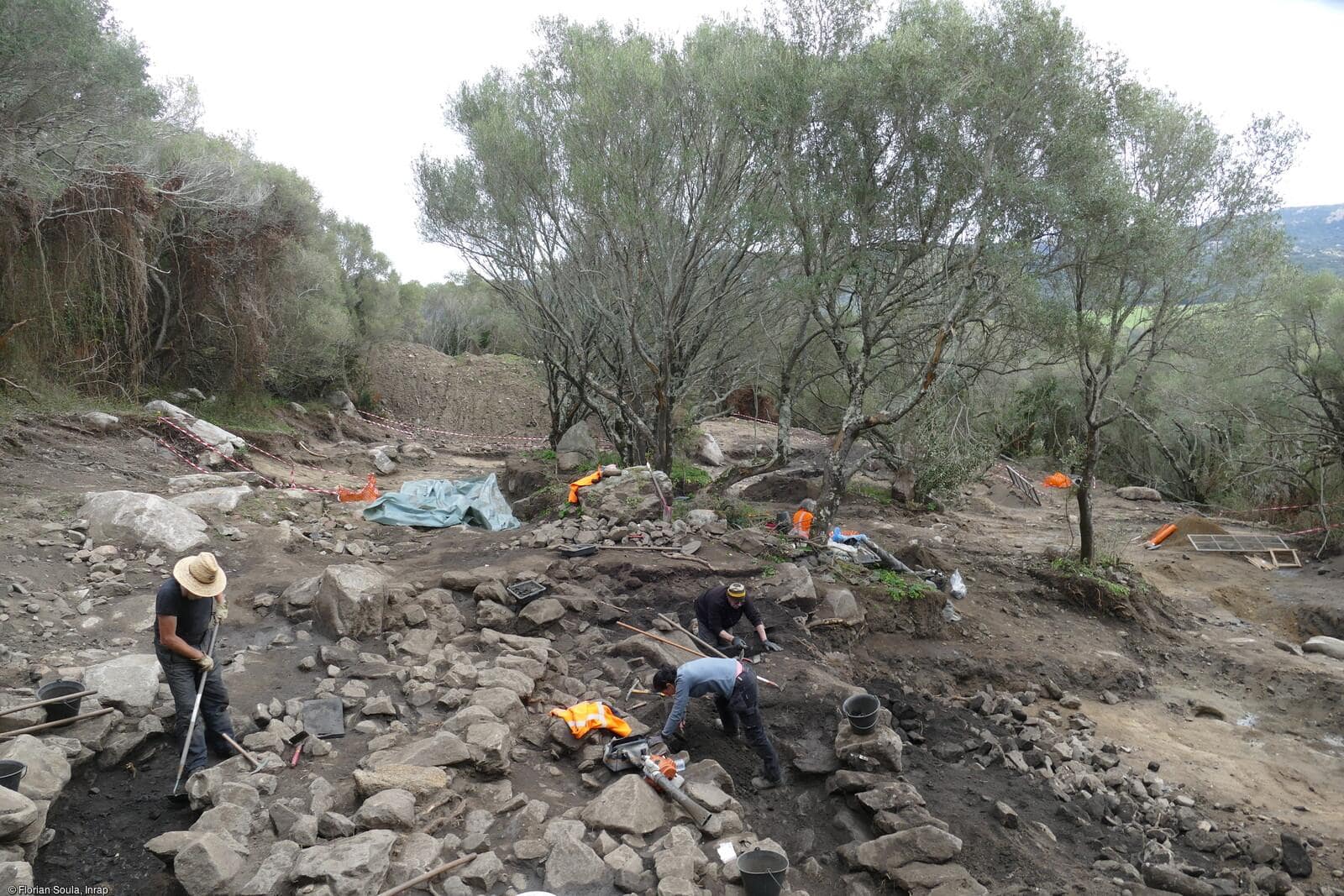
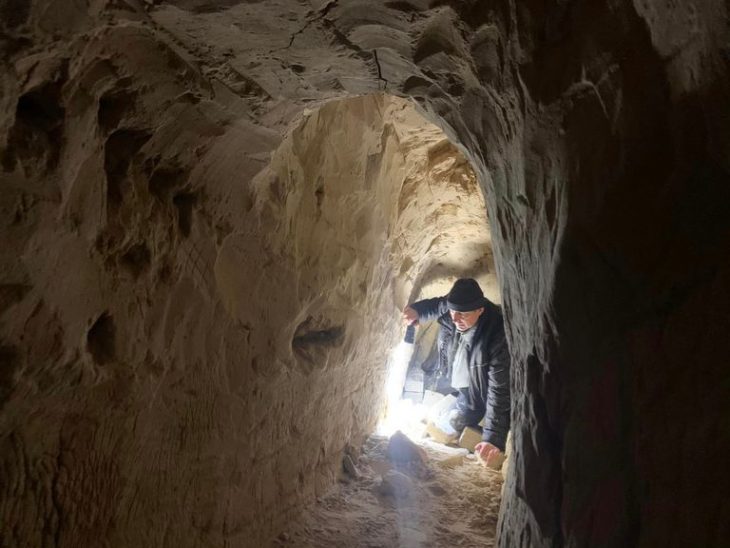
Archaeologists in a French municipality recently excavated the slopes of Punta Campana (island of Corsica) in preparation for a construction project and found an expansive Neolithic site.
