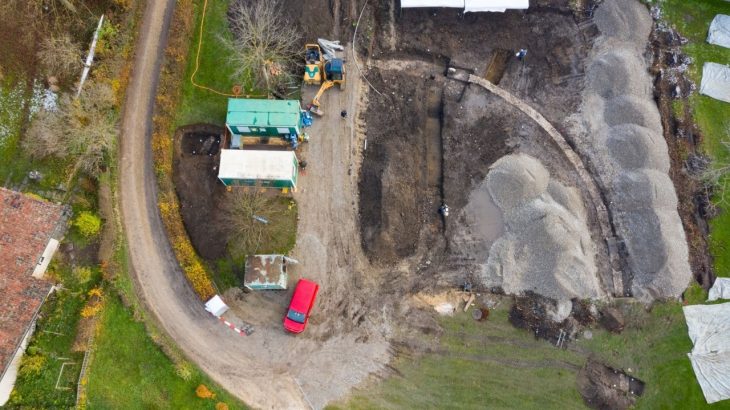
An excavation of a 5,000-year-old Neolithic dwelling on the Danish island of Falster surprisingly revealed a stone-paved cellar.
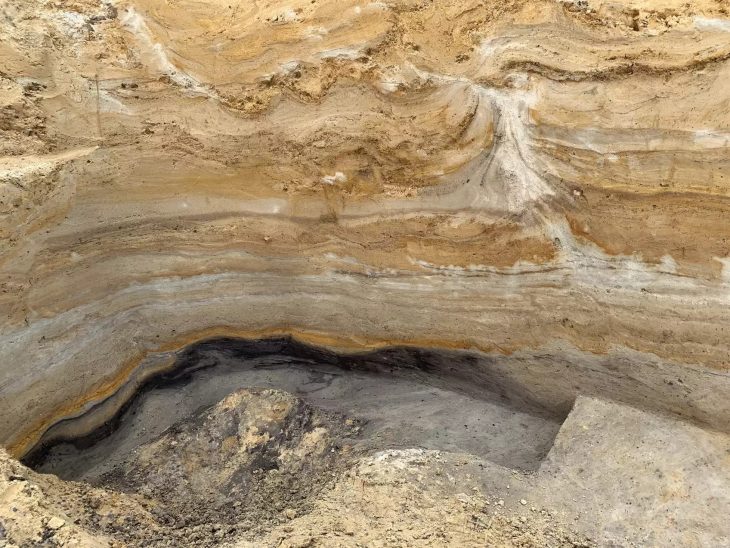
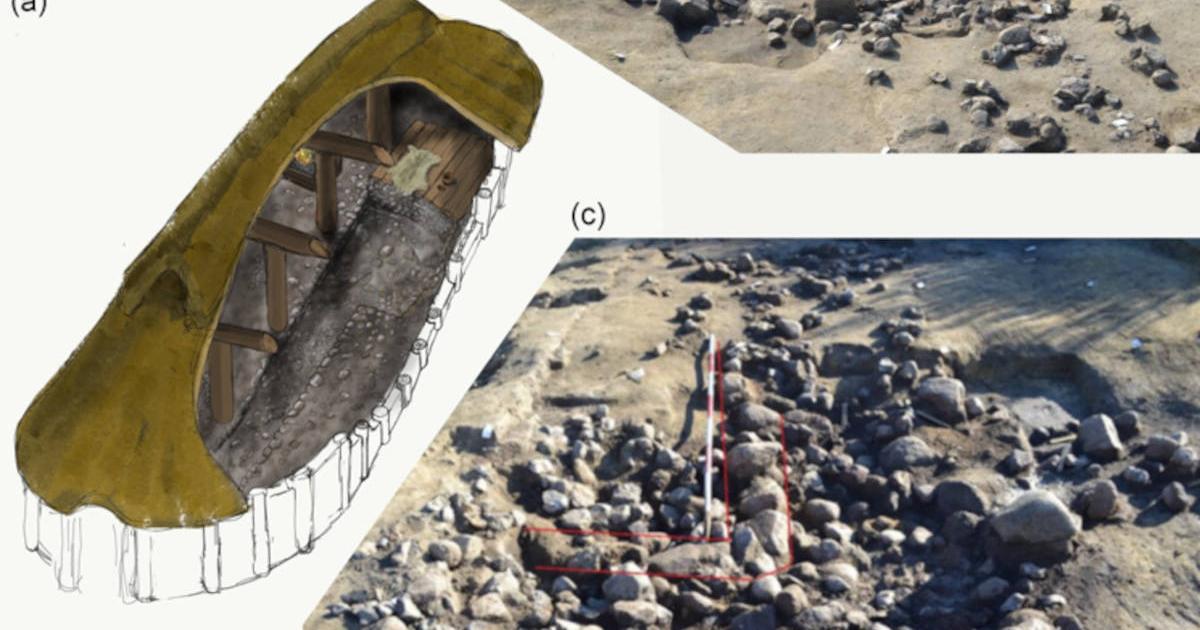
Railroad construction through a farm on the Danish island of Falster has revealed a site hiding advanced technology. The stone-paved root cellar measures roughly 6.5 feet by 5 feet, which may not be a huge find in size, but historically, it could be massive.
