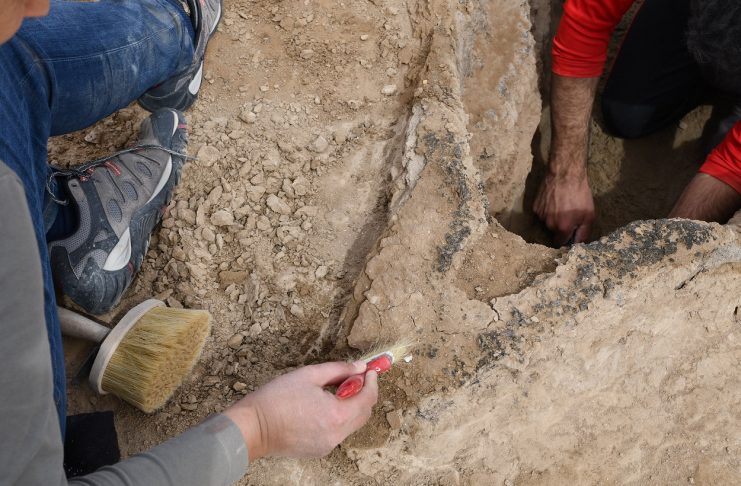
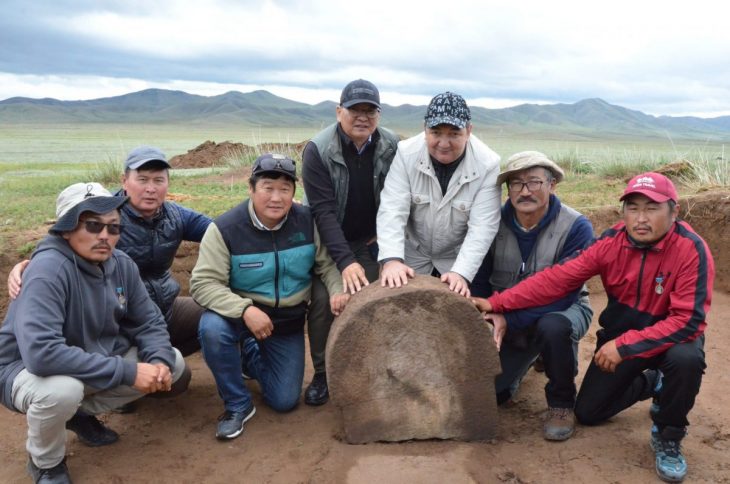
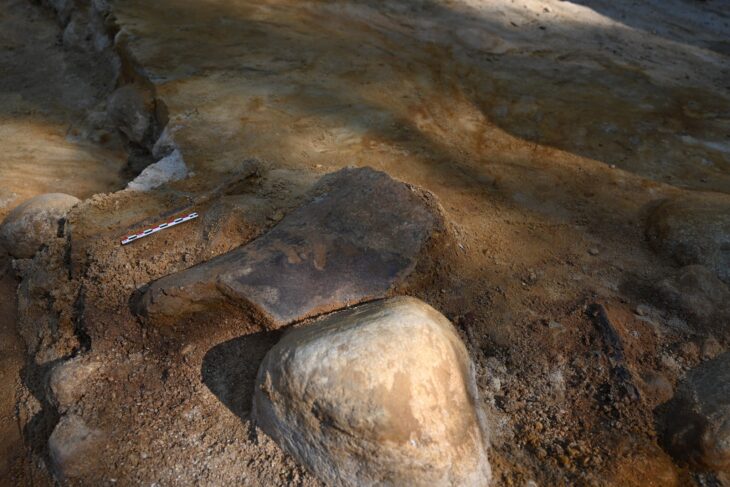
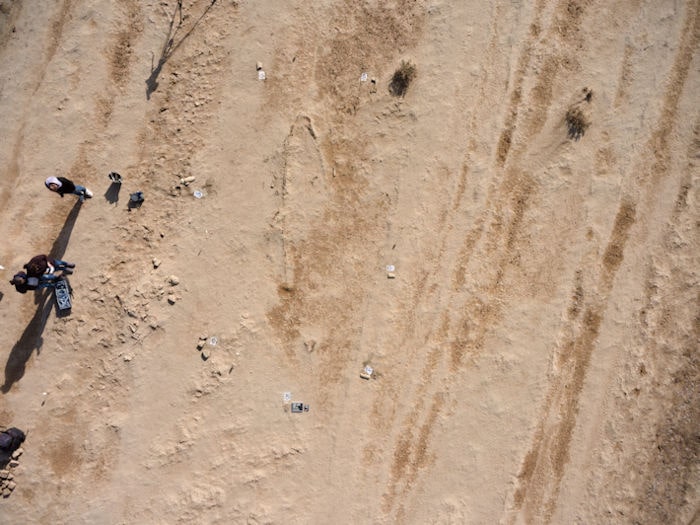
A team of archaeologists from the Iraqi German Mission of the State Board of Antiquities and the Orient Department of the German Archaeological Institute have uncovered a very fragile, unique, well-preserved 4000-year-old boat near the ancient city of Uruk.
Uruk, also known as Warka or Warkah, was an ancient city of Sumer (and later of Babylonia) situated east of the present bed of the Euphrates River on the dried-up ancient channel of the Euphrates 30 km east of modern Samawah, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.
According to the Sumerian King List, Uruk was founded by King Enmerkar around 4500 BC. It was the largest settlement in southern Mesopotamia. Uruk played a leading role in the early urbanization of Sumer and was a major population center until it was abandoned shortly before or after the Islamic conquest of AD 633-638.
The boat was first discovered during a study of the Uruk-Warka environs in 2018, where it was photogrammetrically documented.
The fragile structure has already been partially exposed to erosion in recent years and has recently been visible even above ground. Traffic passing near the exploration area posed a serious threat to the boat’s protection.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Constructed from reed, palm leaves, and wood, the boat was covered in bitumen, a substance produced through the distillation of crude oil that is known for its waterproofing and adhesive properties. The organic remains are no longer conserved and are only visible as imprints in bitumen.
Measuring 7 meters in length and 1.4 meters wide, the archaeological context shows that the boat sank on the banks of a river around 4000-years-ago and became buried in layers of sediment.
During the excavation, the top of the boat was covered with clay and plaster shell to stabilize it, and thus it was possible to save the entire boat.
According to Iraq’s antiquities law, the Mesopotamian boat was taken to the Iraqi Museum in Baghdad for scientific study and further conservation.
Deutsches Archäologisches Institut
Cover Photo: Julia Nador, Deutsches Archäologisches Institut