The site in Sotta (Sotta is a French municipality on the island of Corsica) contains two distinct settlements, according to a news release from the Institut National de Recherches Archéologiques Préventives (INRAP). The first settlement is partially preserved while the second is well preserved.
As part of this excavation, archaeologists have uncovered the existence of a recent Neolithic settlement (Basien) followed by a late Neolithic settlement.
Archaeologists said the first settlement, which dates back to the early fourth millennium B.C., held a stone structure containing the remains of an obsidian knapping workshop.
Within the workshop, there is evidence indicating that ancient people used a variety of methods to make obsidian tools.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
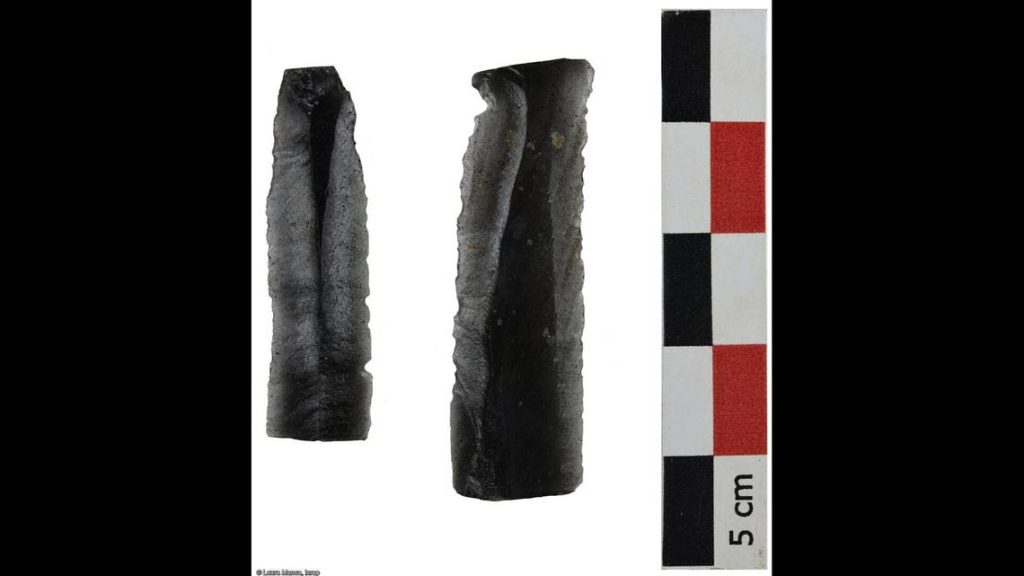

According to experts, the site likely experienced significant erosion until the second, more recent settlement was built on top of the workshop.
Terraced Structures
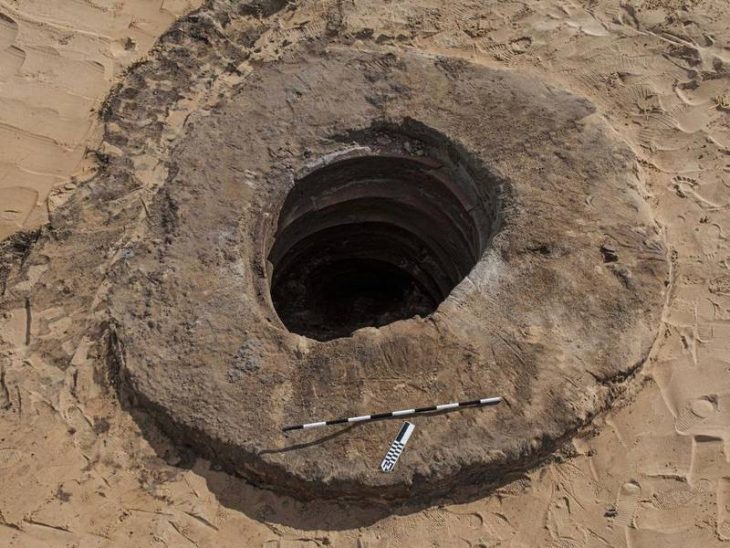
Archaeologists unearthed a terrace system filled with occupation and activities in the second, better-preserved settlement’s, dating to the 3rd millennium BC.