The stone-paved cellar just over a foot below ground level dates to the Middle Neolithic period. It challenges preconceived notions about the era’s social sophistication and building expertise.
Archaeology researchers from the Museum Lolland-Falster, along with Aarhus University, Denmark, have analyzed the site in a paper, published online in the journal Radiocarbon.
The first shift to agriculture and domesticated animals (sheep, goats, and cattle) in the Scandinavian region occurred with the rise of the Funnel Beaker Culture approximately 6,000 years ago, resulting in a more sedentary way of life. The area began building houses, megalithic tombs (dolmens), and landscape-altering structures along with the new way of life, marking a significant departure from the highly mobile hunter-gatherer strategy of the Late Mesolithic.
The team located two housing construction phases linked to the Funnel Beaker Culture near the beginning of the Neolithic period, and the cellar, lined with pebble stones for paving, sat under one of them.
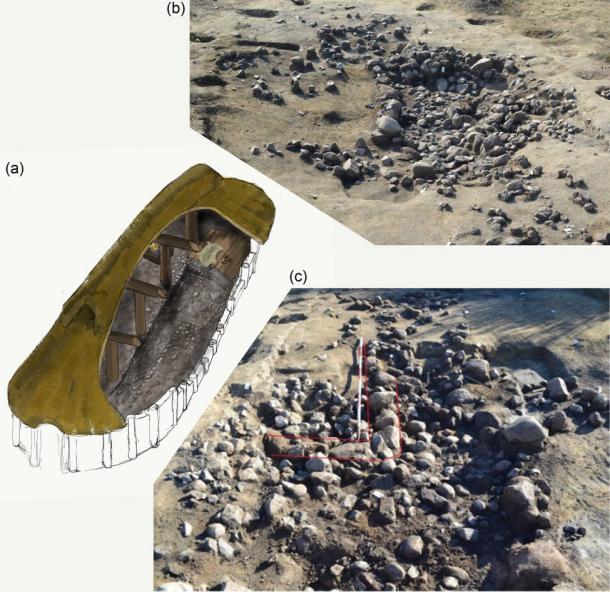
Both structures were built using a common Funnel Beaker Culture design (the Mossby-type), where interior posts provide support for a large double-span roof. Phase one included 38 post holes, while phase two had 35, indicating that a significant amount of architectural planning was involved.
The fact that the site is situated on an elevated area of land and is not close to any bogs or streams suggests that care was taken. It would have been advantageous from a defensive as well as practical standpoint because it offered the benefits of being above flood zones and offering a broad view of the surrounding area.
More than a thousand artifacts were discovered in and around the houses, offering more insight into daily life in Neolithic Denmark. These artifacts included fossilized sea urchins, pottery fragments, and flint tools.
“The presence of this paved cellar challenges our understanding of the construction capabilities of Neolithic societies,” the authors wrote. “It forces us to reconsider the complexity of their domestic structures and, by extension, their social organization.”
The discovery of a stone-paved, underground structure that is thought to be a root cellar is the site’s most noteworthy feature. While the use of such cellars is well documented in later periods, this is the first known example from Neolithic Denmark. This would be a major technological advance for food storage in the area if it is indeed a root cellar.
Root cellars are the perfect place to store food because of their constant temperature because they are underground. In an agricultural society, this would have been needed for preserving crops and other resources through harsh winters and between harvests. A technological advance in resource management during the Neolithic era, food preservation of this kind would have substantially improved the inhabitants’ chances of survival.
The discovery changing the narrative about the people, who were thought to be highly primitive at the time. “The discovery forces us to reevaluate our assumptions about the technological capabilities of Neolithic societies,” the authors wrote. “The presence of a paved cellar implies not only advanced construction skills but also long-term planning and a sophisticated understanding of storage and food preservation.” This insight could redefine the social fabric of the Stone Age.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/RDC.2024.79
Cover Image Credit: Radiocarbon (2024).