The terraces were topped with an approximately 3-foot tall or fortified wall made of granite blocks, according to researchers.
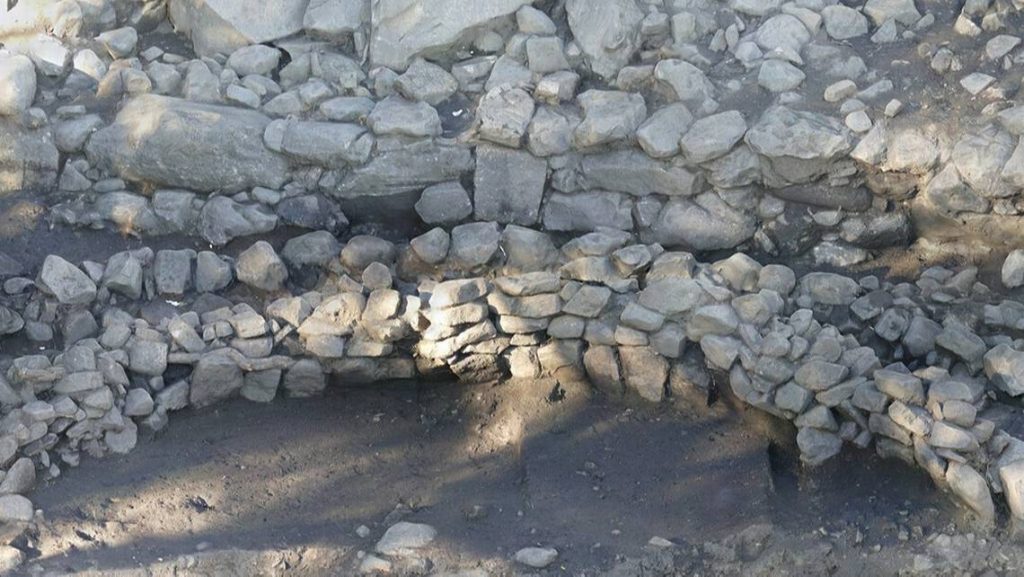

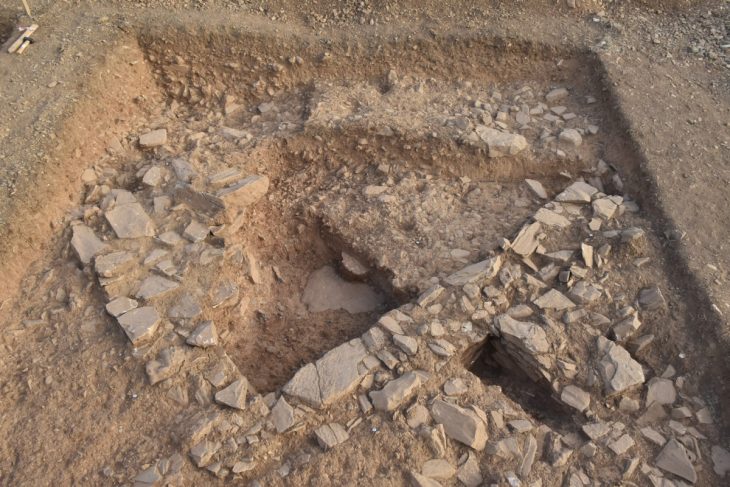
A stone arc made of granite blocks was located on the first terrace below it. The building methods used in the arc indicate it was used as a roof of some sort, but experts aren’t unknown its yet precise function.
Archaeologists also discovered a staircase and corridor inside the terraced building that appeared to serve as a pathway to the system’s upper level.
The team discovered two other similar but more refined terraced systems at the site. It is still unknown what these structures were used for, but archaeologists believe they could have been used for food storage, metallurgy, or other artisan activities.
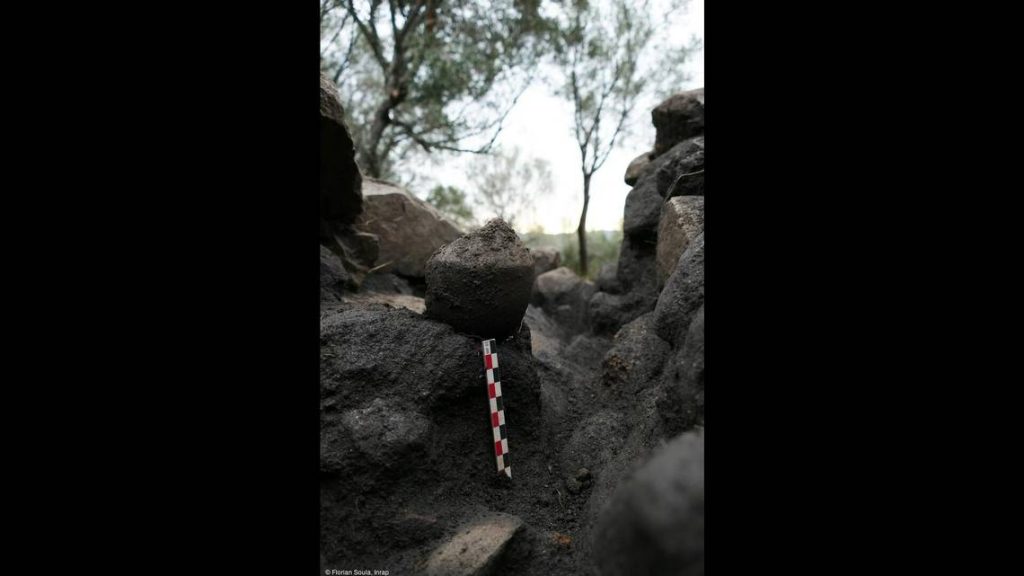

Archaeologists discovered thousands of unusual copper and other metal artifacts at the Neolithic site, particularly in the terraced area. Some remain indicated traces of melting that took place at the site. Cattle teeth and unusual cranial skeletal remains that appeared to have been burned were also discovered, according to INRAP.
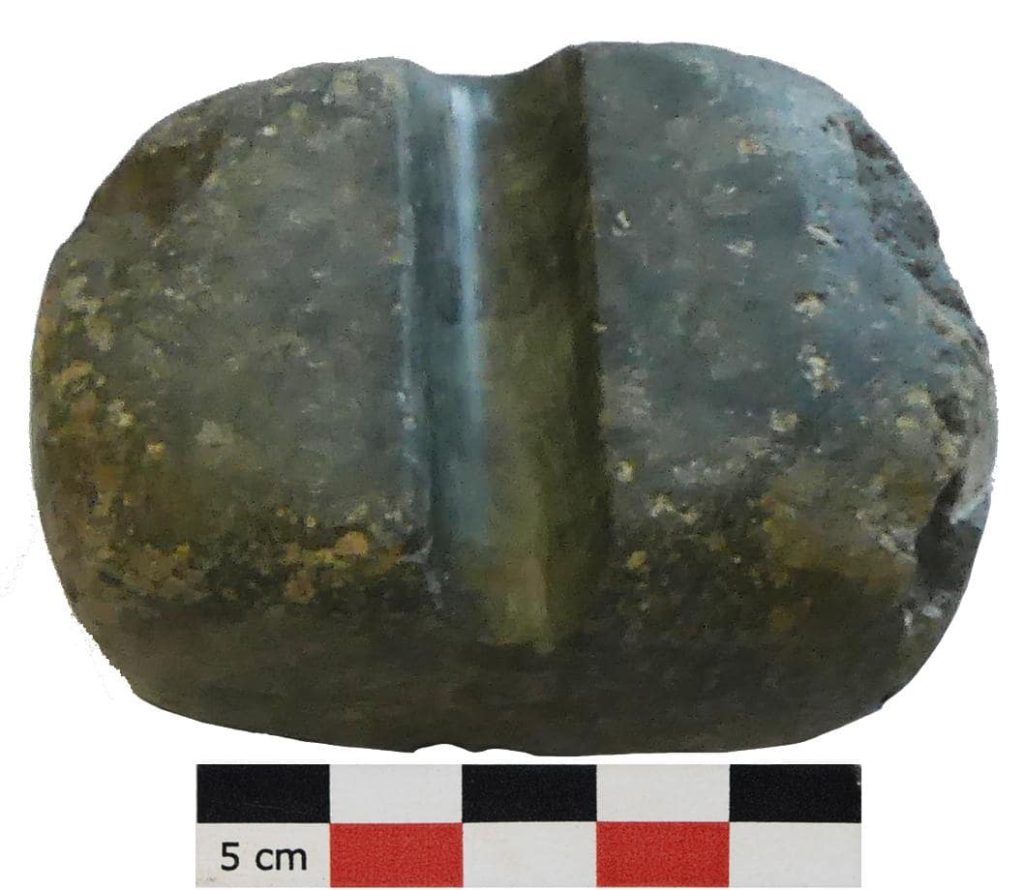

Archaeologists also unearthed ceramics, flint, obsidian, quartz, arrowheads, polishers, axes, wheels, and tools. Further studies on the finds are ongoing.
Cover Photo: Florian Soula, Inrap